In order to get maximum yields of strawberries (garden strawberries), you need to properly care for them. Agricultural technology can correct many mistakes made during planting, as well as reveal all the advantages of the variety. If not properly cared for, strawberries produce small, sour berries, and varietal differences are reduced to nothing.
Introduction to strawberries
Strawberries are a perennial plant grown for their berries. The plantation produces high yields for no more than 4 years, then the berries become smaller and their taste becomes sour. Although bushes with proper care can live for more than 20 years, their yields will be small.
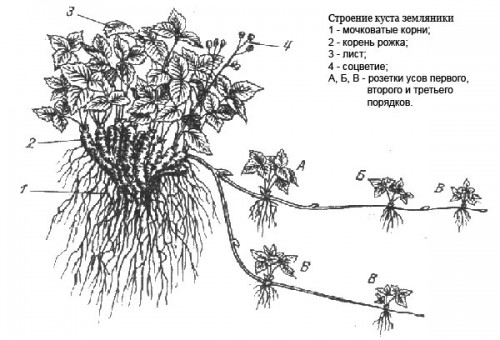
Horns
The bush has about 30 rosettes (horns). The older the bush, the greater the number of horns
it consists, their number depends on the care and variety. The growth of rosettes begins after the end of fruiting; every year they form higher and higher above the ground. Strong strawberry bushes have many horns, weak ones have few.
Peduncles appear from the tops of the rosettes; accordingly, the more magnificent the bush, the more abundant the flowering and fruiting. At the bottom, the rosettes grow together into one small stem, on which adventitious roots are formed. Powerful bushes produce many flower stalks, bloom for a longer time and produce a higher yield.
Mustache
The plants produce the strongest tendrils in the first year of cultivation; every year the tendril formation becomes weaker, while the tendrils become smaller. By the fourth year, strawberries usually no longer produce whiskers. If someone receives vegetative shoots from his 5-6 year old plantation, it is because it was poorly cared for and there are bushes of different ages, and the shoots are produced by young rooted plants.
Vegetative shoots begin to form when daylight hours are more than 12 hours and temperatures are above 15 °C. The formation of flower buds on rooted runners occurs after 2-3 months (therefore, when planting in autumn, very few buds are formed, they do not have time to ripen and the yield for the next year is low).
Berries
The quality of strawberries is influenced by several factors.
- Soil composition. Strawberries growing in poor soils have a less pronounced flavor than those grown in fertile soils.
- Weather. The more direct sun the bushes get, the sweeter the berries. Strawberries growing under the canopy of trees, no matter how you care for them, usually have sour berries.
- Variety Most European strawberry varieties are sweeter than domestic ones.
Properties of berries.
- Berries picked unripe turn red during transportation and storage, but they will not be completely sweet.
- The berries acquire the taste characteristic of the variety only when fully ripened on the bush. To reveal the taste, completely reddened berries are not removed for 2-3 days. Such berries are unsuitable for storage or transportation, but their taste is fully evident.
- To obtain maximum yields, the berries are picked unripe, as this stimulates the growth of the remaining ovaries. As a result, strawberry productivity increases.
- Unripe berries of any variety have the same sweet and sour taste.
On a personal plot, where good taste is more valued than an increase in yield by 300-500 g, it is better to let the strawberries fully ripen and taste their true taste. But in wet weather, you should pick the berries not fully ripe, since it is the ripe berries that are affected by rot and mold first.
Advantages and disadvantages of culture
The main advantages of strawberries.
- Strawberries can produce good yields with very small doses of fertilizer and simple care. The main thing is to fertilize the soil well before planting the crop.
- Annual harvests. Strawberries do not have a periodicity of fruiting, like some other berries (for example, raspberries).
- Quick first harvest.
- Very simple and easy propagation.A bush is capable of producing several dozen tendrils per season, from which the best ones are selected and rooted. Over the summer you can plant a bed of the most valuable variety.
- Unpretentiousness of plants. Strawberries can grow under the crowns of young trees, in flower beds, among weeds (but yields in such thickets are reduced).
