Growing eggplants in a greenhouse is both simple and difficult. On the one hand, they are not as demanding of care as peppers; on the other hand, it is difficult for them to create the necessary conditions for normal growth, since the crop is very demanding of heat. This especially applies to the northwestern and central regions, where eggplants are grown only in a greenhouse, and the harvest is not obtained every year.
How to grow eggplant seedlings at home read this article
| Content:
|
Eggplant varieties for greenhouse cultivation
Since eggplants are grown in greenhouses mainly in the middle zone and to the north, there are a number of requirements for the varieties.
- The variety or hybrid must be early, the ripening period is 100-110 days.
- Small-fruited eggplants are grown because large-fruited ones, even mid-early ones, do not have time to ripen.
- Low-growing varieties are chosen, since tall plants spend too much time growing tops and begin to bear fruit later.
- Eggplants should set fruit well when temperatures fluctuate.
- It is desirable that varieties be resistant to unfavorable growing conditions.
|
These are the different varieties of eggplants |
Taste of mushrooms. Early ripening white-fruited variety. Fruits well in fluctuating temperatures. The fruits are small. Under favorable conditions, you can get 6-10 fruits from a bush.
Marzipan. They are grown in greenhouses in the Central Black Earth regions and further south. In the north, even indoors, there is not a harvest every summer. Mid-season, tall hybrid. The fruits are large, with a slightly sweetish, pleasant taste. The hybrid is very unpretentious. It tolerates both heat and drought, as well as cold, damp weather.
Banana. An early ripening variety, the period from germination to technical ripeness is 101 days. The fruits are small but long, average weight is 150 g. The yield is high and the keeping quality is excellent.
Japanese dwarf. Early ripening low-growing variety.Unpretentious, tolerates unfavorable growing conditions. The fruits weigh 160-170 g. They have excellent taste.
Umka. Tall early white-fruited variety. The fruits are large, weighing up to 300 g, the taste is excellent, without bitterness.
Black Prince. Mid-early variety. The fruits are purple, long, strongly curved. Fruit weight is 150-200 g. The pulp is slightly greenish, good taste.
Caviar. Mid-season hybrid. The fruits are pear-shaped, elongated, medium in size, dark purple in color. The pulp is without bitterness, white. The fruits of this variety produce high quality caviar.
Rules for growing eggplants in a greenhouse
Growing and caring for eggplants indoors is not particularly difficult. You just need to know the agricultural technology of the crop and some of its preferences.
Greenhouse preparation
What do eggplants like? Eggplants love organic-rich, neutral soil. However, they are not as picky as peppers, and can grow and bear fruit well in soils with a low humus content and pH 5.5. For culture, it is more important that the soil is warm, water- and breathable. When grown in heavy soils, plants form a more compact bush and stand stronger than in light soils.
It is advisable to have eggplants in the greenhouse grow after cucumbers and undesirable after the peppers And tomatoes. After them, the soil is steamed in the fall by pouring boiling water over it. The same should be done in the spring before planting seedlings, since eggplants have common diseases with peppers and tomatoes.
In a polycarbonate greenhouse, the soil warms up quickly in the spring, so there is no need to further increase its temperature. In glass and film greenhouses, the soil warms up more slowly, therefore, for earlier planting of seedlings make warm beds.
Preparing a warm bed
It is advisable to prepare them in the fall so that, if possible, pathogens and wintering pests freeze out in winter. And in the spring the bed is steamed.
|
To prepare a warm bedding on the bed, make 1-2 furrows (depending on the width of the bed) 20-25 cm deep, put half-rotted manure, hay, plant debris, kitchen scraps (except for potato peels) there and cover them with earth. |
To grow, eggplants do not require large quantities of either phosphorus or nitrogen, so in the fall, only organic matter (manure or green manure). Of the mineral fertilizers, only phosphorus is applied for autumn digging, since eggplants experience some deficiency of it at a young age.
