Caring for apple trees includes 3 stages: caring for young apple trees, caring for fruit-bearing trees and caring for the harvest. This article describes in detail how to care for young apple tree seedlings: what and when to feed them, at what time to water them, and how to properly form the crown of a young tree. The next article will be devoted to the rules of caring for fruit-bearing trees.
| Content:
|
|
Young apple trees require more care than older trees. |
Caring for a young apple orchard
Before the apple tree enters the period of full fruiting, it is considered young. For different varieties, this period occurs at different times. For example, in columnar apple trees, fruiting begins already 2-3 years after planting. Some varieties begin to produce crops 10-12 years after planting. As a rule, tall varieties begin to bear fruit later, while low-growing varieties begin to bear fruit earlier. The same variety of apple tree behaves differently on different rootstocks.
Before the fruiting period begins, the apple tree is actively growing, and it will not produce crops until it reaches its required height. On young trees, annual growth should be at least 50 cm.
During this period, special attention is paid to crown formation. It must be strong and very thin in order to withstand high loads in the future and not break under the weight of the harvest in the summer-autumn period and under the weight of snow in the winter.
Don't forget to read:
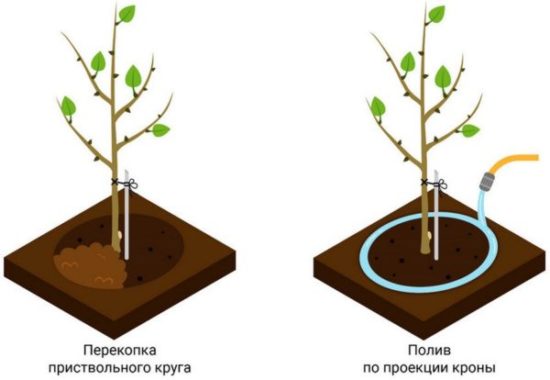
Tillage
It consists of:
- deep digging in the fall;
- early spring loosening;
- removing weeds in summer.
In young trees, the trunk circles are treated. As the apple tree grows, the trunk circle expands:
- for one- and two-year-old apple trees, a trunk circle with a diameter of 2 m;
- for three- and four-year-olds - 2.5 m;
- for five and six year olds - 3 m;
- for seven- and eight-year-olds - 3.5 m.
Further, the tree trunk circles are not expanded, even if the tree has not yet entered fruiting.But usually in small dachas the diameter of the tree trunk circles does not exceed 2-2.5 m. In this case, fertilizers are applied to nearby beds, burying them deeply.
The soil under young apple trees is dug up in early October. The tree trunk circles are dug very shallowly at the trunk, 5-6 cm, and as you move away from it - to a full bayonet. When digging, the summer resident places the shovel so that its edge faces the tree. This reduces the risk of damage to the roots, and if a root is caught, the damage is minimal.
|
It is better, of course, to dig up the tree trunk with a pitchfork in a young garden; they are much safer for the roots. |
In the spring, if no digging was done in the fall, the soil is deeply loosened with a pitchfork. You can even turn over a layer of earth.
Summer care involves keeping the tree trunk circles clean. Perennial weeds are not allowed to germinate, especially such malicious ones as wheatgrass, cowgrass, thistle, etc. The root system of these weeds goes deep, and they can compete in the nutrition of 2-3 year old apple trees.
You can sow a lawn under 4-5 year old apple trees, leaving a circle around the trunk. At this time, the root system of the tree has gone deep down, and grasses will not compete with it. Just don’t sow timothy; its root exudates have a bad effect on fruit trees.
What and when to feed young apple trees
Simultaneously with autumn digging, fertilizers are applied. If everything was applied properly during planting, then the following year on podzolic soils and 2 years on chernozems no fertilizing is required. After a year (or 2), manure is applied around the perimeter of the tree trunk:
- for 3- and 4-year-old trees 2-3 buckets of manure;
- for 5, 6 year olds 4-5 buckets;
- for 7 and 8 year olds 5-6 buckets.
Manure is placed on the spade along the perimeter of the crown, preferably along the outer ring of the tree trunk circle. Fertilizers are never buried near the trunk, since there are no sucking roots there and it will not bring any benefit.
If there is little organic matter, then it is introduced locally not throughout the entire tree trunk circle, but only in a certain part of it. The circle can be divided into 3-4 parts and fertilizer can be dug in every year in a new part of the circle, where it has not yet been applied. This technique allows the roots to develop very evenly along the entire perimeter of the crown.
