Blossom rot is a physiological disease of tomatoes that is not associated with pathogenic factors. It appears with improper care and affects tomatoes both outdoors and in the greenhouse. Peppers are more sensitive to the disease and are the first to be affected. If blossom end rot appears on them, then simultaneously with their treatment, preventive measures are taken on the tomatoes.
Why do tomatoes suffer from blossom end rot?
The main cause of the disease is improper agricultural practices.
Causes of blossom end rot.
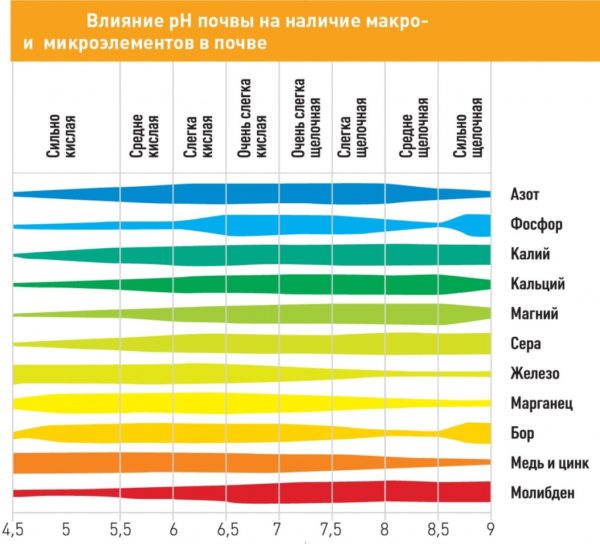
- Lack of microelements, especially calcium. Calcium is part of the cell walls of the skin of tomato fruits, and if it is deficient, they become deformed and destroyed. Lack of the element occurs in highly acidic soils and peat bogs.
- Boron deficiency. Boron is a trace element, but if it is deficient, the absorption of calcium is significantly reduced. The lack of both elements inevitably leads to the appearance of blossom end rot on tomatoes. It is especially common in acidic soils.
- High temperature with insufficient soil moisture. In the northern regions, this factor leads to blossom end rot only in greenhouses. In the south, drought and heat provoke the appearance of the disease both in open and protected ground. When it is hot and there is no watering, water and nutrients flow from the fruits to the leaves and stems. Tissues, lacking fluid, dry out and die.
- High acidity of the soil, which prevents the absorption of calcium. As a result, a thin cell wall is formed, which is then destroyed.
In the northern regions it is more common in greenhouses; in the south, the frequency of its occurrence in open and protected ground is the same.
Signs of defeat
During drought and heat, mainly the tomatoes of the first three clusters are affected. In acidic soils and with a lack of calcium, tomatoes become diseased on all bunches as they set.
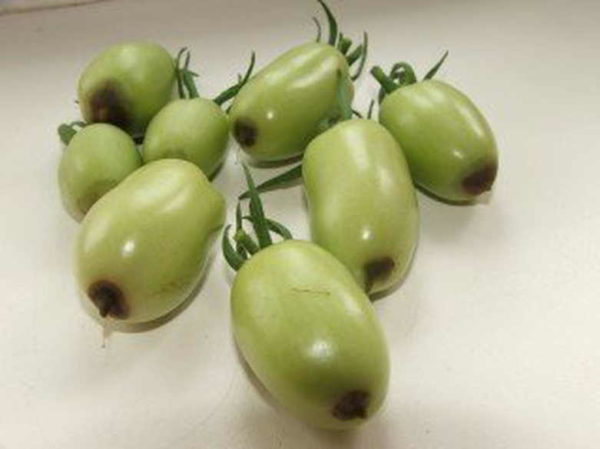
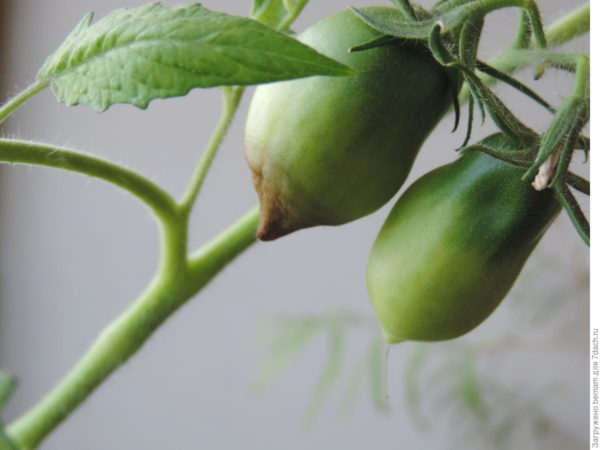
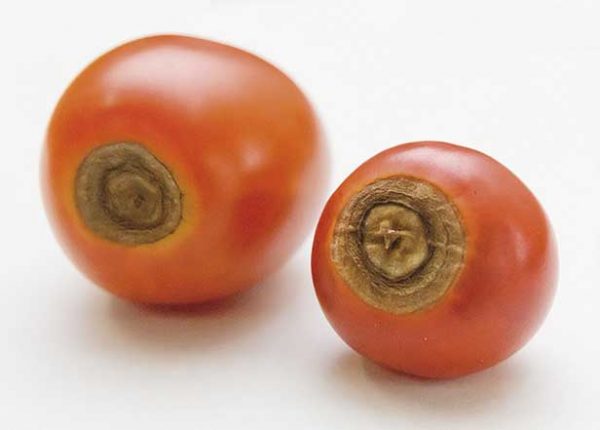
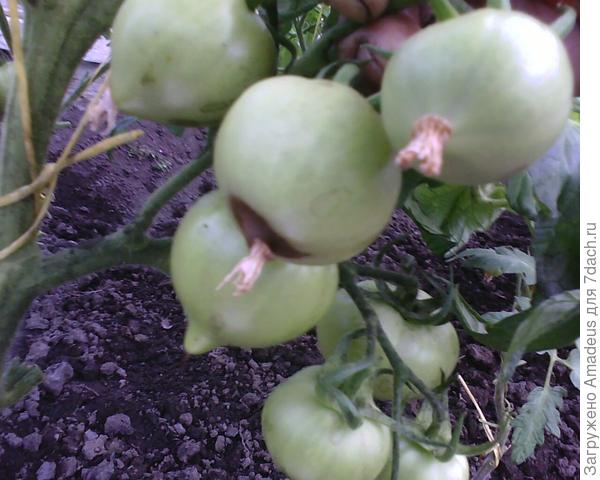