There is no need to add potassium, since the crop does not need it much, and its excess leads to the death of the root tips. Potassium deficiency is easily compensated for during the growing season.
In the spring, before planting seedlings, the soil is spilled with boiling water. When it becomes warm to the touch, seedlings are planted (provided that the outside temperature is not lower than 13-15°C).
Transplanting
Eggplants are very demanding of heat and sun, so planting dates depend on the weather. Planting in a greenhouse is carried out when the temperature at night is at least 8-10°C (in the greenhouse, accordingly, it is 4-5°C higher). In the south, the crop is planted in a greenhouse in late April - early May, in the center in mid-late May.
There is no point in planting it later, since it will still not have time to produce a harvest. All dates are very approximate and highly dependent on weather conditions.
- In the middle zone, seedlings are planted at the age of 70-80 days
- In the south, 30-40-day-old seedlings can also be planted.
- It is desirable that by the time of planting the plant has 5-6 true leaves.
But in the middle zone, eggplants with 3-4 leaves are often planted in a greenhouse, since in cloudy weather they do not grow well on the windowsill.
Such plants, under favorable conditions and proper care, can also produce a harvest, although it will be smaller. In the southern regions, such seedlings grow into full-fledged plants and produce a good harvest.
|
Before planting, the crop is hardened off for 3-5 days by opening the windows or taking it out onto the balcony; the temperature, however, should not be lower than 12-13°C. |
For normal growth, eggplants still require nitrogen, so add 1 tbsp to the planting holes. l. azophosphate or urea, lightly sprinkling the fertilizer with soil. The hole is filled with hot water 2 times (in cold regions), and as soon as the water is absorbed, the eggplants are planted. If they are elongated, then the plants are buried 1-3 cm.
- Distance between low-growing plants 30 cm
- Between medium and tall 50-60 cm.
- Row spacing is 70-90 cm.
However, thicker eggplants can be grown in greenhouses, provided that the lower leaves are subsequently regularly removed.
After planting, the seedlings are watered abundantly. In the northern regions, they must be planted under cover, since at night the plants are cold even in a greenhouse. In the south, if the nights are warm (not lower than 15°C), then the eggplants do not need to be covered. Immediately after planting, eggplants are shaded from the bright sun, since in direct sun they can get burned and die.
Caring for eggplants after planting
In the center and north, the crop is planted under cover, even in a greenhouse. Immediately after planting, the bed with plants is mulched with straw and covered with spunbond or lutrasil on top. When the temperature at night is above 12°C, the covering material is removed.
|
In the central regions, eggplants are opened in sunny weather and covered again with lutrasil at night. Sometimes plants have to be kept under cover until mid-June because the nights are too cold. |
The mulch is removed 2-3 days after planting. However, if frosts are expected, the plants are mulched again, covered with spunbond and the greenhouse is completely covered.
How to water seedlings
Planted seedlings are watered when the soil dries out. The appearance of a new leaf indicates that the plant has taken root. Eggplants require quite a lot of water before flowering, but do not like waterlogging. If the weather is warm, then watering is done 2-3 times a week, if it is cold - 1-2 times. Water abundantly, only with warm water.
|
The greenhouse is regularly ventilated. Even on the coldest days, open the windows for 40-60 minutes. |
Feeding plants before flowering
Before flowering, 2 feedings are carried out. In the first half of the growing season, eggplants need nitrogen more; potassium and phosphorus are practically not required. The first feeding is done 10-12 days after planting the seedlings. Before flowering, feed only with mineral fertilizers, otherwise the crop will go to the tops and will not bloom for a long time.
- 2-3 tbsp. urea is diluted in 10 liters of water and fed at the root. However, in regions with long summers, you can feed humates, infusions of weeds, and even manure; Over a long growing season, the plants will produce a full harvest.
- The second feeding is carried out 10 days after the first. Take any nitrogen fertilizer (urea, azofoska, nitrophoska, ammophoska, etc.). However, if the eggplants are frail, you can also feed them with humate, since they still won’t bloom until they gain vegetative mass.