Disadvantages of culture.
- Defeat by gray rot. Most modern varieties are quite resistant to this disease, but with improper care you can lose up to a third of the harvest. Domestic varieties are more resistant to the disease than European ones.
- Insufficient self-fertility of strawberries. To ensure good berry set, several different varieties are grown on the plot.
- Winter hardiness is the ability not only to withstand negative temperatures, but also winter thaws without being damaged. In domestic varieties it is quite high, and the loss of bushes in spring is insignificant. European varieties of strawberries have lower winter hardiness; the plants freeze slightly, and in severe winters they freeze completely. But some imported varieties grow successfully in our conditions; The bushes are covered for the winter, which somewhat reduces plant loss.
- Short fruiting period. The berry plant produces maximum yields for 3-4 years, then it must be completely renewed.
All the shortcomings of the berry plant can be overcome; the main thing is not to leave the strawberries without proper care.
Features of growing and caring for strawberries
The main components of proper care are:
- weeding;
- loosening;
- water regime;
- feeding
Caring for strawberries is not difficult, but it requires patience and systematicity.
Weeding strawberry beds
Strawberry plantings should always be free of weeds. This crop does not like competitors and, if the plot is overgrown, produces small sour berries.Weeding is carried out as the weeds grow, 6-8 times per season.
Simultaneously with the removal of weeds, the mustache is also trimmed, especially in the spring. If they are removed in time, the plants will switch to flowering, otherwise all the strength of the bushes will go into the formation of berries and there will be no berries.
Loosening
Strawberries love loose, well-permeable soil. There should always be free access of air to the roots. Before flowering, the soil is loosened 3 times, and after picking the berries - once every 2 weeks. If the weather is rainy and the soil quickly compacts, then loosening is carried out more often. Cultivate the soil to a depth of 3-4 cm.
Starting from the second year, strawberry bushes spud up as adventitious roots appear on the stem. Hilling stimulates root formation, the growth of horns, the bushes become more luxuriant, which gives an increase in yield.
How to water strawberries
Strawberries are most demanding of moisture in June, when the berries, tendrils and leaves are growing at the same time. If the weather is dry, then the plot is watered once every 2-3 days to a depth of 30 cm, and if possible, then every day.
It is better to water between rows; for this purpose, make a furrow in the middle of the bed when planting, which will collect water when the snow melts and during watering. The plants are not watered at the roots, since the strawberry root system is spreading and the bulk of the roots are located on the periphery of the above-ground part of the plant.
After harvesting, plants begin a second peak of root formation and foliage growth. At this time, the plot is watered 1-2 times a week. If there is no rain, watering is carried out daily. Before and after flowering, the bushes can be watered by sprinkling; strawberries love high air humidity.
During the flowering and fruiting period, only the row spacing is watered; the water temperature should not be lower than 15°C. The rest of the time, plants tolerate watering well with cold water.
In the fall, moisture-recharging pre-winter watering is done. The soil is shed to a depth of 30-50 cm. Moist soil better protects strawberries from frost, so it is necessary that the plot goes under the snow damp.
During flowering and ovary growth in the event of rainy weather, strawberries suffer from waterlogging. Signs of this are the appearance of large brown spots on the leaves and ovaries (without spoilage). Waterlogging of strawberry plantations especially often occurs on dense clay soils. The roots cannot provide normal nutrition to the above-ground parts and the bushes begin to drop the largest berries.
When signs of oxygen starvation appear, deep loosening (5-7 cm) is carried out. If the berry grower experiences constant waterlogging, then the beds are raised to 15-20 cm. When the strawberries do not have ovaries, they do not suffer from waterlogging, but, on the contrary, produce lush foliage and powerful tendrils.
Fertilizing strawberries with folk remedies (ash, chicken droppings)
Strawberries and berries remove quite a lot of nutrients from the soil; these are not only basic nutritional elements (NPK), but also microelements that need to be replenished. Lack of nutrition begins to appear in the second year of cultivation; in the first year, the plants have enough fertilizer applied before planting.
