- Which varieties are best stored?
- Preparing the harvest for storage.
- Optimal conditions for storing beets.
- Storing beets in the cellar.
- Storing root vegetables in the apartment.
- Covering vegetables in piles.
Storing beets in winter is quite simple. This is the easiest vegetable to keep until the next harvest. Even some errors during storage are not so dangerous for the root crop.
Which varieties are most suitable for storage?
After digging, the root crops enter a winter dormant period. Its duration depends on the conditions created. If they correspond, then the beets are stored in winter for a very long time. The length of the period varies slightly among different varieties.
Early varieties characterized by a fairly short period of winter dormancy. As soon as the temperature in the storage room rises to +7-8°C, they germinate. Related to this is the difficulty of storing them after harvesting. Early varieties ripen in mid-to-late July; it is very difficult to ensure proper storage conditions during this period. But if it is possible to create at least the necessary microclimate, then it will lie for 3-4 months. If not, then use the root vegetables within 2-3 months, otherwise they will wither and become unfit for consumption.
Beet middle and late varieties kept well. Even at home, they can last until February-March, and in the cellar the root vegetables are stored until the new harvest. However, as the temperature rises, the beets begin to germinate. Mid-season varieties germinate faster than later ones.
Preparing the harvest for storage
Preparation for storage includes:
- drying root crops;
- removal of tops;
- root pruning;
- sorting.
Drying. Immediately after digging, the beets are left in the garden for 3-5 hours so that they dry and ventilate. If the day is inclement, then to dry the root vegetables are removed under a canopy, where they are laid out in one layer and left for 2-3 days, turning them over regularly.
There is no need to ventilate the beets for too long, otherwise they will begin to lose moisture and become flabby and tasteless.
Removing tops. If the beets have been ventilated in the air, then remove the leaves under the canopy before harvesting.If the vegetables were lying in the barn, then the tops are cut off after 1-2 days.
Leaves are cut with a knife or twisted. It is preferable to twist the tops, since they break off at just the right height, leaving the apical bud intact.
If the leaves break off badly, then they are cut off with a knife, leaving a tail of 1 cm. It is important not to damage the apical bud, otherwise the beets will rot during storage.
Root pruning. After trimming the leaves, remove all roots. Root vegetables are carefully cleared of soil and the side roots are torn off or carefully cut off with a knife.
The main root is cut to 1/3 of its length. If it is not pruned, then in winter the tip of the root dries out, becomes rotten and rots. Typically, rot spreads from here (if the apical bud is not damaged). A very long root is shortened by half.
Sorting. Next, the root vegetables are sorted by size. Small beets contain less fiber and store better. Large, more fibrous ones are stored somewhat worse; by mid-winter they already wither and dry out or sprout. Therefore, small and large vegetables are stored separately from each other, or large beets are placed on top for quicker use.
Damaged vegetables should not be stored, but used immediately. Root crops injured during digging are not stored. Beets are more difficult to form cork tissue at the site of damage than, for example, carrots or potatoes. Water gradually accumulates in the wound and the beets rot.
Conditions for storing beets in winter at home
For best preservation in winter, vegetables need:
- Dark place. In the light they germinate quickly.
- Free air circulation. If there is insufficient air flow, the crop rots.
- Temperature 1-4°C.As the temperature rises, the respiration of root crops increases, they rapidly lose moisture and become flabby. At a temperature of 7-8°C they germinate. In the first 2 months, the temperature should be maintained no higher than 4°C, otherwise the crop will germinate. After this period, all winter until spring, root crops are in a state of deep dormancy and do not germinate even when the temperature rises by 1-2 degrees.
- Humidity 90-95%. As it decreases, the beets gradually dry out, wrinkle, become flabby and unsuitable for food.
However, even with a slight deviation in the indicators in winter, the safety of root crops is high, although their shelf life is somewhat reduced. At home, in the absence of balconies, it is more difficult to store beets; their shelf life is reduced to 3-5 months.
Root crops are sorted once a month. Remove rotten, lost elasticity, and pest-damaged specimens.
Storing root vegetables
Beets can be stored in boxes, plastic bags (without tying them), next to potatoes and carrots, in dry sand, ash, in bulk, or in the refrigerator. Fodder root crops and beets grown on an industrial scale are stored in piles.
How to store beets in cellars and basements
The cellar is the best place for beets in winter. Here vegetables are stored until the new harvest.
- Root vegetables are placed in bulk on dry sand in a layer of no more than 5 cm. If the floor is concrete or wooden, then the crop is poured onto pallets 10-15 cm high. This is done for better air circulation.
- If stored in the cellar potato, then the beets are scattered on top of it. Potatoes in winter require a humidity of 75-80% to keep well. When tubers respire, a significant amount of moisture is released, and beets absorb it well. Under such conditions, both potatoes and beets are stored ideally.
- The harvest is stored in boxes and place them on the floor and shelves without covering them with anything.