Care during flowering and fruiting
Pollination
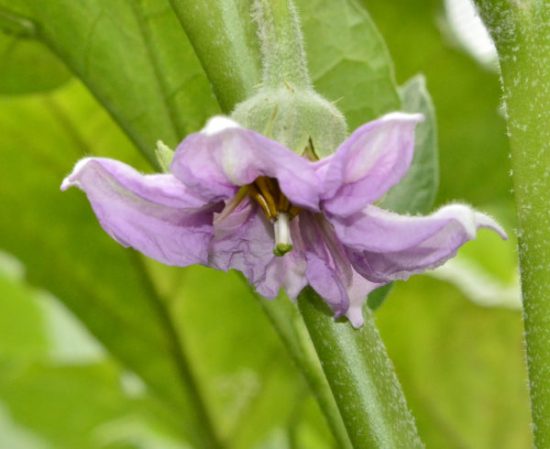
After 4-5 weeks, the eggplants begin to bloom.Their flowers are large and bright purple. When grown in greenhouses, pollination of flowers is difficult because there are no pollinating insects, so they have to be pollinated by hand. Flowering lasts 7-10 days. Its peculiarity is that in newly opened flowers the pistil is at the same level as the stamens, and the pollen is immature, so pollination is impossible.
|
In the second half of flowering, the pistil lengthens and there are more stamens, and the pollen matures; it is at this moment that the flowers need to be pollinated. |
If manual pollination is not possible, eggplants are treated with Gibbersib, Ovary, Bud. They contain the hormone gibberellin, which stimulates the growth of the ovary. When pollinated, the seed itself begins to produce this hormone. If pollination does not occur, then gibberellin is not produced and the barren flower falls off.
When sprayed with these drugs, the level of the hormone increases, and even without pollination, the plants begin to set fruit.
The main indicator of a flower's readiness for pollination is the appearance of spines on the calyx. If the calyx is still thornless, then the flower is not yet ready for pollination. However, now there are varieties that do not form thorns at all. In this case, the readiness of the flower for pollination is determined by the size of the pistil.
|
In addition to single flowers, the culture sometimes forms inflorescences of 2-3 flowers. There is no need to remove them; they form normally developed fruits. But most often only one flower per inflorescence is formed. |
In cold weather, flowers are not pollinated even if done manually. The same thing happens in extreme heat, when the temperature in the greenhouse is above 40°C. Even under favorable conditions, no more than 50% of flowers form the ovary.
Watering rules
During the flowering and fruiting period, the water requirement of eggplants decreases somewhat, and the need for constant ventilation increases. Plants do not tolerate waterlogged soil well, but they can withstand short-term lack of moisture well.
Watering is carried out 2 times a week; in hot weather, more frequent watering is possible. During this period, the crop becomes less sensitive to cold water, so irrigation water can have a temperature of 18-20 ° C, since the soil in the greenhouse is warm.
Eggplants love warmth
Eggplant is the most heat-loving crop of all grown in a greenhouse. In terms of heat requirements, they are superior to both cucumbers and peppers. True, with a lack of heat, plants do not shed flowers and ovaries (like peppers), and do not stop growing (like cucumbers). The vegetative mass grows, but the plants do not bloom.
In cold weather for eggplants (20°C and below), the air in the greenhouse must be artificially heated, especially at night. To do this, hot bricks from the bathhouse are laid out in the passages or hot water is placed in buckets in the greenhouse. But it is desirable that the heat be dry and no condensation form, therefore, if there is, instead of water, put buckets of hot ash. At night temperatures below 20°C, the greenhouse is completely closed.
|
In cold weather, eggplants are watered with warm water, and hay is laid out between the rows. The wet hay inside heats up and releases heat to the outside. |
They do not put hay under the bushes themselves, since during greenhouse cultivation the soil is always warm and there is no need to warm it up additionally.
