Raspberries are a perennial berry bush that is very popular among most summer residents and gardeners. In one place, a crop can grow for about eight to ten years. Every year new young shoots and daughter plants - offspring - are formed on the bushes. With their help, raspberries are renewed and reproduced.
|
Vegetative propagation of raspberries by shoots and roots is the most effective among many other methods. |
| Content:
|
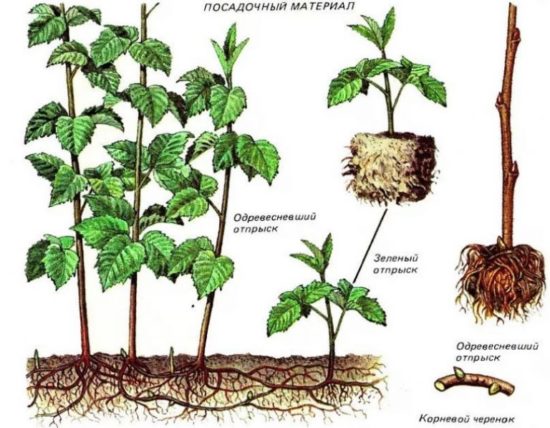
Raspberry propagation methods
To grow raspberries, you can use several methods simultaneously on your plot. To create a new raspberry tree, you will need one healthy plant aged two to three years, as well as its root shoots, root cuttings, green cuttings, rhizomes and seeds. With any method, it is very important to end up with strong, healthy and fertile seedlings. This article provides detailed information about the various methods, basic rules and features of raspberry propagation.
Propagation of raspberries by root suckers
Propagation of raspberries by root suckers or nettles is the easiest and most accessible way for young gardeners to propagate raspberries.
The shoot or root sucker already has its own root system and is an excellent seedling, although it still depends on the mother bush. All you need is to correctly separate the offspring and plant them correctly. This method is one of the simplest and most common among gardeners. For propagation, green and lignified offspring are used.
|
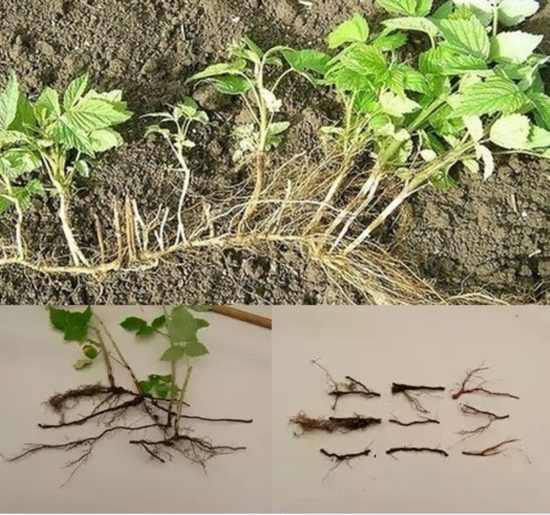
Raspberry root shoots |
Green offspring - young shoots (shoots) that appear in the spring around the mother bush.
Lignified offspring - the same shoots, but in the fall with coarsened, lignified stems.
What is the best time to breed?
A favorable time for propagation of raspberries by green offspring is the spring season.Preparatory activities begin in the first half of April.
Lignified offspring are planted in the fall, from approximately the tenth to the twentieth of September, always before the leaves begin to fall. The seedlings must have time to take root before the first frost arrives. Planting times will vary in different regions.
Choice of offspring
It is believed that offspring taken at a distance of about thirty to forty centimeters from an adult bush take root faster in a new place. Their root part is already well developed, the roots are long (10 to 15 centimeters) and strong. The average height of the plant is from fifteen to thirty centimeters. Preserving a clod of earth when digging up shoots is a must.
|
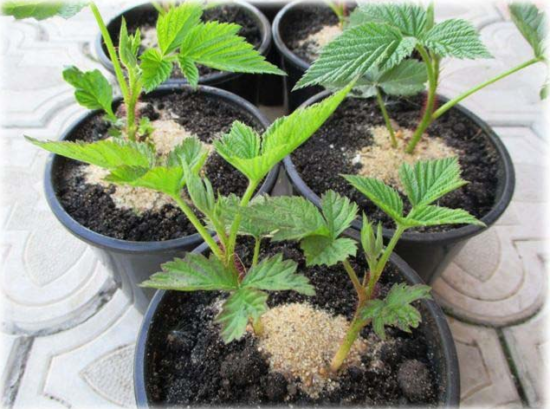
Harvesting green root suckers for subsequent transplantation |
Important! A root shoot with a withered top is not suitable for propagation. Sick and weakened offspring are not recommended for use.