Nutritional deficiency never manifests itself in any one element, so complex fertilizers containing microelements are always applied to the plot. It is better to feed strawberries with organic fertilizers, since they act more gently and last longer.
In the first year of cultivation, if the soil has been properly prepared, fertilizers are not applied. In the second and subsequent years, the berry garden is fed 2 times per season. In the spring, ash is added to the surface of the soil around the bushes, and then the soil is loosened shallowly. On infertile soils in May, humates, humus or grass fertilizer.
Ash should not be added with manure because a chemical reaction occurs that releases large amounts of nitrogen, which can damage plants.
To prepare an herbal infusion, the herb is placed in a plastic barrel, filled with water and left to ferment for 10-15 days. At the end of fermentation, 1 liter of infusion is diluted in 10 liters of water and the bushes are watered at the rate of 1 liter per plant.
After harvest, strawberries begin a second wave of root and leaf growth, and at this time they need nitrogen. Fertilize with a solution of mullein or bird droppings (1 l/10 l of water). Bird droppings are preferable for strawberries and are now sold in garden centers. This is the most concentrated fertilizer in terms of nutrients.
In case of excessive use of organic matter, overfeeding and fattening of strawberry bushes may occur. With proper application of fertilizers, the size of leaves and berries increases and the yield increases.
Excess nitrogen manifests itself in the appearance of large leaves and crushing of berries, and plant productivity is significantly reduced. Overfeeding occurs due to the frequent use of grass fertilizer or non-compliance with the norms for applying other organic fertilizers.
To prevent fattening of plants with organic matter (except manure and compost), ash is added, which does not contain nitrogen and creates a predominance of potassium and phosphorus in the soil.Plants overfed with nitrogen do not tolerate winter well and are more susceptible to diseases and pests.
Underfeeding for strawberries (and not only for them) is better than overfeeding, since in this case the situation is easier to correct.
Is it necessary to feed strawberries with yeast, iodine, boric acid and ammonia?
Fertilizing with folk remedies (yeast, iodine, boric acid, ammonia) is extremely undesirable for the crop.
Firstly, this is a monofertilizer that does not provide plants with the entire set of microelements.
Secondly, the bushes can be easily overfed (especially with ammonia), which will cause significant damage to the plantation.
Thirdly, iodine, boric acid and ammonia are volatile solutions that quickly evaporate; they must be immediately washed into the lower layers of the soil, which is impossible with a large plot area.
Fourth, yeast is an excellent protein feed for animals, but does not contain any plant nutrients.
Fertilizer for a strawberry plantation must be systematic, fully providing the plants with the necessary elements, and no experiments with fertilizing are allowed.
Strawberry plantation care
Regular care is the basis for a high yield. With proper agricultural technology, strawberries can produce up to 300 g of large berries per bush in the first year. On the garden plot you need to have four plots (beds) of strawberries: the first, second, third and fourth years of fruiting.
How to care for strawberry seedlings
When planting seedlings, no fertilizers are applied. The soil must be fertilized in advance. The newly planted mustaches are shaded from the sun, otherwise the seedlings will wilt, since the roots cannot yet replenish the water that is lost when it evaporates by the leaves.Wilting is not very dangerous for seedlings; when the evening coolness sets in, they will straighten out.
To shade the mustache, cover it with newspapers, white cloth, or throw a little grass over it. After 2-3 days, the shelter is removed; by this time, the plants have already taken root and can independently extract water from the soil. In the first days, the planted mustaches are well watered. In the future, the soil under the young bushes should always be moist. In the case of a warm and dry autumn, water the strawberries once a week.
It is important to prevent strawberries from becoming overgrown with weeds. If this is not done in the year of planting, then in the future the fight against them will become much more difficult. Weeds will grow through the bushes and it will no longer be possible to remove them without damaging the crop.
Young strong mustaches, after rooting, themselves begin to produce mustaches, which must be removed, since they weaken the plant and interfere with its preparation for winter.
