When the apple tree slows down and begins to bear fruit, both the metabolism and their distribution change. An adult apple tree requires different care than a young one. Therefore, agricultural technology is also changing. The article provides step-by-step recommendations for caring for fruit-bearing apple trees in spring, summer and autumn.
|
Fruiting trees require more careful care than young seedlings. Apple trees that have begun to bear fruit require attention throughout the year. |
Caring for fruiting apple trees
Caring for fruit-bearing trees is significantly different from caring for young apple trees. Everything changes: soil care, fertilizing, and watering. And crop care is also added.
Dates of fruiting
When the garden begins to produce crops, it becomes fruitful. The timing of fruiting varies and depends on the variety. As a rule, apple trees on dwarf rootstocks begin to bear fruit at 3-4 years, on semi-dwarf ones at 5-7 years, and tall apple trees begin to bear fruit at 8-12 years. There are, of course, many exceptions to this rule, but in general this is the case. In addition, winter varieties begin to bear fruit later than autumn ones, and autumn varieties later than summer ones. Columnar apple trees begin to produce crops already in the second year after planting.
The timing of fruiting is very arbitrary; it depends on the climate, care and pruning. Tall varieties will not produce crops until they reach the height required by the variety.
In the garden, with proper care, apple trees live up to 150-200 years, but in nature they live only 80-100 years. The fruiting period is long: 10-30 years and depends on the height of the apple tree. Varieties on dwarf rootstocks finish bearing fruit faster than tall trees.It is believed that medium-sized and tall trees reach maximum productivity at the age of 20-25 years, and then the yield decreases. But all this, again, is very conditional. I have trees on my property that are 45 years old, which reached maximum fruiting about 10 years ago. So far the yield is not decreasing, although it is not increasing. But perhaps this is a special case.
Soil care
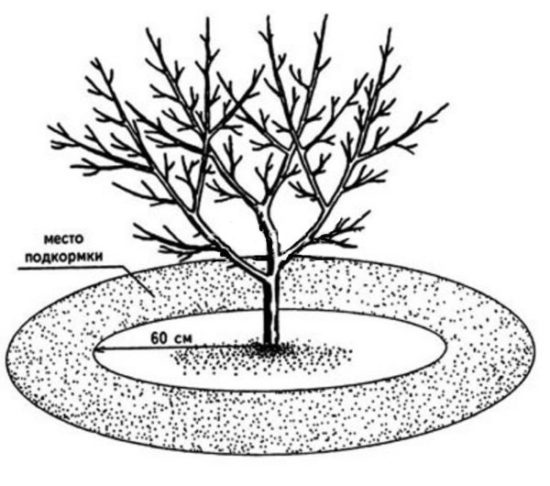
Soil care consists of autumn digging and spring loosening. The tree trunk circles expand to 3-3.5 m in diameter. In the fall they dig:
- at the trunk to a depth of 5-6 cm;
- as you move away from it, the depth increases to 12-15 cm;
- along the edge of the trunk circle they dig up to a full bayonet.
|
It is better to dig with a pitchfork; it is much safer than with a shovel. Damaged roots in a fruiting apple tree take longer to recover than in a young one. The shovel or pitchfork is placed sideways to the trunk, so the risk of damage to the roots is significantly reduced. In spring, the ground is loosened, breaking up the soil crust. This retains moisture in the soil. This is especially true for the southern regions, where the land dries out quickly. |
In tree trunks, it is permissible to grow shade-tolerant vegetables and herbs: cucumbers (in the southern regions), peas, dill, parsley, or flowers (violets, nasturtium, calendula, marigolds). Parsley is grown only as leaf parsley. It is not sown within the crown every year. Long-term cultivation of parsley under an apple tree has a negative effect on the latter: root secretions, especially root parsley, are poorly tolerated by the apple tree, although, of course, they cannot cause serious damage to an adult tree. But the roots of the apple tree go deeper from these secretions and access to nutrients decreases.