Organic matter can be added from the end of September to mid-October in the north and central regions, and until the end of October in the south. During this period, the applied fertilizers are completely absorbed. At this time, trees experience a nitrogen deficiency, which in the fall is necessary to prepare for winter (in particular, for the ripening of young growth and the appearance of a waxy coating on the branches). The applied manure makes up for this deficiency, but no longer causes shoot growth. By this time, the apple tree has switched to “self-preservation mode” and uses nitrogen for other needs.
If there is no manure, then fertilize with mineral fertilizers. For 10 liters of water take 2 tbsp. l. potassium and 2 tbsp. l. phosphorus. The solution consumption rate for 3-4 year old trees is 2 buckets, for 5-7 year old trees 4-5 buckets. Mineral fertilizing is done earlier: in the middle zone in mid-September, in the south in mid-October.
|
Feeding seedlings during planting |
If possible, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers can be replaced with ash. It contains not only phosphorus and potassium, but also many microelements necessary for a young garden. For 10 liters of water, take a liter jar of ash and let it sit for 24 hours. The solution consumption rate is 1-1.5 buckets per tree.
On highly alkaline soils, ash is not used, since it causes even greater alkalization of the soil. Also, do not add ash along with manure, as a chemical reaction occurs that can damage the plant.
Dry ash is not used, since the phosphorus and potassium it contains are firmly bound by the soil and do not reach the sucking root zone.
In spring, young apple trees are watered with a urea solution. Young growing trees require nitrogen for normal growth. For 10 liters of water take 2 tbsp. l. urea. The consumption of the working solution is 20 liters per tree. Fertilizing is carried out when the buds open. At the end of summer, a young apple tree also needs nitrogen for the synthesis of amino acids, therefore, if there is no autumn application of manure, then at the beginning of September they give another nitrogen supplement, preferably ammonium nitrate. 1 tbsp. l. saltpeter is diluted in 10 liters of water, the consumption rate is 1-1.5 buckets per tree.
But mineral water is an extreme case. It can be used no more than once every 2 years. Such fertilizers acidify the soil, and this inhibits the growth of the apple tree. It is better not to feed the tree at all than to feed it with mineral water year after year.
|
Before watering with fertilizer solutions, the soil under the tree is well watered. |
A young apple orchard is very responsive to foliar feeding, especially on poor soils. It is done to enhance the growth of young shoots. Usually in mid-summer, apple trees enter a summer dormant period, when shoot growth slows down. It falls in mid-summer - the second ten days of July. Therefore, fertilizing is done in early August, using liquid fertilizers: Effecton, Malyshok, Agricola, etc. For young trees, the concentration is taken as for flowers, the consumption rate is 2 liters of solution per tree.
Watering
Watering, as one of the measures for caring for a young garden, is not always required. In wet, rainy weather, there is no need to water the trees. And even when it's dry and hot, weekly watering is usually not required unless the trees grow in sandy soil and light loam. An apple tree is not a cucumber; even a young apple tree has roots deep into the ground, and it does not suffer from heat unless there is a drought.
When should you water an apple tree?
- During a dry and warm spring, when the snow melts quickly and there is no precipitation.
- In summer, if there is no precipitation for more than 4 weeks. Or, if there are summer showers, which do not wet the soil, but only add dust. The water consumption rate for an annual tree is 20 liters, for 2-3 year old trees - 40 liters, for 4-6 year old trees - 50-60 liters.
- During dry autumn. The apple tree is preparing for winter and at this time it undergoes intensive metabolism and accumulation of plastic substances.
- In autumn, moisture-recharging watering is mandatory for apple trees of any age. For 1-2 year old trees 15-20 liters of water, for 3-4 year old trees 30-40 liters, for 5-6 year old trees - 50-60 liters. If it rains and wets the soil well, then no additional watering is required.
|
There is no need to water the apple tree like berry bushes once a week. For them, one spring watering, 2 summer waterings, 1 autumn watering and one late autumn water-recharging watering are enough if there is no rain. |
But here it is worth considering that if garden crops grow within the crown, which are watered every other day, and it also rains, soaking the soil, then watering is not required in the central regions and in the north. But in the southern regions, watering is required even when growing other crops under trees.
Watering is carried out along the perimeter of the crown.Throwing a hose directly to the trunk is impractical: there are no roots there, and the water will go aimlessly into the soil without reaching the roots. Water evenly around the perimeter (and not just in one place) to increase the effective suction area.
The bark of young apple trees may burst if you water them too much during a drought. If there is no moisture for a long time, first give half the amount of moisture, and after 2-3 days the remaining amount.