Planting green suckers
First, the soil on the site is loosened, humus, manure or other fertilizers are added. Half a glass of wood ash is poured into the prepared holes and watered. Immediately after being removed from the soil, the seedling along with a lump of earth is planted in a new place in moist soil. The planting depth should be equal to that at which the plant was located at the mother bush. The seedling is sprinkled with soil, watered, and mulched. The upper part of the offspring, which exceeds twenty centimeters, is cut off before planting.
|
Green raspberry shoots before planting |
Reference! After pruning, upward growth stops; the offspring devotes all its energy to growing the root mass and awakening dormant buds, which are needed for the formation of young shoots.
Planting woody offspring
Chopped thin branches, wood shavings, vegetable compost, and a small layer of soil mixture with the addition of potassium and phosphorus are placed in a previously prepared trench, the depth of a shovel bayonet. Then the seedlings (about twenty-five centimeters high) with the top part and leaves cut off are installed, the root part is sprinkled with soil, moistened and a mulching layer is applied.
|
Planting woody raspberry shoots |
Important! In hot weather, under direct sunlight, the raspberry root system dies within 2-3 hours
Care
The main care for transplanted green and woody offspring is proper watering and mulching. Mulch regulates air exchange and maintains the required temperature. The soil is enriched with nitrogen, which is very important for the growth of the roots of a young crop. In the warm season, raspberries are watered abundantly; they do not tolerate drought and lack of moisture.
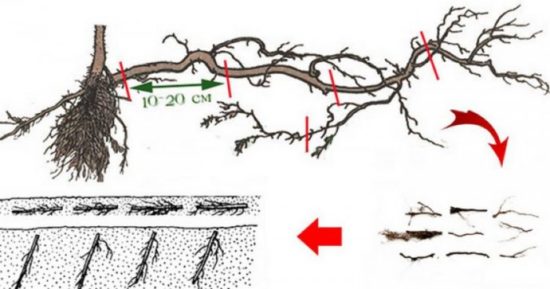
Propagation of raspberries by root cuttings
Using this method, you can obtain a large number of young raspberry seedlings, but it is somewhat more complicated and longer than propagation by root suckers.
A root cutting is a part of the root (about 10 cm long and more than three millimeters thick) with a lateral shoot, which is capable of growing and developing independently. This propagation method is especially relevant for old bushes of very high quality and rare varieties of raspberries, which are difficult or expensive to acquire.
Depending on the type of soil, the raspberry root system may be located at great depths or close to the surface. For example, on heavy soils, the roots are located at a depth of ten to forty centimeters, and it is much easier to get to them for harvesting root cuttings.
|
This is what raspberry root cuttings look like |
Reproduction time
Cuttings are harvested in spring and autumn, but planting them on the site is recommended only in the spring, in well-warmed soil, when the weather is warm.
Watch a video about propagating raspberries using root cuttings:
Harvesting cuttings
Cuttings harvested in the fall must be stored in a cool room (from 0 to +4 degrees), in a container with damp sand, having previously wrapped them in canvas. You can sprinkle leaves on top. The planting material should not be allowed to dry out or freeze.
In spring, cuttings are conveniently prepared when transplanting raspberry bushes to a new place or when digging up shoots. At a distance of twenty to thirty centimeters from the bush, the soil is dug up, the adventitious root with shoots and branches is carefully removed, and only healthy roots with a diameter of five millimeters to two centimeters are selected. After dividing into cuttings, each part must have at least one bud. The length of one cutting is from nine to fifteen centimeters.
|
This is how root cuttings are prepared |
Important! After cutting, all cuttings must be placed for several hours in a container with a growth stimulator, which will allow them to quickly develop the root part and take root in a new place.