Don't forget to read:
You can also grow bulbous flowers that bloom before the apple trees bloom. In autumn, the soil must be dug up, removing plant debris and foliage.
The soil should be loose and free of weeds. The overgrown crowns now provide dense shade, and growing compaction crops becomes difficult. Along the edges of the crown, of course, they continue to grow various shrubs (raspberries, currants, gooseberries), and also place beds with vegetables. This is called “edge feeding,” and the more beds there are around the perimeter of the crown, the better for the apple tree. If the trees are not additionally fertilized, then the apple tree receives all nutrients only from regional nutrition.
Under the crowns, where the shade is thickest, you can grow green manure, planting them in the ground in the fall. Suitable legumes are: meadow clover, lupine, sweet clover, alfalfa, as well as mustard and phacelia.
If the crowns of apple trees close together, then the space between them in regions with sufficient moisture is sown with a lawn (except for the tree trunk circles). Mixtures of legumes with herbs that form loose turf are well suited for this purpose:
- red clover with bluegrass;
- red clover with timothy in a ratio of 3:1;
- meadow fescue with shoot-forming bentgrass, etc.
Lawn in an apple orchard
For the lawn, you need to choose plants that do not form too dense turf, since the soil must breathe and be well moistened.
Grasses that form a dense turf (timothy, foxtail, red and alpine fescue, perennial ryegrass, wheatgrass) are not suitable for sowing under apple trees.You should not sow creeping clover (white), since it has a powerful root system that goes to a depth of 50-60 cm, and this can constitute significant competition for water and nutrition even for an adult apple tree, especially on dwarf and medium-sized rootstocks.
The turf, even loose ones, is regularly pierced with a pitchfork to ensure air access to the root system of the trees. Once every 3-4 years, the turf is dug up, while applying fertilizer. But you can’t dig deep right away, especially if it’s perennial turf. When the space under the tree is grassed, the roots rise higher in search of air. Therefore, the old lawn is always dug up with a pitchfork in the spring to a depth of 6-8 cm. By autumn, the roots will give rise to deeper branches, and digging will not be so traumatic. In the fall, they dig again to a depth of 10-15 cm, simultaneously adding manure. If you often come across roots when digging, then reduce the depth.
|
In arid regions, growing a lawn under apple trees is unacceptable. It interferes with the normal moisture supply of the apple tree, absorbing a significant part of the water. When dense turf is formed, severe suppression of trees and even, in some cases, death of dwarf and semi-dwarf apple trees is observed. |
Digging of the soil in the fall is carried out in lean years as early as September. This improves root growth and function in the fall. In fruitful years, digging under summer varieties is also carried out in the fall. Under autumn and winter - only after harvesting. The soil should be loose, so large lumps are broken up.
Watering apple trees in spring, summer and autumn
Fruiting trees require much more water than young, growing trees. A fruiting apple tree has 4 tasks:
- maintain the necessary green mass;
- pour fruit;
- give an annual increase in young shoots;
- lay fruit buds for next year.
And for all these purposes much more water is required than for a young tree. With proper watering, trees are healthier, they shed less ovaries and fruits, produce good growth, and even during years of active fruiting, they lay fruit buds for the next year, which, accordingly, reduces the frequency of fruiting.
|
Good watering improves the frost resistance of apple trees. It is especially necessary in arid regions. |
During the season, the apple tree requires 4-6 waterings. Their number depends on the weather.
- The first watering is done during flowering or immediately after it. In the north and in the middle zone, it is usually not required, since at this time there is still enough moisture in the soil (with the exception of a very quick hot and dry spring, which in these regions happens once every 12-15 years). But in the south it is desirable, since the winters there have little snow, and in the spring there are strong winds that dry out the soil.
- 3 weeks after the end of flowering, when the ovaries are the size of a cherry. It is especially necessary for summer varieties that quickly fill the ovary. With a lack of moisture, the ovaries begin to fall off, and the greater the lack of moisture, the more the apple tree sheds ovaries. One day we had hot and dry weather, and the water was turned off. I had to save on apple and pear trees, watering only vegetables. And although water was given after 3 days, the trees dropped up to 1/3 of all ovaries during this time.