Only green tomatoes are affected by blossom end rot. At the top of the fruit (where the flower was) a watery dark green spot appears, which quickly darkens, the tissue dries out, is pressed into the fruit and hardens. Over time, the spot becomes brownish-brown in color.Depending on the strength of the damaging factor, the spot may be small at the very top of the tomato, or it may grow, covering up to half of the fruit.
Diseased tomatoes stop growing and ripen quickly. Sometimes the disease occurs in a latent form. There are no external signs of the disease, but the cut shows browning or hardening of the tissue at the top of the tomato.
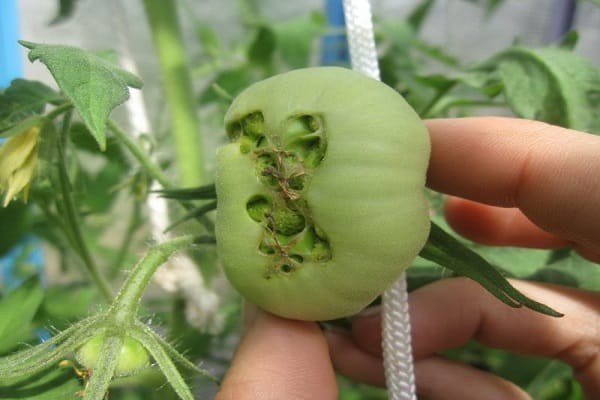
In large-fruited varieties, a ring more often appears at the top of the fruit, which, gradually growing, turns into a spot. The tissue inside it is pressed in, the top of the fruit becomes lumpy and gradually darkens. But if bleached tomatoes become sick, the ring stops growing.
Bleached tomatoes do not consume nutrients, so the disease does not progress. Such fruits can often be seen in stores. They are edible; you just need to cut off the top of the fruit.
Photos of tomatoes affected by blossom end rot
Treatment of blossom end rot on tomatoes
The method of treating blossom end rot depends on the cause of the disease.
Acidic soil
If the soil is highly acidic, calcium is not absorbed by tomatoes at all, and blossom end rot will appear from year to year. To prevent it, the area is limed. Indicators of acidic soil are the strong growth of plants such as sorrel, horsetail, plantain, and heather.
Among garden plants, lupine (in such conditions it grows lush, up to 1.5 m high) and hydrangea love high acidity. Potatoes and carrots grow well in slightly acidic soils, and horseradish grows very strongly. If these crops are not at the dacha, then the acidity can be judged by cabbage and beets: these crops grow poorly in an acidic environment.
To reduce the acidity of the soil, it is deoxidized.Typically, dolomite or limestone flour, chalk, and gypsum are added in the fall at a rate of 300 g/m2 on clay soil and 200 g/m2 on the sandy one. It is preferable to apply chalk since it does not burn the roots. Since lime promotes the leaching of potassium from the soil, potassium fertilizers must be applied in the spring (potassium sulfate is preferable for tomatoes).
Calcium deficiency
Calcium deficiency can occur due to high acidity of the soil, as well as due to calcium deficiency in it.