Site preparation
The site is cleared of weeds and debris in advance, dug up, organic fertilizers or mineral fertilizers are applied, moistened and loosened.
|
To plant cuttings, you will need grooves about five to six centimeters deep. Before planting, they are watered abundantly. |
Planting cuttings
The cuttings are placed in furrows at intervals of five to ten centimeters, sprinkled with soil, watered and covered with polyethylene. Before sprouts appear, the plantings are ventilated daily, briefly lifting the film. After they appear, the polyethylene is removed forever. Instead, they build a small shade in the form of a nylon mesh, which will protect the still fragile seedlings from the burning spring sun.
Caring for young plants
Care consists of regular watering, weeding and loosening the soil. Approximately two weeks after the sprouts appear, it is necessary to fertilize. IN early autumn raspberry seedlings can be transferred to a permanent growing location.
Propagation by green cuttings
This method of propagating raspberries is considered troublesome and time-consuming, therefore it is used by gardeners in rare cases, mainly for propagating rare and valuable varieties. This method guarantees the preservation of the varietal characteristics of the plant. With this method of propagation, it is necessary to build a special small greenhouse in which the raspberry seedlings will be in favorable conditions. Young plants require a stable average air temperature of about 25 degrees Celsius and humidity in the range of 90 - 93 percent.
Timing of cuttings
The optimal time for propagating raspberries by green cuttings is the summer months, but if necessary, the procedure can be carried out in spring and autumn. One of the important conditions is to carry out the procedure on a cloudy day.
Harvesting cuttings and preparing them for planting
The rooting process of green cuttings is much faster if they were harvested from shoots with a height of the above-ground part of no more than five to six centimeters.
|
Harvesting cuttings |
Cuttings can be taken from root suckers or young healthy shoots. To prevent diseases, it is recommended to use only disinfected garden tools. Each cutting must have at least three full leaves, its average length is from five to fifteen centimeters. In the upper part the cut is made straight, and in the lower part - at an acute angle. It is recommended to make three to four longitudinal cuts about two centimeters long (to a shallow depth) in the lower part of the cutting. This will stimulate root formation.
Attention! Before planting, the cuttings (bottom side) are placed in a solution of “Kornevin”, “Heteroauxin” or another stimulant and left there for 12 – 14 hours. The temperature of the solution should not be lower than 18 - 19 degrees.
Landing technology
The cuttings are planted in a substrate of sand and peat at an angle of forty-five degrees with an interval of about seven centimeters. The distance between rows is ten centimeters. First remove half the leaves from each seedling. Plantings are watered. If there is no greenhouse, you can cover the cuttings with glass jars or cut plastic bottles.
|
Rooted raspberry cuttings |
Conditions for good survival
The soil should always be loose, allow water and air to pass through well, and have all the necessary nutritional components. Air temperature - from twenty-three to twenty-six degrees, air humidity - at least 90 percent.
Basic care
Rooting of the cuttings occurs within approximately a month. It is during this period that watering should be frequent and abundant. When the cuttings begin to grow, the watering regime changes. Seedlings will require less water, but frequent and regular ventilation.
Fifteen days after planting, the cuttings are fed with mullein (one liter of slurry per ten liters of water) or other organic fertilizer.
Transplantation into a raspberry garden is carried out together with a lump of earth.
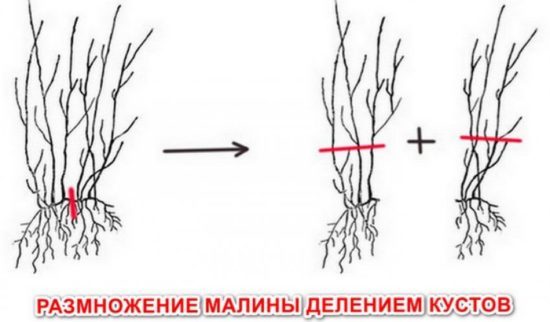
Dividing the bush
If some raspberry varieties hardly produce shoots, then this propagation technique will come to the rescue. This method can be used in early spring, when the buds are just swelling, and in mid-autumn, when the shoots stop growing. From one adult raspberry bush you can get three to five full-fledged viable seedlings.