Preparing strawberry beds for winter
European varieties require special care when preparing a plot for winter, since they are less winter-hardy. In the fall, if the weather is dry, water-recharging irrigation is carried out. Water protects rhizomes well from freezing by conducting heat from below to the roots of plants.
For better wintering, strawberries are insulated by laying straw, fallen leaves and pine needles under the bushes and between the rows. They cover only bare ground; there is no need to cover the plants themselves, since they go into winter with leaves, which themselves act as insulation.
The main thing in winter is to prevent the roots from freezing. If there is no insulation, then add a 3-4 cm layer of soil between the rows and under the bushes.
Caring for strawberries in spring
In the spring, after the snow melts, dry leaves are cut off from the bushes, insulation is removed from the garden bed (if it was used), weeded from the first weeds and loosened. Old bushes that have a small woody stem with adventitious roots are additionally spudded to make them more powerful. Large plants have better flowering and higher yields.
Loosening is carried out to a depth of 2-3 cm, since the roots of strawberries are shallow. With this treatment, the earth warms up faster and the plants begin to grow.
The main task in spring is to ensure rapid warming of the soil so that plants quickly grow foliage and begin flowering. With an early start of the growing season, flowering will occur in moister soil. To warm up the soil as quickly as possible, you can put black film between the rows.
Some gardeners, on the contrary, do not remove the insulation for a long time, fearing damage to the strawberries by frost. But, firstly, it is not afraid of frost in the spring, and secondly, strawberries bear fruit from mid-June to mid-July (depending on the variety), and in May they need time to prepare for flowering. The better it is prepared, the larger the berries will be.
Old dry leaves along with last year's tendrils are removed, but young foliage does not need to be trimmed. Trimming green leaves in the spring delays flowering for 2 weeks (until new ones grow); the plant spends a lot of energy growing foliage, which is why the berries become smaller.
During a dry, warm spring, when the soil dries out quickly, watering is carried out. After the young leaves grow, do spring feeding.
If plants are weakened after winter and grow poorly, they are sprayed with growth stimulator “Zircon” or “Epin”.
How should strawberries be cared for after harvest?
After fruiting, the spring leaves look yellow and spotted; they are removed along with overgrown tendrils and weeds. You cannot mow down all the foliage, since the roots growing at this time require starch, which comes directly from the leaves; if they are removed, this will slow down the preparation of strawberries for winter.
After harvesting, be sure to carry out a second feeding to replenish the nutrients carried out with the berries.
In the second half of summer, strawberries begin to grow whiskers more actively. Under no circumstances should they be allowed to take root. They compact plantings and weaken bushes, which leads to a decrease in yield and taste of berries.
If the bushes are intended for fruiting, then all emerging mustaches are cut off. The plot is inspected once every 4-5 days, since the shoots appear until October, and the spears of shoots that have just appeared are removed.
Strawberries have a balance between bean formation and fruiting: if plants are not given the opportunity to form tendrils, then it increases fruiting and, conversely, if they are not picked, the yield is greatly reduced.
The plantation should always be free of weeds, fertilized, and the bushes should have their tendrils trimmed.
In the fall, moisture-recharging irrigation is carried out, if necessary, insulation is laid out between the rows.
Caring for the plantation in the last year of cultivation
When fertilizing in spring, you can give a little more nitrogen, the bushes will not have time to get fat, and this will not reduce the yield. When the soil is dry, watering is carried out. Immediately after fruiting, the bed is dug up. This year you can plant early cabbage on it, which will have time to ripen before the onset of cold weather (this is why increased doses of nitrogen were given).
Mulching strawberries
When caring for a plantation, mulching materials are used to protect berries from dirt and rot, insulate bushes in winter and protect the soil from premature warming up during a thaw. Mulch suppresses weed growth and prevents the formation of soil crust after rains or watering.
Using mulch when growing strawberries is the best way to keep the plot clean and makes it much easier to care for. To prevent undesirable effects when using it, mulch is applied under certain conditions.