Since all lime fertilizers contain calcium, their application is both a feeding and replenishment of its deficiency in the soil.
To treat tomatoes from blossom end rot, foliar feeding is used. The most commonly used and gives an excellent effect is calcium nitrate. 7-10 g are dissolved in 10 liters of water, treatment is carried out early in the morning or in the afternoon. With increased soil acidity, spraying is carried out 2-3 times with an interval of 10 days.
For preventive purposes, tomatoes are not sprayed, since excess calcium leads to impaired nitrogen absorption, and the top of the fruit does not turn red and remains green; when cut, the tissues look green and compacted.
Blossom rot is widespread in black soils, rich in calcium. However, here it is contained in a form inaccessible to tomatoes. To eliminate its deficiency, fertilizers are used in chelated form.
Chelates contain the active substance enclosed in a water-soluble shell. When it enters the soil or lands on tomatoes, it is immediately absorbed by them. The most commonly used chelates are Brexil calcium, Kalbit C (liquid chelate fertilizer), Vuxal calcium (complex chelate fertilizer containing, in addition to calcium, other microelements and nitrogen).
Chelates act faster than potassium nitrate. Treatments should not be carried out during the daytime, since in the bright sun the leaves and stems can get severely burned. On cloudy days, spray tomatoes at any time.
The number of treatments depends on the severity and prevalence of the disease. If the disease does not manifest itself on the next cluster, then treatment should be stopped, since excess calcium also negatively affects the filling of tomatoes.
Boron deficiency
Boron is a trace element that affects the absorption of calcium and increases the fruit set of tomatoes. Its deficiency is manifested by poor fruit set. To eliminate microelement deficiency, as well as to treat blossom end rot, the drug Brexil Ca, which contains both nutrients, is used.
Drought
Tomatoes in southern regions and in greenhouses suffer especially badly from it if watered incorrectly. The disease is more severe at high temperatures. In cold and dry weather, tomatoes practically do not suffer from blossom end rot, although rot may appear in the absence of watering for a long time.
When there is severe drought, plants begin to take water from the fruit and direct it to the growing point. As a result, the cells at the top of the fruit die. Signs of the disease increase as the drought intensifies; the longer it lasts, the more fruits become diseased. Tomatoes are also affected on the upper trusses, and technically ripe tomatoes fall off.
If the disease appeared against the background of fertilizing with complex fertilizers, then the conclusion is clear - the tomatoes do not have enough moisture.
Treatment of tomatoes for rot begins with very little watering of the bushes.Immediately carried out abundant watering causes cracking of bleached and ripe fruits, as well as dropping of the ovaries. Conduct three moderate waterings every other day. In the future, water the bushes 2 times a week in small doses, preferably using drip irrigation.
If after regular watering the disease continues to spread, then additional foliar feeding with calcium nitrate or chelate solutions is carried out. In the absence of water, calcium also ceases to be absorbed and its absorption from the soil is restored more slowly than the water balance.
To protect the soil from drying out and overheating, it is mulched with sawdust, grass, and on chernozems it can be peat. On acidic soils, peat is not used as mulch, since it acidifies it very strongly.
In the northern regions, ground tomatoes do not suffer from drought, so if blossom end rot appears on them, the reason is clearly not a lack of moisture. Most often this is due to high acidity of the soil and low calcium content in it. Therefore, treatment consists of the necessary feeding. There is no need to water the tomatoes, otherwise you may cause root rot.
How to treat blossom end rot with folk remedies
The most commonly used folk remedy for calcium deficiency is ash. To water the bushes, 1-1.5 cups of ash are poured with water and mixed thoroughly. Water the roots with a freshly prepared solution at the rate of 2-4 liters per plant.
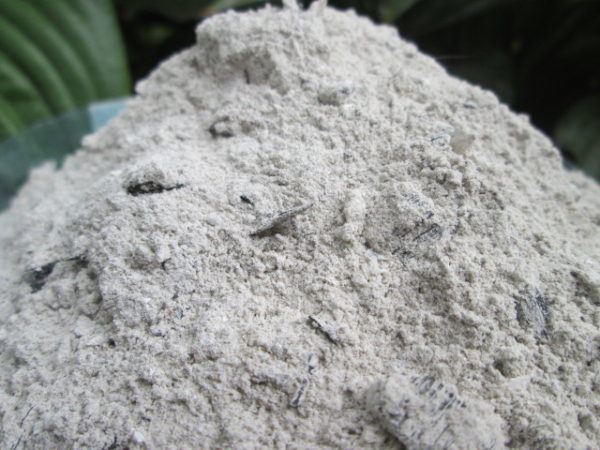

Ash is often used to treat many tomato diseases.