- In extreme heat and drought, summer varieties may begin to drop unripe fruits. Then watering is done in mid-July, 2 weeks before the start of apple picking. They focus specifically on summer varieties, since they have fast fruiting, they require more moisture, and they react more quickly to its lack.In addition, at this time new flower buds are laid, and if there is a lack of moisture, they simply do not form, and there will be no harvest the next year.
- After the complete harvest of summer varieties. Not only summer varieties are watered, but also autumn and winter ones. Usually this is the end of August.
- During a dry autumn, trees are watered abundantly at the end of September.
- Moisture-recharging irrigation in late autumn. In the central and northern regions, long rains completely replace it. In all other areas it is mandatory.
In the middle zone and in the north, if the weather permits, you can get by with 2 waterings per season: during the period of intensive fruit growth and after harvesting summer varieties. In semi-arid areas this is usually 3 waterings, but in the south you will have to carry out all 6 waterings.
|
Watering is always done around the perimeter of the crown. The trunk has no roots and watering around the trunk is completely useless. They do not water at one point, but constantly move the hose so that the flow of moisture to all roots is more even. You can do sprinkling by moving the sprayer to another location from time to time. |
When watering with buckets, if the apple tree does not bear fruit that year, then they pour out as many buckets as the tree is old. If it bears fruit, then the watering rate is the number of years of the tree plus another 2-3 buckets. On soils where water stagnates, the rate is reduced by half.
Feeding apple trees throughout the year
All varieties of apple trees are very susceptible to fertilizing. The fertilization regime for fruit-bearing apple trees (like all trees) varies greatly in comparison with young growing trees.
In a fruit-bearing garden, fertilizing is carried out 3-4 times per season.
- Late autumn fertilization.
- Spring feeding.
- 1-2 summer feedings.
- Early autumn feeding.
The main fertilizer is still manure. It is introduced in late autumn (in the middle zone - late October, in the south - late November). 1/4 of the annual nitrogen requirement is added to manure (preferably ammonium nitrate). This is especially important for winter varieties that have just been harvested. This nitrogen speeds up the preparation of the tree for winter, but does not cause shoot growth. However, when applying manure annually, you do not need to add nitrogen to it.
|
When applying manure to summer varieties, nitrogen is not added. They had enough time and were well prepared for winter. Excess nitrogen will cause unwanted growth processes. |
Do not miss:
Fertilizing apple trees in spring
Spring feeding is mandatory both during the years of fruiting and during the resting years of apple trees. At this time, flowering and leaf blossoming occur, which requires a lot of nitrogen, and at this time there is just not enough of it in the soil.
Spring and summer feeding should be either liquid or foliar. In dry form, fertilizers, even deeply embedded in the soil, do not reach the sucking roots and, therefore, are useless.
The first part is given when the kidneys are swollen. To do this, rotted manure is infused for 3-5 days (2-3 shovels per 200 liter barrel), stirring it regularly. Water around the perimeter of the crown, the consumption rate is 5-6 buckets per tree. If there is no organic matter, then 500 g of urea is diluted in a 200-liter barrel. Consumption rate 4 buckets/tree.
But usually at this time there is still no water in the dachas, so feeding is postponed until the buds open after flowering. Here they provide complex fertilizing, especially if a large harvest is planned. In a 200-liter barrel, dissolve 1 kg of superphosphate, 800 g of potassium sulfate and add 1 shovel of manure.If you don’t have it, you can buy a ready-made concentrate in stores (dissolve according to the instructions). The mixture is stirred, left for a day and watered. The consumption rate is 50-60 liters per tree.