How to prune young apple tree seedlings
This is an essential component in garden care. Fruit trees can do without loosening, without fertilizing and even without abundant watering, but if there is no pruning, the fruits will be small, the crown will be very thick and the tree will be broken by strong winds very quickly. I have a very clear example of this. Back in the 70s, when they first gave my grandfather a dacha, he planted 9 apple trees. There was practically no pruning. Over the course of 3 years, a dense crown formed. One day in the spring there was a wind of 12 m/s (this is not the strongest wind, it does not blow off roofs), and 7 out of 9 apple trees were broken. On the remaining 2, pruning began to be carried out properly. These 2 apple trees still grow in our garden.
In the first year after planting, the apple tree takes root, grows its root system and produces very little growth; there is practically nothing to prune.
From the second year, the plant begins to produce strong growth and it is necessary to form a crown. The event should be carried out in the fall after the beginning of leaf fall, or in the early spring before the start of sap flow (March-first ten days of April). During the growing season, it is permissible to remove only tops - branches that extend from the trunk at a very sharp angle and grow vertically upward.Removing the remaining branches on a young tree during the growth period is unacceptable, since the leaf surface is reduced and the exchange of plastic substances between the root system and the crown is disrupted.
Pruning can be thinning or shortening
Shortening suppresses the growth of shoots in length and causes their thickening. It allows you to regulate the growth force of the branches. At the same time, in varieties with strong shoot-forming ability, shortening leads to increased growth of young growth and thickening of the crown. Branches that quickly grow in length are shortened by 1/3 of their length, weak growth is cut off by 20-30 cm or not cut at all.
When shortening the developing skeletal branches, they are cut to the desired side branch, which has the required direction. Do not allow any branch to become thicker than the trunk.
|
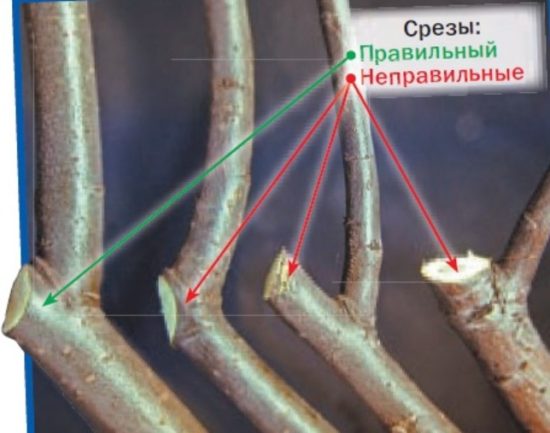
The green arrow shows how to properly trim the branches into a ring. With this pruning, wounds heal best. |
At thinning pruning First of all, remove all unnecessary shoots that thicken the crown, branches growing inside the crown, branches extending from the main branch at an acute angle. When forming the crown, only those shoots are left that extend from the trunk at an angle of more than 45°.
Shoots extending from the trunk at an angle of less than 45° are places of potential faults, since the smaller the angle of departure of the shoot, the weaker its connection with the trunk or skeletal branch.
Remove branches running in parallel. Here they choose not the strongest one, but the one that is better located relative to other branches. During thinning, all branches are removed into a ring.
|
If it is necessary to leave a branch growing at an angle of less than 45º, then bend it and insert a spacer |
If the shoots grow very quickly, they are pinched, removing 2-4 upper buds.If the shoot extends at an angle of less than 45°, but it is thick and has already turned into a full-fledged branch, then the outer overgrown branches on it are cut off to the outer bud. As a result, young growth will appear on the outside of the shoot and pull the branch outward, increasing its angle of departure from the trunk.
All cuts larger than 1 cm are carefully covered with garden varnish.
Pruning for reverse growth
Sometimes in very harsh winters the trees freeze a lot. The most frost-resistant part of an apple tree is the core. The most resistant are the bark at the beginning of the branches and the cambium. In case of severe damage, the tree's branches begin to die and the bark peels off. But this will be noticeable only in June. If the tree has an intact cambium, it will try to heal the wounds; new young shoots will grow on the tree from the trunk.
If such a situation occurs and there are shoots growing above the grafting, then remove the entire crown until there is a strong shoot growing from the trunk above the grafting site. All shoots below the grafting site are removed. The apple tree will grow its crown in 3-4 years.
|
If there are no shoots, then the crown is cut down anyway, leaving only a stump 15-20 cm above the graft. This part of the trunk is usually kept under the snow and does not freeze. |
It should be remembered that pruning for reverse growth is done only when there is significant damage and 3/4 of the crown has dried out. If only individual branches are frozen, then they are cut down into a ring without touching the rest of the crown.
Crown formation
These are measures of extreme importance when caring for a young apple tree. Currently, even in nurseries, young seedlings are beginning to form sparsely tiered crown.
