Tomatoes come from South America, so when growing tomato seedlings in the house you need relatively dry air, a lot of light and heat. In this article we will look in detail at how to properly plant and care for young seedlings.
|
We will grow seedlings like this |
Choosing the right variety
Before you start growing tomato seedlings, you need to decide on the choice of varieties. Before planting seeds, you need to decide which varieties will be grown and where. It is fundamentally important to know whether there will be tomatoes grow in open ground or in the greenhouse.
According to the method of growth, all varieties are divided into indeterminate, semi-determinant and determinant. This sign is indicated on the bag of seeds and is decisive for growing plants in open or protected ground.
|
Indeterminate (tall) tomatoes |
- Indeterminate tomatoes have unlimited growth and, if not pinched, can grow up to several meters. On South can be grown in a greenhouse either outside on a trellis, or tied to high stakes. In the middle zone, Siberia, and the Far East, these tomatoes are grown only in protected soil, tying them vertically. The first brush is laid after 9-10 sheets, the subsequent ones - after 3 sheets. The fruiting period is long, but occurs later than in other types.
- Semi-determinate varieties and hybrids. Tomatoes stop growing after 9-12 inflorescences are formed. They tend to set a large number of fruits to the detriment of the roots and leaves, and, if overloaded with the harvest, tomatoes can stop growing long before the formation of the 9th cluster. Flower brushes are laid through 2 sheets.In the south they are grown mainly in open ground; in the middle zone they can be planted both in a greenhouse and outside.
- Determinate tomatoes - These are low-growing plants. They are intended for planting in open ground. Their growth is limited, they lay 3-6 clusters, the tip of the shoot ends in a flower cluster and the bush does not grow upward anymore. The first brush of this type is laid after 6-7 leaves. These are early-ripening tomatoes, but their yield is lower than that of the indeterminate type. However, significant differences in the yield of varieties are noticeable only in the south. In the middle zone and to the north the difference is minimal, since indents do not have time to reveal their full potential.
Determinate (low-growing) tomatoes
What to choose - a hybrid or a variety?
Variety - these are plants that can retain their characteristics for many generations when grown from seeds.
Hybrid - These are plants obtained through special pollination. They retain their characteristics only in one generation; when growing tomatoes from collected seeds, their characteristics are lost. Hybrids of any plants are designated F1.
| Sign | Varieties | Hybrids |
| Heredity | Varietal characteristics are transmitted to subsequent generations | Traits are not transmitted and are a feature of one generation for one growing season |
| Germination | 75-85% | Excellent (95-100%) |
| Fruit size | The fruits are larger than those of hybrids, but can vary significantly in weight | The fruits are smaller, but aligned |
| Productivity | May fluctuate from year to year | High yield with proper care. Typically higher than varieties |
| Disease resistance | Susceptible to various diseases, some of which can be inherited | More resilient, less susceptible to disease |
| Weather | Better tolerate temperature changes | The varieties tolerate temperature fluctuations much worse. Sudden and severe temperature changes can cause death. |
| Conditions of detention | Less demanding on soil fertility and temperature | Requires more fertile soils and higher temperatures for fruiting |
| Feeding | Regularly needed | For good fruiting, the dose should be greater than for varieties |
| Watering | Can tolerate short-term drought or waterlogging well | They tolerate both lack and excess moisture very poorly. |
| Taste | Each variety has its own taste. | Less pronounced. All hybrids are inferior in taste to varieties |
The cooler the summer in a region, the more difficult it is to grow hybrids. In these regions, the varieties should be preferred. Also, if in the future there is a desire to grow a crop from your own seeds, then make a choice in favor of the variety.
If the goal is to obtain the maximum amount of product, and weather conditions in the region allow it, then growing hybrids is preferable.
Timing for sowing seeds for seedlings
The timing of sowing seeds for seedlings depends on the early maturity. First of all, the timing of planting tomatoes in the ground is determined and the required number of days is counted from this date - the date for sowing the seeds is obtained.