If there is no water yet at this time, the apple trees are sprayed with urea at the rate of 40 g per 10 liters of water. As a last resort, if there is nothing at all, spray with fertilizers for vegetables: Effecton, Agricola, Krepysh, Azotovit, etc., taking half the dose of vegetables. You will have to take water from the well and wait until it warms up in the air. Do not spray with ice water.
The apple tree bears fruit periodically. If the previous year was fruitful, then this year there will be very few apples or no apples at all. In lean years, the tree still blooms and to increase fruit set, fertilizing is done before flowering. In productive years, fertilizing is done after flowering so as not to stimulate excessive flowering.
Too high a percentage of ovaries greatly overloads the apple tree. She tries to fill all the formed ovaries, becomes very depleted, gives little growth and practically does not lay flower buds.
Summer feeding
In high-yielding years, after the June shedding of excess ovaries, another feeding is given with the above fertilizer. Consumption rate 3 buckets/tree. It contributes to less shedding of the ovaries during the period of their filling. This stage is optional and is carried out only in high-yield years.
Basic summer feeding. Take a complete complex fertilizer (ammophoska or nitrophoska) 30g, dissolve it in 10 liters of water and water the apple trees. Consumption rate 30 l/tree.
|
But it is better to do foliar feeding, because fertilizer from the leaves is absorbed completely and much faster. Spraying is done in the evening. |
Since nitrogen is not paramount for the apple tree during the fruit-filling period, you can take an infusion of ash and spray it with it. Time: early to mid-July. Varieties of all ripening periods are processed.
Autumn feeding of apple trees
It is carried out immediately after harvesting apples of summer varieties. The trees are watered with infusion of manure, 3 buckets per tree. All apple trees are fed, not just summer ones. There is no need to add nitrogen at this time, otherwise intensive growth will begin and the ripening of wood will be delayed. This can lead to freezing in December. For the same reason, foliar feeding is not carried out, since substances from the leaves are absorbed very quickly and lead to unnecessary growth at this time.
Well, this is how it should be in theory. But most summer residents will not bother with apple trees to the detriment of cucumbers and tomatoes. Therefore, everything is entered according to a simplified scheme:
- in the fall - applying manure;
- in spring, in low-yielding years, they spray with urea, in high-yielding years - with the same urea, but after the June fall of the ovaries;
Even with such a “meager diet,” the apple trees will bear fruit. Still, the dachas do not have industrial plantings, and too much harvest is a disaster for the dacha owner. Most of it is thrown into the manure pit. Therefore, it is worth regulating and feeding the tree based on how many apples you can process.
Soil improvement
Liming is carried out on too acidic soils every 7-8 years. Lime is usually used. Application rates: 600-800 g of lime per 10 m2. It cannot be mixed with anything. You can take dolomite flour. It is mixed with potassium-phosphorus fertilizers, the consumption rate is 0.8-1.0 kg.
|
Fluff is a fast-acting fertilizer. The effect of it manifests itself in the year of application, and it is limited to that.Therefore, it is not applied to fruit trees. A long-lasting deoxidizing effect is needed here. |
On highly alkaline soils, peat is added. Work is carried out once every 5-6 years. Fresh peat cannot be added, it is very dense. If you apply too much of it, the roots will suffer greatly from lack of oxygen.
|
Even decomposed peat is never brought in alone; manure or compost must be added to it. This reduces the alkalinity of the soil, enriches it with nutrients, and makes them more available to trees. The rate for applying peat manure compost is 5-6 buckets around the perimeter of the crown. |
Don't forget to read:
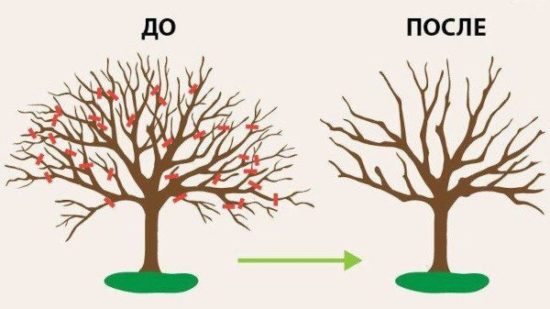
Pruning and crown reduction of fruiting apple trees
The period of fruiting of an apple tree continues for many decades, only at the end of this cycle does a decrease in fruiting begin and the tree fades away. At the beginning of the fruiting period, the trees continue to grow, giving excellent growth, on which fruits are formed: ringlets, spears, fruit twigs. But with age, the growths begin to weaken, the number of fruitlets on them decreases, and the resulting ones are not as powerful as before. Fruits live 12-15 years, but their maximum productivity occurs at 5-7 years of age. At this time, flower buds are more often laid on them, and the apples are larger than on older fruits.