An extract from ash is prepared for spraying. 300 g of ash is boiled for 30 minutes in 2 liters of water, stirring constantly, then left for 10-12 hours, then filtered. The resulting solution is brought to 10 liters and sprayed.An adhesive must be added to the solution: scented soap or shampoo.
Laundry soap with ash is not used, since the solution is too alkaline and can burn leaves and set tomatoes. Leaves and fruits should be well moistened.
To prevent, as well as treat, rot where it appears, ash is added annually to the holes when planting seedlings. It must be remembered that ash burns the roots of tomatoes, so when directly added to the hole, it is sprinkled with earth so that the roots do not come into contact with it.
Eggshell
Eggshells are 95% calcium. To ensure there is sufficient quantity of it, some summer residents collect it all winter. The shells are ground into powder and stored as fertilizer. When applied, it does not burn the roots and does not cause burns to the leaves.
If it is collected in the fall, then it is cleared of the inner film, crushed and stored in a dry place. If it is used in the summer, then immediately after cleaning the eggs the shell is ready for use.

Egg shells are used to treat tomatoes
Egg shells are placed in a liter jar and filled with water. Leave for 3-5 days. The infusion should become slightly cloudy. If an unpleasant odor appears, it means there is protein left on the shell. This infusion can be used, but it is used when an odor appears, without infusing for the prescribed time. The finished infusion is mixed, filtered, water is added to 3 liters and sprayed.
Crushed shells are added to the holes when planting seedlings.
Using eggshells is the cheapest, safest and most accessible way to treat blossom end rot on tomatoes.
Soda Ash
Soda ash (sodium carbonate) has a very strong alkaline reaction and is not used on carbonate soils.The drug is highly soluble in water and is used for root and foliar feeding. To prepare a medicinal solution, 1 tbsp. soda is diluted in 10 liters of water.
Spraying on leaves can only be carried out in cloudy weather, since the solution can cause severe burns to plants, and if the proportions are not observed, destroy tomatoes.
Watering rate is 0.5-1 l per bush. Fertilizing is done only after watering the tomatoes, otherwise you can burn the roots.
Feed or construction chalk. Foliar feeding is carried out during the growing season. 500 g of chalk are diluted in 10 liters of water and the plants are treated by leaves.
Prevention of rot on tomatoes
During drought, the best prevention of blossom end rot is drip irrigation. The tomatoes do not experience a lack of moisture, and, at the same time, there are no sudden changes in soil moisture that negatively affect the ripening of tomatoes. If the cause of the disease is a lack of moisture, then with drip irrigation it will never appear.
Proper watering also prevents the occurrence of disease. In the south, in hot weather, tomatoes are watered in a greenhouse every 2-4 days. The main criterion is that the soil dries out by 3-4 cm. You can determine the humidity by sticking a stick into the ground to a depth of 5-6 cm. If the earth sticks to it, then the soil is moist and watering is not required, but if the stick is covered with dust or the earth sticks only to at its end, it is necessary to water.
Acidic soils are deoxidized by applying lime fertilizers in the fall. The only exception is the fluff. It gives a quick but short-term effect, so it is applied in the spring when digging up a greenhouse or future tomato plot, but before planting seedlings.
Calcareous soils are not limed, since calcium is found in excess there, and its additional application only increases the alkalinity of the soil. The disease occurs due to the fact that it is contained in a form inaccessible to plants. Here, when planting seedlings, 1 teaspoon of eggshells or ash is added directly to the hole.
Treating tomatoes with baking soda, as some recommend, is useless. It does not contain calcium, which is so necessary for treating tomato rot. All it contains is sodium and carbonic acid, which tomatoes do not need. The effect of such treatment is zero.
Unresistant and disease-resistant tomato varieties
Long-fruited tomato varieties suffer from blossom end rot more often. When forming elongated fruits, more calcium is required than for round tomatoes. Therefore, with a high risk of developing rot, long-fruited tomatoes get sick more often than others. These are, for example, such popular varieties as:
- Banana (yellow, orange and red)
- Cream
- Jessica
- Havana cigar, etc.
In addition, early-ripening and large-fruited tomatoes are affected more than late-ripening ones. This is due to the fact that the bushes need to provide all the filling tomatoes with the required amount of nutrients in a short time. If the root system of the seedlings was not sufficiently developed, then it cannot cope with the needs of the above-ground part, which leads to disease.
Late-ripening tomatoes suffer from blossom end rot very rarely.
Currently, tomato varieties have been developed that are resistant to the disease even under unfavorable conditions and poor agricultural practices. These include varieties
- Crown
- Summer resident
- Lunar (small-fruited)
- Delicacy.
















 (25 ratings, average: 4,48 out of 5)
(25 ratings, average: 4,48 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.