For mid-season varieties, the age of tomato seedlings before planting in the ground should be at least 65-75 days. They can be planted in a greenhouse at the end of May, and in open ground when the threat of frost has passed, that is, in the first ten days of June (for the middle zone). If we also add the period from sowing to the emergence of seedlings (7-10 days), then it is necessary to sow 70-80 days before planting in the ground.
In the middle zone, the sowing time for mid-season varieties is the first ten days of March.However, growing mid-season varieties in the northern and central regions is unprofitable: they will not have time to fully develop their potential, and the harvest will be small. Mid-ripening and late-season tomatoes are suitable only for the southern regions of the country.
Seedlings of early ripening tomatoes are planted in the ground at the age of 60-65 days. Consequently, seeds are sown after March 20. They are suitable for all regions of the country.
There is no need to sow tomatoes for seedlings too early. When sown early in conditions of light deficiency, they become greatly elongated and weakened. In case of poor lighting during the seedling period, flower clusters are laid later, and the yield becomes lower.
If the soil in the greenhouse has warmed up, then early-ripening tomatoes for indoor soil can be sown directly into the greenhouse in early May and grown without picking. When grown without seedlings, tomatoes begin to bear fruit 1-2 weeks earlier than seedlings.
Soil preparation
To grow tomato seedlings, it is better to prepare the soil yourself. The soil must be loose, nutritious, water- and air-permeable, must not crust over or become compacted after watering, and be clean from pathogens, pests and weed seeds.
For seedlings, make up a mixture of peat and sand in a ratio of 1:0.5. For each bucket of obtained soil, it is advisable to add a liter jar of ash. Peat is acidic, and tomatoes need a neutral environment to grow well. Ash just neutralizes excess acidity.
|
Another option for the earth mixture is turf soil, humus, sand in a ratio of 1:2:3; instead of sand, you can take high-moor peat. |
In garden soil, after special treatment, you can also grow healthy tomato seedlings, the main thing is that it does not contain spores of diseases and overwintering pests.But, since it becomes too compacted in containers, sand or peat is added to loosen it. They take soil from planting legumes, melons, greens, and green manure. You cannot use soil from greenhouses after nightshades. If the soil at the dacha is acidic, then be sure to add ash (1 liter/bucket). It is better to use garden soil for preparing soil mixtures.
Purchased soils contain a lot of fertilizers, which is not always good for seedlings. If there are no other options, then store soil is diluted with sand, garden soil or turf soil. Peat is not added to purchased soil, since it itself, most often, consists only of peat. It is better to prepare the soil mixture in the fall.
If the moment is missed and there is nowhere to get the soil, you will have to buy several types of soil from different manufacturers and mix them in equal proportions, or add soil from flower pots to the purchased soil. But this is the worst option when growing seedlings.
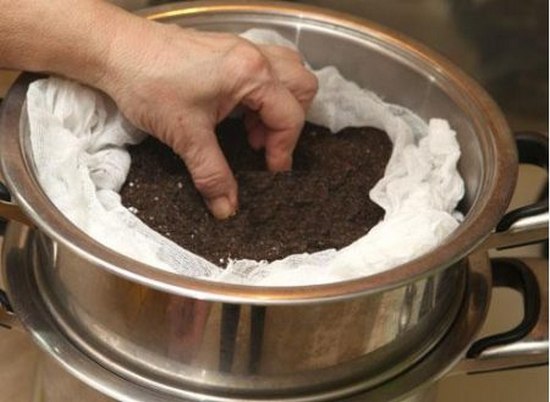
Soil treatment
|
After preparing the mixture, the land must be cultivated to destroy pests, diseases, and weed seeds. |
The soil can be treated using various methods:
- freezing;
- steaming;
- calcination;
- disinfection.
Freezing. The finished soil is taken out into the cold for several days so that it freezes. Then they bring it into the house and let it thaw. The procedure is repeated several times. It is advisable that the frost outside at this time should not be lower than -8 -10°C.