Sawdust, straw, dry moss, fallen leaves, and pine needles are used as mulching materials. Their disadvantage is the fixation of soil nitrogen, which causes nitrogen starvation of plants. Therefore, mulch is applied in the fall as insulation between rows; by spring, the process of decomposition of fiber (of which it consists) will be completed and nitrogen fixation will not occur.
In the spring, the insulation is removed to better warm the soil, then it is returned as mulch, and a fresh portion of material is added to it. When adding mulching materials in the spring, they must be soaked with a solution of humates, mullein or bird droppings.
To do this, either soak them in a barrel with a fertilizer solution (sawdust), or water them very generously with these fertilizers so that the mulch is completely saturated with the solution. Then the binding of soil nitrogen will not occur, and the plants will not experience nitrogen starvation.
Mulching strawberries with sawdust. Sawdust strongly acidifies the soil; watering it with urea as a nitrogen fertilizer enhances acidification. This effect gives excellent results on leached chernozems. This should not be allowed on acidic soils.To prevent acidification of the soil, sawdust is first soaked in a barrel with humates or chicken droppings, after which they become an excellent mulching material. Spread on the beds in a layer of 6-10 cm. Sawdust inhibits the growth of weeds more than hay and straw.
Mulching with grass and straw. Hay and straw consist of almost the same fiber and very strongly bind soil nitrogen. They are introduced in the fall. When using hay or straw as mulch in the spring, crumbled manure is added along with them, or the freshly spread mulch is irrigated with nitrogen fertilizers (humates, mullein, herbal infusion). In this case, nitrogen fixation does not occur and the yield does not decrease. They are laid out between rows in a layer of 5-7 cm.
Leaf mulch. It is advisable to add foliage from deciduous trees in the fall, laying it out in row spacing in a layer of 15-20 cm. In winter, it will serve as insulation. When used in spring, freshly spread leaves are watered with humates, mullein, or herbal infusion.
Mulching strawberries with pine needles. Pine and spruce bark and needles protect plants well from diseases, as they contain phytoncides. The material is taken only under healthy trees, scattered between rows and under bushes in a layer of 7-10 cm. Since this material strongly acidifies the soil, it is applied with manure crumbs.
Peat as mulch they are not used on strawberries because it has a number of significant disadvantages:
- strongly acidifies the soil;
- has a very high moisture capacity, which makes it almost impossible to saturate it with a nitrogen solution;
- in wet weather it gets wet and interferes with normal breathing of the roots;
- In winter, it can become covered with an ice crust, which leads to damping off of plants.
Proper use of mulch not only makes it easier to care for the plantation, but it itself is a good fertilizer.
Protecting berries from dirt
Berries lying on the ground become contaminated with soil, and they are more susceptible to gray rot. To prevent the berries from coming into contact with the soil, you can make various supports for the bushes: from wire, plastic bottles, planks, film; stores sell special rings on legs. But all this is suitable for a small plot.
On a large plantation, plucked lower peripheral leaves are placed under the green berries. If the bush is healthy, the red berries can lie on the ground for some time without being damaged.
When growing strawberries, you do not need to maintain a plantation with a more productive fruiting period. The berry picker should move around the site in frequent rotation.
Other useful articles on growing strawberries:
- Strawberry pests. What pests can threaten your plantation and how to effectively combat them.
- Strawberry diseases. Treatment of plants with chemicals and folk remedies.
- Strawberry propagation. How to propagate strawberry bushes yourself and what mistakes gardeners most often make.
- Growing strawberries from seeds. Is it worth it for ordinary summer residents to do this?
- The best varieties of strawberries with photos and descriptions. A selection of the newest, most productive and promising varieties.
- Growing strawberries in a greenhouse. Growing technology and all the pros and cons of this matter.
- Planting strawberries in open ground. Are you going to tackle strawberries? Then this is the very first article you need to read.
- Features of caring for large-fruited strawberries. In order for strawberries to grow large, they will have to be carefully looked after.












 (17 ratings, average: 4,41 out of 5)
(17 ratings, average: 4,41 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.