The next year after planting, the crown continues to be formed, developing either the form that was laid down in the nursery, or creating its own.
All branches growing below 1.2-1.5 m are removed. From young growth located approximately at the same level, 3-4 well-placed branches are left, the rest are cut out. Only those shoots that extend at an angle of more than 45° are left. If the branch that is left extends at an angle of less than 45°, then to correct the angle of departure, a spacer is placed between it and the trunk. Then all branches of one tier are cut at the same distance from the ground. The central shoot of a two-year-old seedling is cut off at a distance of 40-50 cm from the tops of the branches of the first tier. Then it will branch, and from these shoots a second tier of branches is formed.
When, after removing the central conductor, new branches appear, the 2-4 strongest and best located ones are also selected and the second tier is formed, etc. The central conductor and the main skeletal branches should have no competitors.
Side shoots on skeletal branches are left at a distance of at least 30 cm from the connection of the main branch with the trunk.
Crown spindle very simple for a novice gardener. A spindle is a crown shape in which all the skeletal branches of a tree are transferred to a horizontal position. Typically, such a crown is formed in dwarf and semi-dwarf varieties. The spindle is formed as the skeletal branches grow. To give them a horizontal position, they often make a trellis and tie the branches to wire. In a horizontal position they grow more slowly. The branches should be distributed more or less evenly along the trunk.
There are other forms of crown formation, but usually amateur gardeners are not too concerned with any formation at all: they cut off the excess, shorten it, cut out the sick and dry ones, and then it will grow.
Formation of the crown of young apple trees:
Don't miss: photos and descriptions of various varieties of autumn and winter apple trees
Autumn varieties of apples with descriptions and reviews from gardeners ⇒
Winter varieties of apple trees with descriptions and photos ⇒
Caring for the trunk
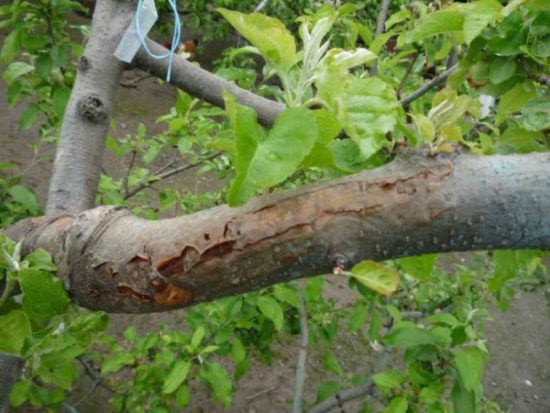
The trunk is a conductor between the root system and the crown. Any damage to it invariably leads to disruption of the nutrition of part of the crown or roots. And ring damage to the trunk always leads to the death of the tree.
The main damage to the trunk is sunburn, gnawing of the bark by rodents, various cracks in the bark, and frost damage. Caring for the trunk includes preventing damage and treating the trunk if damage does occur.
Young apple trees have a standard don't whitewash. The bark of apple trees and, especially pears, becomes very old from whitewashing, microcracks form on it, and it becomes rough. And cracks in the bark are a direct path to disease. You can whitewash apple trees starting from 6-7 years of age; the bark of such trees has already become coarsened and whitewashing does not damage it.
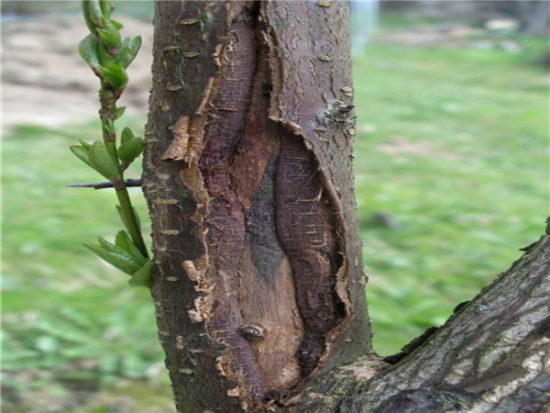
Pdamage the standard possible with tools. Often, a young apple tree gets damaged when mowing the grass if there is no tree trunk, and a lawn grows under the tree. For shallow injuries, the edges of the wound are cleaned and covered with garden pitch. With deep ones they do the same, but the likelihood that the apple tree will survive is extremely low, especially for young 2-3-year-old trees.