Steaming. The earth is heated for an hour in a boiling water bath. If the soil is purchased, then the sealed bag is placed in a bucket of hot water, covered with a lid and left until the water cools down.
Calcination. The earth is calcined in an oven heated to 100°C for 40-50 minutes.
Disinfection. The earth is watered with a strong solution of potassium permanganate dissolved in hot water. Then cover with film and leave for 2-3 days.
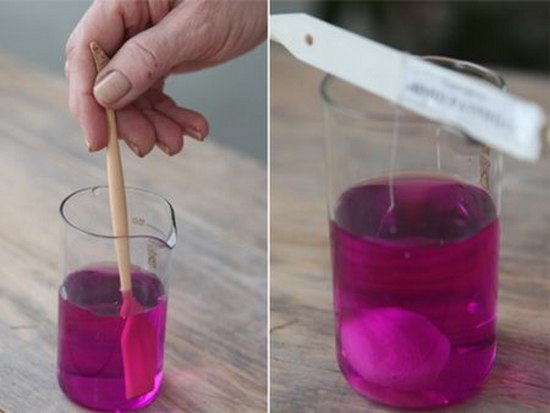
Preparing tomato seeds for sowing
If the bag says that the seeds have been processed, then they do not require additional processing. The rest of the seed must be processed.
First of all, calibration is carried out. Place the seeds in a glass of water and wait 3-5 minutes until they get wet. Then the floating seeds are thrown away; they are unsuitable for sowing, since the embryo died, which is why they became lighter than water. The rest are soaked for 2 hours in a solution of potassium permanganate.
|
For treatment, seeds can be soaked in water heated to 53 ° C for 20 minutes. This temperature kills disease spores but does not affect the embryo. Then the hot water is drained, the seeds are slightly dried and sown immediately. |
To speed up germination, the seed material is soaked. It is wrapped in cotton cloth or a paper napkin, moistened with water, placed in a plastic bag and placed on the battery. Treated seeds also need to be soaked. As practice shows, they sprout faster than without soaking, and the protective effect of the treatment remains quite high.
Many people treat planting material with growth stimulants. But in this case, all the seeds, including the weak ones, germinate together. In the future, a large percentage of weak plants are rejected. Therefore, it is better to treat bad seeds (expiring, overdried, etc.) with stimulants; simply soak the rest in water.
Sowing seeds
When the seeds hatch, sowing is done. You should not wait until the sprout is larger; if you delay sowing, long sprouts will break off.
|
You can sow the seeds in separate containers, 2 seeds each, if both sprout, then they are planted when picking. |
Tomatoes are sown in shallow boxes, filling them 3/4 with soil. The earth is lightly crushed. The seeds are placed at a distance of 2 cm from each other. Sprinkle dry soil on top.
If the soil is not crushed or the crops are covered with damp soil, the seeds will go deep into the soil and will not germinate.
Varietal tomatoes and hybrids are sown in different containers, since their germination conditions are different.
The boxes are covered with film or glass and placed on a radiator until germination.
Seed germination time
The timing of seedling emergence depends on temperature.
- Seeds of varieties germinate at a temperature of 24-26°C in 6-8 days
- At 20-23°C - after 7-10 days
- At 28-30°C - after 4-5 days.
- They can also sprout at 18°C in 8-12 days.
- The optimal germination temperature for varietal tomatoes is 22-25°C.
The germination rate of hybrids is much better, but often they do not germinate well at home. For good germination they need a temperature of +28-30°C. +24°C - COLD for them, they will take a long time to germinate and not all of them will sprout.
Weak seeds germinate later than others; the seed coat usually remains on them. Therefore, shoots that appear later than 5 days after the main group are removed; they will not produce a good harvest.
Caring for tomato seedlings
To grow good tomato seedlings, you need to monitor the following parameters:
- temperature;
- light;
- moisture.