- How to store beets in sand or sawdust. The bottom of the box is covered with sand and root vegetables are laid out. Each layer is sprinkled with sand. Sand (and sawdust) prevents moisture from reaching the crop and also delays the evaporation of moisture from the surface of vegetables.
You can store beets in the basement of apartment buildings if the temperature there in winter is not too high. Root crops are placed in boxes and baskets, you can sprinkle them with sand. It is not recommended to store beets in bags in the basement, since air circulation there is still limited, and the bag makes it even more difficult, and the crop may rot.
How to store beets in an apartment
Storing vegetables in winter in a city apartment if there is neither a basement nor a balcony is quite difficult. It will not be possible to create the necessary conditions here. In winter, the air in the apartment is quite dry and warm. Therefore, the coldest place (corridor, pantry) is chosen for the harvest. Place polystyrene foam at the bottom of the box, lay out the beets and sprinkle them with sand. The top of the boxes is covered with a second sheet of foam. Polystyrene foam prevents moisture evaporation and heat exchange between root crops and the environment. As a result, the inside of the box maintains a relatively constant temperature and humidity. In such conditions, the crop is stored for 3-5 months, depending on the room temperature.
Beets are stored in bags in the same way.
If there are only a few beets, then prepare a dressing for borscht. This preservative can be stored for up to 1.5 years. You can grate the root vegetables and freeze them in the freezer. But after defrosting, re-freezing is impossible, otherwise the vegetable will lose its taste and shape.
If the harvest is large and it is impossible to preserve it all in processed form, then the root crops are dipped in a clay solution and dried. In this form, they can be stored even in relatively warm conditions (temperature 10-12°C) for 4-6 months.
Storing beets on the balcony
If the apartment has a balcony or loggia, then the harvest can be stored there all winter. It is put into boxes, sprinkled with sand. You can put it in plastic bags that do not need to be tied, otherwise the crop will rot. Root vegetables are left on the balcony and, depending on the weather in winter, they are covered with rags, blankets, foam rubber, and polystyrene foam. If the winter is very cold, then on the coldest days (temperature below -28°C) root vegetables are brought indoors. A few days in warm conditions will not have any effect on the safety of the crop.
Storing root vegetables in the refrigerator
The keeping quality of the vegetable in the refrigerator is low. Beets can be stored in these conditions for no more than 2-3 weeks, then the root crops begin to get wet and rot. The reason for this is insufficient air exchange. There is almost no flow of fresh air into the refrigerator and the moisture released by the root crops again settles on them, condensation forms. The crop gets wet and rots.
Therefore, if the refrigerator is the only place to preserve the crop, every 2 weeks the beets are removed and dried for 18-24 hours, then removed again. This technique somewhat increases the shelf life of root vegetables in the refrigerator.
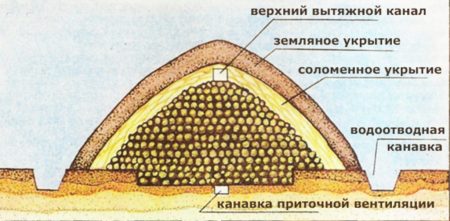
Sheltering vegetables in piles
Table beets grown on an industrial scale, as well as fodder beets, are stored in piles. The preservation of the crop in piles is very good. Despite the fact that vegetables are stored on the ground (or in a small depression), they do not freeze in winter and last almost until summer.
The piles are installed at the highest and driest place with a groundwater level of at least 1 m. If the place is flat, then a ditch is dug along the perimeter of the future storage facility to drain rain and melt water. The collar must have ventilation, the simplest type is supply and exhaust ventilation. The width of the storage directly depends on the climate: in the middle zone 2-2.2 m, in Siberia at least 3 m, in the south 1-1.3 m. Vegetables are placed in a mound with a ridge, and the storage is covered. The piles can be buried 15-30 cm into the ground.
The bottom of the pile is lined with a layer of spruce branches or hay. All material must be absolutely dry.
The covering material and the thickness of the covering layer directly depend on the winter weather. The colder the winters in the region, the thicker and more layers should be in the storage. The root crops are first covered with spruce branches to protect them from rodents, then covered with a layer of hay or straw and covered with earth on top. On the crest of the collar, the covering layer should be smaller than on the sides, since it is through the crest that excess heat is removed. If there is heavy rain in the fall, the ridge is covered with film to prevent water from penetrating into the storage, otherwise the crop will rot. Until the onset of stable cold weather, the collar is not completely closed.
To measure the temperature inside the storage facility, thermometers are placed: one on the ridge, the second on the north side of the pile. At a temperature of +2-4 degrees inside the storage facility, it is completely closed for the winter. If the temperature inside in winter drops to +1°C, then the pile is additionally insulated by throwing snow on it.
Burts are a solution for those who have absolutely no place to store their harvest. You can also store other vegetables in such storages.





 (4 ratings, average: 4,50 out of 5)
(4 ratings, average: 4,50 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.