Pruning during the early fruiting period
In the first period of fruiting, the main task is thinning and lightening the crown. Continue to cut out all branches growing inside the crown, curves directed in an undesirable direction, extending from the trunk at an acute angle. The tops are removed.
Tops are powerful fatty shoots that extend at a very acute angle and grow almost vertically upward.In a later period of the apple tree’s life, they can be transferred to skeletal branches, but at this stage they only compete with the central conductor, without producing crops.
The formation of the crown continues in varieties that enter fruiting early, and the maintenance of shape in varieties that enter fruiting late. All branches should be well lit. Shading and thickening shoots are cut into a ring. If it is necessary to remove many shoots at once, then cut out half in the first year, and the remaining ones the next year.
If you immediately do severe pruning, this will provoke a massive appearance of tops, which will have to be removed immediately, and this is a serious burden on the apple tree.
If the top has already grown and its removal would be traumatic for the apple tree, then it is transferred to the skeletal branch. In the first year it is cut by 1/3. In the second year, it is cut off above the lowest branch, and if it is weak, then above the first powerful branch, cutting off all branches below it. After pruning, the top will stop growing quickly, turn into a skeletal branch and become overgrown with fruits.
Anti-aging pruning
With age, the amount of growth produced decreases, and, consequently, the formation of fruitlets on it decreases. Due to the lengthening of the vascular pathways, the development of the fruit branches themselves slows down greatly, and the flower buds and fruits they lay are no longer so large. Therefore, with age, the nature of pruning apple trees changes.
|
Anti-aging pruning is carried out not in one year, but in several years. The crown of the apple tree is divided into several parts and one part is cut out every fall. |
The essence of anti-aging pruning.
- Skeletal branches are cut to 1/3-1/2 length. Select a strong, powerful, healthy and young branch from the skeletal branch and cut the branch to it.They choose not only a young and powerful branch, but also look at its angle of departure from the main branch (at least 45°). But since on an old branch, especially tall varieties, such a branch occurs infrequently, a spacer is installed to increase the angle of branching. They also shorten it in the desired direction of growth, choosing a branch on the skeletal branch that grows upward (to make the crown more compact) or downward (for a more spreading crown).
- Each skeletal branch has a pronounced layering. The first large branch of the skeletal branch is the first tier, the second large branch is the second tier, etc. If the skeletal branch has poor fruiting and flowering, then it is shortened by 2-3 tiers until there is strong branching. The degree of shortening depends on the age and condition of the apple tree. The older the tree and the weaker the fruiting, the stronger the shortening.
- In the upper part of the crown, when pruning large branches, it is advisable to transfer them to branches tending to a horizontal position. This will thin out the crown at the top and create better lighting conditions there.
- If a lot of tops appear on an old branch, this indicates that it is beginning to die off. In this case, the skeletal branches are pruned to the top closest to the trunk or better located, cutting out all competing tops. The top of the top is cut off to the outer bud, and they try to give it a more horizontal position by placing a spacer or tying it to a stake driven into the ground. The next year, the top stops growing so quickly, begins to branch, and after a few years turns into a skeletal branch.
- If possible, the semi-skeletal branches inside the crown are shortened in the same way.