Great damage is caused to the trunk and young skeletal branches sunburn. They occur at the end of winter, when the sun is hot during the day and cold at night. As a result, the cells of the cortex awaken during the day, metabolic processes begin in them, and at night they freeze and die. Sunburn occurs more often on the south side. To prevent sunburn, the trunk and large skeletal branches are wrapped in light material.Small boles can generally be sprinkled with 40-50 cm of earth. In the spring, after the snow melts, the earth needs to be removed quickly.
|
At the site of sunburn, the bark darkens and a black or slightly pinkish spot appears on it. When it appears, the bark is cut down to healthy tissue, and the wound is covered with garden varnish. Young apple trees easily heal damage. |
Damage by rodents extremely detrimental to young trees. If the bark is damaged on only one side, the tree may survive, but some skeletal branches may dry out and need to be replaced with new ones. If the damage is circular, then the tree will die, since the connection between the roots and the crown completely stops. In industrial gardens with ring damage, of course, they will try to restore the metabolism between the underground and above-ground parts by grafting a bridge across the damage. But it’s unlikely that anyone will do this at their dacha.
To protect against hares, the trunks are tied with spruce branches, placing them with the spines down. You can tie them with strands of reeds. You should not use hay or straw as binding, as this attracts mice.
|
To protect against mice, the snow around the trunk is compacted tightly; it is advisable to do this after each snowfall. Mice make their way to the trunk under the snow, and when it is trampled down, it is cold for them and it is more difficult for them to gnaw passages. |
Frostbreakers - deep cracking of the bark. Often occurs when the tree is not protected from cold winds in winter. Damage usually appears from the prevailing winter winds. They arise due to alternating exposure to low negative and weak positive temperatures.If the temperature difference between day and night is very large (10 - 30 ° C), then the bark bursts and deep cracks appear.
|
Caring for the wound consists of treating it with potassium permanganate or hydrogen peroxide and applying garden varnish. |
The condition of the apple tree depends on the depth of the damage. If there is a small crack, after treatment the wood heals the wound. However, even without treatment, if there is no infection, it will grow and bear fruit. With deep cracks, some skeletal branches may die. In very severe frosts, the tree dies.
Covering and wrapping the trunks protects against frost damage. The covering material should be light, since dark material increases the likelihood of frost damage even more.
Video on how to care for young apple trees in the fall:
If strong cold winds blow in the area in winter, then covering the trees for the winter is a must!
If the apple tree dries out after winter, there is no need to cut it down that same year. The apple tree is a leisurely tree. If there is still living cambium on the trunk and the roots are not damaged, then very small red specks appear on the bark. These are the formation of buds, from which new shoots will subsequently develop. If specks do not appear, then the tree is cut down, leaving a small stump. If the root system is functioning, then root shoots will appear. One powerful shoot is selected from it, the rest are cut out. This is wild, and next year the desired variety is grafted onto it.
All apple and pear trees over 4 years old should be whitened in late autumn to protect against sunburn in the spring. Yes, yes, trees are whitened in the fall, using whitewash that is resistant to washing off. In the spring it is too late to whitewash trees, but, unfortunately, it is customary to carry out whitewashing in the spring, supposedly to protect against pests.But its main purpose is precisely to protect the bark from damage. When covering the trunk for the winter, only large skeletal branches that remain without shelter and have thick bark are whitened.
What can be planted under young apple trees
While the apple trees are young, various garden plants can be placed in the tree trunks and along the perimeter of the crown.
- Open ground cucumbers.
- All green crops.
- Legumes: peas, beans, beans.
- Onion garlic.
- Strawberry.
- Flowers.
In compacted plantings outside the tree trunk circle, you can plant raspberries, currants, and gooseberries. Ornamental shrubs: spirea, barberry. But you should always remember that in a few years the crowns will grow, and some perennial shrubs will have difficulty growing in dense shade. And too much compaction will make maintenance difficult.
|
It is quite possible to plant flowers in the tree trunks of young apple trees. |
You should not plant cherry, viburnum, hawthorn, peach, apricot, or walnut next to the apple tree. Shrubs include jasmine, mock orange, and lilac. Conifers include fir and juniper. All these plants greatly suppress the growth of young apple trees.
Do not miss:
Conclusion
Caring for an apple tree should begin from the moment you select seedlings and continue throughout the life of the apple tree in the garden. The first years of life for a tree are the most important. Maintenance mistakes made at this time can be corrected later, but this is associated with significant stress for the tree. Improper care delays the start of fruiting by several years. Therefore, caring for the apple tree must be correct and timely.
If it is not clear why you should do something, then it is better not to do it at all than to do it incorrectly.The apple tree is a very demanding, but also very flexible crop; it will grow the way the gardener grows it. And proper care is the key to a healthy tree and good harvests.











 CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.