If it’s warm during the day and cold at night, then the greenhouse with eggplants is completely closed at night, opening only when the air warms up
Ventilation of greenhouses
Greenhouse eggplants must be ventilated; they cannot tolerate high humidity. When the humidity rises to 85%, various rots immediately appear on the crop, which are incredibly persistent on eggplants.
The greenhouse is ventilated daily in any weather.
Even if it is very cold outside, open the windows for 40-60 minutes. In hot weather, the greenhouse is opened all day, and if the nights are warm (20°C and above), then it is left overnight.
As soon as the fruits have set, the greenhouse is opened for at least 2-3 hours a day, since rot primarily affects the ovaries. To increase the crop's resistance to low temperatures, plants are sprayed with Epin or Zircon.
Feeding eggplants when grown in a greenhouse
As in the initial growth period, eggplants need nitrogen most of all. At this time, the need for potassium and microelements increases, although not as significantly as in other crops. After setting the first fruit, eggplants can be fed with manure. During this period, organic matter will not stimulate increased growth of tops, but the appearance of new shoots and buds.
|
Greenhouse eggplants are fed every 7-10 days. |
- The first feeding is carried out with infusion of manure (1:10), chicken manure (1:20) or weeds 1:5). The consumption rate is 1 liter per plant.
- In the second feeding, potassium humate is added with any microfertilizer. Next, alternate fertilizing with organic matter and microfertilizers.
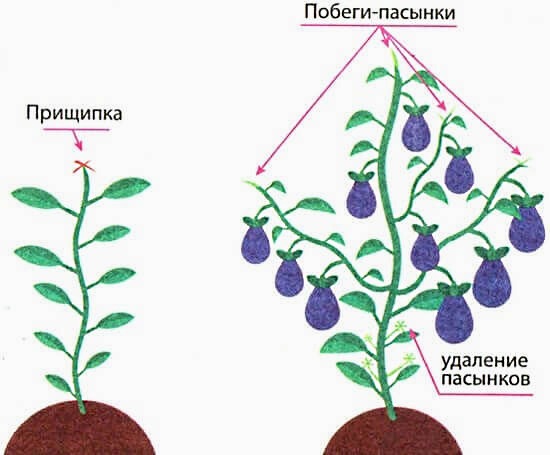
Forming eggplants in a greenhouse
When grown in a greenhouse, eggplants must form. In the northwest, plants form into one stem, in the center - 1-2 stems, in the southern regions - 3-5 shoots. In cold regions, all shoots coming from the root and from the axils of the leaves are removed, leaving only the central stem.
If buds have already appeared on the stepson, then pinch off the top. But, most likely, the flowers on the stepson will fall off, since there is not enough heat for the formation of fruits. If the flowers do not produce ovaries, the shoot is removed.
|
Scheme of formation of an eggplant bush |
In the middle zone there is more heat, so the plant can feed 2 shoots. It is better to leave either the strongest root shoot or the stepson from the first leaf. The shoot is pinched after 3-4 pairs of buds appear. The remaining stepsons are removed when they reach 6-8 cm.
In the southern regions, there is enough heat and sun to allow eggplants to branch. Here they leave from 3 (Central Chernozem regions, Middle Volga region) to 5 stepsons (Crimea, Caucasus, Krasnodar Territory). However, they make sure that the bushes in the greenhouse do not turn into a complete jungle; Light must always penetrate down to the ground.
The strongest stepsons are left, coming from the roots and from the axils of the lower leaves. The remaining shoots are removed. The tops of new shoots are pinched after 3-5 pairs of flowers appear. Young shoots are tied to pegs, preferably each separately.
Removing the lower leaves
In addition, regardless of the growing region, the lower leaves of greenhouse eggplants are removed. The plant no longer needs them and only blocks the access of light to the lower flowers and fruits. In addition, remove the leaves that block direct sunlight from reaching the buds and flowers.
It is believed that, among other things, eggplants set fruit only when the flowers are exposed to direct sunlight. Therefore, in cloudy summers there are practically no fruits.