As a result of these measures, the apple tree will give strong young growth, which in a few years will form a new crown.It is advisable to carry out pruning in parts so that it is not too traumatic for the tree. Although, when the skeletal branches die off, pruning is carried out immediately.
|
This is how we extended the life of a very old apple tree. It had already begun to dry out, so they did some anti-aging pruning. More precisely, they even “shaved his head”, leaving only 2 skeletal branches and 2-3 semi-skeletal ones on them. Two years after that, it gave excellent growth, and from the 3rd year it began to produce huge yields, surpassing everything that was before. |
The effect of anti-aging pruning lasts for several years, after which the effect fades. Every 5 years it must be repeated again.
Rejuvenating pruning, of course, does not restore the apple tree, but it gives time for the young trees to grow and begin to bear fruit.
Crown reduction
Such care is necessary for apple trees on tall rootstocks, since it is impossible to care for and harvest from a 4-6 meter tree. Admission is carried out as needed, but not more often than 8-10 years.
|
Initially, the main trunk (or trunks, if there are several of them) is shortened, leaving no more than 3-4 cm of growth. All branches (skeletal, semi-skeletal and overgrown) growing upward are shortened. They should always be 15-20 cm below the main conductor. Otherwise they will try to either take the place of the main trunk or become a competing trunk. |
The growth formed at the pruning site is shortened again. If the apple tree stubbornly strives upward (features of the variety), then the top (tops) are cut off, and the underlying branches are greatly shortened so that they are lower than the rest of the conductor. The branches are given as horizontal a position as possible. Then their growth slows down, and they will not strive to turn into a new trunk.
All large cuts and cuts are covered with oil paint on drying oil.
Root rejuvenation
This method of caring for the roots of apple trees is quite labor-intensive, but in combination with pruning it gives an excellent effect. The productive period of the tree can increase by 7-8 years. The event is carried out every 2 years, rejuvenating half of the roots annually.
At a distance of 3-4 m from the trunk, the apple tree is dug in a circular groove, 60-70 cm deep. They dig, trying not to damage the roots, although at such a digging depth, they are still damaged. The removed soil is mixed with fertilizers:
- semi-rotted (5 buckets) or rotted (7 buckets) manure;
- compost 8-10 buckets;
- green fertilizer (all you have, or specially infuse a 100-liter barrel);
- ash, if there is no manure (2 kg);
- if there is nothing, then use mineral fertilizers: superphosphate (2 kg), potassium sulfate 0.5 kg; No nitrogen fertilizers are applied.
The soil mixed with fertilizers is again poured into the ditch and compacted. Then do abundant watering. In the spring, feed with infusion of manure or nitrogen fertilizers.
|
Rejuvenation of the roots of an old apple tree |
Do not miss:
Caring for the trunk
In mature trees, the bark is rough and covered with a network of cracks and tubercles. The main damages are: freezing of the bark, sunburn, breaking off of skeletal branches, breaking the tree.
Freezing of the bark They are more common in mature apple trees than in young ones. Particularly common in areas with strong winds. Winds blow funnels around the trunk and cause it to freeze. In spring the bark falls off. To prevent damage, snow is thrown onto the trunk, preventing the formation of craters around the tree.
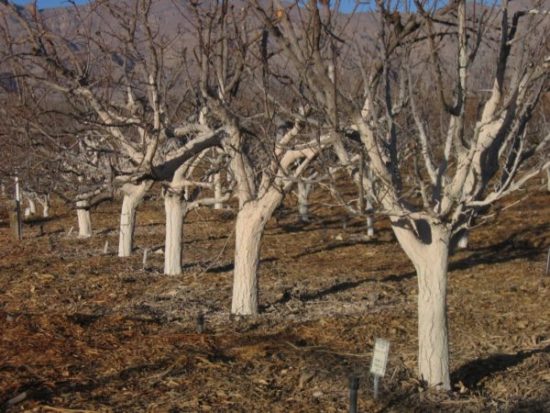
Sunburn are formed for the same reasons as in young apple trees: heating of the branches and awakening of the cells during the day and their death at night from low temperatures.For prevention, the trunks and skeletal branches are wrapped in light material or whitened.