Before removing the bush from the ground, trim the upper part of the shoots to a height of twenty centimeters.
|
The raspberry bush is removed from the soil and divided into parts using an ordinary garden shovel. In some cases, pruning shears or an ax may be required. |
It is recommended to dust the cut areas of the root part with ash or sprinkle with activated carbon powder.
On a note! After dividing the bush, the seedlings are planted immediately, since the root part of the raspberry quickly dies under the sun's rays. There should be two to three living buds on each division.
One handful of ash is poured into pre-prepared holes, watered abundantly, a seedling is placed, sprinkled with earth and lightly compacted.
Caring for the separated parts consists of regular watering, applying fertilizers and fertilizing, loosening and weeding.
Propagation of raspberries by seeds
The seed method of propagating raspberries is often used in breeding work to develop new varieties. At home, it will require a lot of time and attention, so it is used last. Persistent and very diligent gardeners successfully grow raspberries from seeds and get good yields. To do this, you need to start by purchasing high-quality seed.
Seed preparation
Seeds can be purchased in specialized stores or obtained independently from the varieties available on the site.
It is necessary to choose the healthiest and most productive raspberry bush, collect the ripest berries (without pests and visible damage), place them on cheesecloth and squeeze out the juice. The remaining mass is dipped into a vessel with water, the seeds are washed, all floating specimens are thrown away, and the remaining ones are laid out on a paper napkin to dry.
|
Harvesting raspberry seeds at home for seed propagation |
To increase germination, seeds must undergo stratification. For three months (for example, from December to February), moistened seed material in small fabric bags is kept in a container with wet sawdust at a temperature of three to ten degrees. The bags must be turned over periodically and the sawdust must be moistened. You can use a cellar, basement or a regular refrigerator.
Sowing seeds and further care
At the beginning of spring, seeds are sown in containers with sand to a depth of about five millimeters, sprinkled with a thin layer of sand, and covered with glass or transparent film.You can germinate the seeds and then sow them into individual cups, 1 to 2 seeds each.
Boxes with crops are kept in a warm and bright room, away from direct sunlight. Moisten the soil with a spray bottle every three to four days.
After two weeks, the crops are fed with a weak urea solution.
|
Grown raspberry seedlings |
In general planting containers, as the seedlings grow, it is necessary to thin out.
Seedlings are planted in separate containers when two to four leaves are fully formed.
For autumn sowing, planting boxes and seed stratification are not required, since the seeds are sown immediately in open ground to a depth of at least two centimeters. Sprinkle the top with a substrate of fine river sand and rotted humus. Natural hardening will occur until spring.
Hardening of seedlings
During the period from the moment full leaves appear until approximately mid-May (depending on the local climate), young crops undergo a hardening procedure. They need to be prepared for life in direct sunlight and in conditions of temperature changes. They usually start with an hour-long walk, gradually building it up to a full day.
Transfer
The site for raspberries should be in an open sunny place, with fertile soil of neutral acidity. At the bottom of the prepared groove or hole, pour one glass of sand and ash (for each seedling), as well as a nutrient mixture of peat, humus and compost. The seedlings are transferred along with a clod of earth, watered, and a layer of mulch is applied between the rows.
|
When planting, raspberry seedlings are transferred to the ground along with a lump of earth. |
Important! When choosing a site for a raspberry garden, be sure to take into account the predecessor plants. Where raspberries previously grew, the same crop cannot be planted.
Don't forget to read:
It is difficult to imagine homemade preparations without raspberry jam or compote, dried or frozen healthy vitamin berries. In order for the harvest to be better and more generous every year, it is worth expanding the size of raspberry plantings. To do this, every gardener and summer resident must choose the most suitable method for propagating raspberries and make every effort to achieve one hundred percent results. We wish you success!












 CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer.The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer.The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.