You can remove 2-3 bottom sheets at a time. Besides, cut off all diseased leaves at once. If healthy lower leaves are also removed, then the eggplants are fed with infusion of manure.
On the side shoots, as they grow, the lower leaves are also removed. No more than 4-6 leaves can be cut from all shoots at the same time. They are cut off, leaving a stump of 2-3 cm. They are not cut off near the trunk itself, since rot will immediately appear there.
|
Eggplants cannot be “shaved bald” like tomatoes, because their leaf blades grow more slowly, and the photosynthesis occurring in the leaves feeds the growing buds and fruits. The plant should always have at least 6-7 leaves. |
If few buds form on the main stem and the flowers fall off without setting, then pinch off the top of the shoot, allowing the rest to develop stronger. Sometimes when the top is removed (especially when grown in 1-2 stems), it begins to branch intensively.
This method is used in the middle zone. It is believed that the resulting shoots will bloom and bear fruit better.
A properly formed plant should have 1-4 side shoots with 3-4 fruits (exception - north-west).
Harvesting
Eggplants are harvested in the technical ripeness phase, without waiting for them to fully ripen. With biological ripeness, the fruit pulp becomes rough and inedible, and the vessels become hard. Young fruits are tasteless, astringent, and contain a lot of tannins and acid.
Technical ripeness is determined by the strong shine, intense color of the fruit and the beginning of lightening from the tip to the calyx. Technical ripeness can also be determined by the flowering period; it occurs 22-35 days after the formation of the ovary.
|
The first fruits are removed 3-4 weeks after flowering, then every 6-7 days |
When the lower fruits are removed, the rest begin to fill faster.They are cut with a knife, since the stalk of the crop is woody and breaking off can damage the stem.
In addition, most varieties have thorns on the calyx, stalk and veins of old leaves and it is safer to cut the fruits rather than break them off.
The collection is completed before the onset of cold weather (6-8°C).
The fruits are stored for 15-25 days at a temperature of 12-15 °C. At higher storage temperatures, they can be affected by white and gray rot. For long-term storage, immediately after harvesting, eggplants are placed for 2 days in a dark, cold place (8-10°C) with a humidity of 80-90% (usually a refrigerator). They are then kept at 2°C.
It is better not to keep the fruits in the light, since corned beef accumulates in them, which impairs the taste.
Diseases and pests
The main disease of eggplants grown in greenhouses is white rot in the northern regions and Fusarium wilt in the southern ones.
White rot - the scourge of greenhouse eggplants in the north. It appears when there is high humidity in the greenhouse during the flowering period and can completely destroy the plants. It is very difficult to fight her. The basic rule is to thoroughly ventilate the greenhouse and not allow the humidity to rise above 80%.
It primarily affects the stalks and ovaries. In thickened plantings it appears on the stems.
|
To remove the source of the disease, diseased fruits are removed, the stems are stripped down to healthy tissue and sprinkled with chalk, urea, and fluff. |
When the disease appears, the bushes are sprayed with Forecast and Baksis. For minor damage, treat with Trichoderma.
Fusarium wilt widespread in greenhouses in the south. It appears with uneven watering and temperature fluctuations. When the disease occurs, the roots rot, a pink coating appears on the root collar, and the plant withers and dies.
There is no cure for the disease. At the earliest stages, they are watered with Previkur or Tiovit Jet, which delay the development of the disease for a long time. If the disease progresses, the plant is removed, the rest are watered with Previkur or Pseudobacterin.
|
Fusarium wilt |
The main crop pest is Colorado beetle, which can destroy plants in a few days. However, in greenhouses it is not as harmful as in open ground. When the pest appears, it is collected manually and greenhouse eggplants are sprayed with Iskra or Bitoxibacillin. At the same time as the greenhouse, plants in the open ground are also sprayed. In protected soil, the Colorado potato beetle is found much less frequently than outdoors.














 (10 ratings, average: 4,70 out of 5)
(10 ratings, average: 4,70 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea.There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea.There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.