If a sunburn appears on a fruit-bearing apple tree, it does not heal as easily as young trees. In the spring, the bark at the burn site is removed until healthy wood is removed, and the damage is covered with garden varnish or oil paint. In the fall, poorly healed wounds are washed with HOM solution and again covered with oil paint.
|
To prevent burns, trees are whitewashed in the fall. |
Breaking off skeletal branches can happen for various reasons:
- overloading branches with crops;
- branches breaking off under the weight of snow;
- branches break in strong winds;
- branches extending from the trunk at a very sharp angle have a weak connection to the trunk and often break under their own weight.
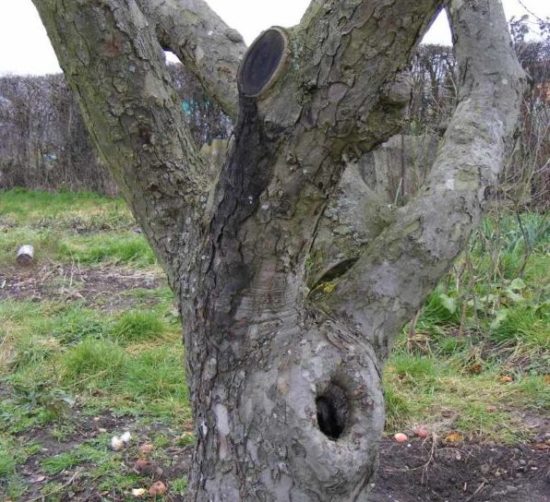
After a branch breaks off, deep damage occurs on the trunk, which can turn into a hollow.
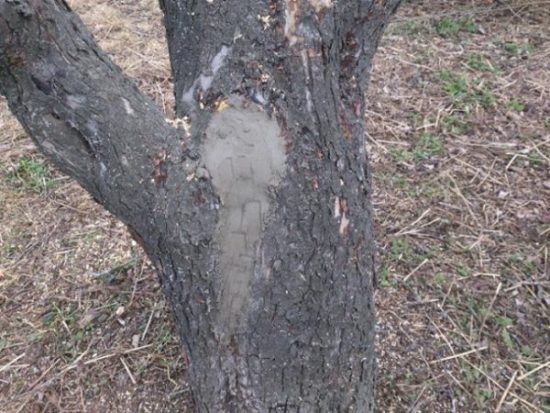
All wounds are cleaned of dead parts, treated with copper or iron sulfate and covered. In the absence of vitriol, you can treat it with brilliant green or potassium permanganate. Cover with clay or cement.
|
If the wound does not heal and the wood underneath rots, a hollow will form. A hollow is the rotted core of a tree. But apple trees, even with a very large hollow, can live and bear fruit well. |
The fact is that the core is dead tissue; it has no conducting vessels. If it rots, the tree will not lose anything from it. The main thing is that the cambium and pathways are alive.
In my dacha there is an old apple tree with a large two-meter hollow running from the root collar to the skeletal branches. Despite this, the apple tree bears fruit well.
However, when forming a hollow in a tree, all rotten wood is cleaned out, treated with a disinfectant solution (copper or iron sulfate, potassium permanganate) and filled with cement.
|
If over time the cement falls off, the hollow is cleaned and disinfected again, and filled with cement again. |
Tree break It often happens that the trunk splits into two in the form of a spear. Breaking off one half of the tree usually leads to the death of the apple tree. But it happens that a tree survives if the broken half is significantly smaller than the other.
In any case, the fracture is disinfected and cemented. If the apple tree dries out, then prune it to reverse growth. (see article “Caring for young apple trees”).
Calendar of work on caring for apple trees throughout the year
Along with the change of seasons, agricultural technology and care of apple trees change. In spring and summer, plants require different amounts of watering, fertilizing, and treatments.
Caring for apple trees in spring
Maintenance is carried out depending on weather conditions.
- In early March, the snow is trampled down around the trunks, destroying mouse holes and crust. When craters form around the trunk, snow is thrown onto the tree. Snow is taken from free areas at the dacha. Snow is not taken from under the crown, so as not to leave the roots unprotected.
- Inspect the crown; if there are frozen branches, they are removed even before the buds swell.
- When breaks appear between the branches, if they cannot be removed, they are tightened with wire or staples.
- On old trees, the bark is stripped and the trees are sprayed with iron sulfate before the buds open. If the buds have already blossomed, then use HOM or potassium permanganate.
- All wounds and hollows are cleaned and covered.
- The soil is loosened.
- Before flowers bloom, if frost is expected, water thoroughly.This delays flowering and prevents the flowers from getting frost.
- The first feeding when the buds are swelling.
- Sowing green manure, flowers, herbs or early vegetables (radish). If necessary, grass the soil between the trees.
- Spraying against diseases and pests.
In productive years, spraying against pests is carried out before and after flowering. During rest years, you can do one spray when the leaves bloom.
Don't forget to read:
Summer care for a fruit-bearing garden
At the beginning of summer, frosts are still possible in the northern regions.
- Protection of young ovaries from frost.
- After the June shedding of excess ovaries, abundant watering is done.
- Early summer feeding in productive years.
- Applying trapping belts to trunks to catch pests.
- Loosening and weeding of tree trunk circles.
- Third watering and fertilizing in July.
- Supports are placed under the branches bending to the ground under the weight of the crop.
- At the end of July during the dry summer, abundant watering is done.
- In lean years, at the end of July and beginning of August, fertilizing is done to intensively set flower buds.
- In the first half of August, the gradual harvesting of summer apples begins.
- Carrion is collected regularly.
- After harvesting summer apples, the trees are watered and fertilized.
If summer apples are picked slightly unripe, they can be stored for 2.5-3 weeks.
How to care for fruiting apple trees in the fall
This is the time for the most intensive care of the apple tree.
- In early September, during dry and hot summers, autumn and winter varieties are watered.
- Remove the hunting belts.
- Autumn feeding of trees.
- At the end of September, autumn apples begin to be harvested.
- On acidic soils, add lime, on alkaline soils - peat manure compost.
- At the beginning of October, the main fertilizer is applied and water-recharging irrigation is done.
- Winter apples are harvested. After harvesting, the main fertilizing is carried out.
- If necessary, root rejuvenation is carried out.
- Pruning is done in early November.
- Trees are being whitewashed.
- Winter apples are sorted and stored.
- Fallen leaves are removed and either composted if they are healthy or burned if they are diseased.
- In regions with sharp spring fluctuations in day and night temperatures, the trunk and main skeletal branches are tied with light fabric to protect against sunburn.
- All trees under 15-17 years of age are damaged by mice in winter. Therefore, even fruit-bearing trees are tied with spruce branches to protect them from mice. Only trees over 20 years old need not be tied. Mice will not eat such tough bark.
All care activities must be completed before the onset of cold weather.
Winter
Conduct preventive inspections of the garden.
- During heavy snowfalls, snow is shaken off the branches to avoid breaking them.
- In winters with little snow, snow is thrown onto the trunks. Snow is taken from open areas outside the canopy.
- The snow around the trunk is regularly trampled down.
In winter, you can do any type of pruning if you did not have time to do it in the fall.
Conclusion
Fruiting apple trees require closer attention. To increase productivity and care, they need more careful care throughout the year. But summer residents, as a rule, have no problems with productivity. Apple trees growing on the site produce good harvests, and summer residents, on the contrary, experience an overabundance of harvest. Intensive care and increased productivity are needed by those who grow apples for sale. If desired, the yield can be increased by 50%. Those who do not need this may not water or fertilize the apple trees at all.They already have enough apples.
You might be interested:















 (1 ratings, average: 4,00 out of 5)
(1 ratings, average: 4,00 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.