Temperature
As soon as the shoots appear, the film is removed and the boxes are placed in a bright and cool place with a temperature of +14-16°C. In the first 10-14 days, the roots of the seedlings grow, and the above-ground part practically does not develop. This is a feature of tomatoes and you don’t need to do anything here.After the allotted time, the seedlings will begin to grow. As soon as growth begins, the daytime temperature is increased to 20°C, and the night temperature is maintained at the same level (15-17°C).
|
Hybrids after germination need a higher temperature (+18-19°). If they are placed in the same conditions as varietal tomatoes, they will wither rather than grow. |
After 2 weeks, they also need to increase the daytime temperature to 20-22°C. If this cannot be done, then the hybrids will develop more slowly, their first flower cluster will appear later and the yield will be lower.
In general, you need to set aside the warmest window sill for growing hybrids, take better care of them than other seedlings, only then will they produce a full harvest.
On warm days, the seedlings are taken out onto the balcony, and at night the windows are opened to reduce the temperature. Those who have the opportunity put tomatoes in a greenhouse on sunny days if the temperature there is not lower than +15-17°C. Such temperatures harden the plants well, make them stronger, and, in the future, their yield is higher.
Lighting
Tomato seedlings must be illuminated, especially late varieties that are sown earlier. The lighting period must be at least 14 hours a day. With a lack of light, the seedlings stretch out greatly, become long and fragile. In cloudy weather, additional lighting for plants is increased by 1-2 hours compared to sunny days, and the temperature is reduced to 13-14°C, otherwise the tomatoes will become very stretched.
Watering
Water tomatoes very sparingly. Watering is carried out as the soil dries and only with settled water. Unsettled tap water forms a bacterial-limescale deposit on the soil, which tomatoes really don’t like.At the initial stage, each plant needs only 1 teaspoon of water; as it grows, watering is increased.
|
The soil in the seedling box should be neither too wet nor too dry. You need to water abundantly so that the soil is sufficiently saturated with moisture, and the next watering is carried out only after the earthen clod has dried. |
Usually tomatoes are watered no more than once a week, but here they focus on individual growing conditions. If the plants have wilted, they need to be watered without waiting for a week to pass.
Overmoistening combined with high temperature and poor lighting causes the tomatoes to become very stretched.
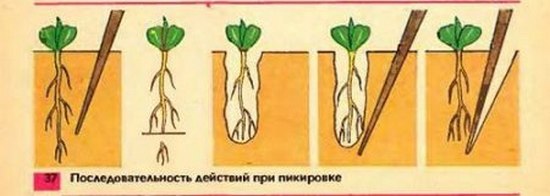
Picking seedlings
When the tomato seedlings have 2-3 true leaves, pick them.
For picking, prepare pots with a volume of at least 1 liter, fill them 3/4 with earth, water and compact. Make a hole, dig out the seedling with a teaspoon and plant it in a pot. When picking, the tomatoes are planted somewhat deeper than they grew previously, covering the stem with soil up to the cotyledon leaves. Strongly elongated seedlings are covered up to the first true leaves. The seedlings are held by the leaves; if you hold it by the thin stem, it will break.
|
Tomatoes tolerate picking well. If the sucking roots are damaged, they quickly recover and grow thicker. The roots should not be allowed to bend upward, otherwise the seedlings will develop poorly. |
After picking, the ground is well watered, and the tomatoes themselves are shaded for 1-2 days so that the evaporation of water by the leaves is less intense.
How to feed tomato seedlings
Feeding is carried out 5-7 days after picking. Previously, fertilizing is not recommended, since the soil was filled with ash, which contains all the necessary elements for seed growth.If seedlings are grown on purchased soil mixture, then fertilizing is especially not needed.
After 14-16 days from germination, tomatoes begin to actively grow leaves, and at this time they need to be fed. Fertilizer should contain not only nitrogen, but also phosphorus and microelements, so it is advisable to use a universal fertilizer. During this period, you can feed tomatoes with fertilizer for indoor plants. It gives excellent results.
|
You cannot feed tomato seedlings with nitrogen alone. Firstly, for relatively small plants it is difficult to calculate the required dose. Secondly, nitrogen causes increased growth, which, with a limited amount of land and insufficient light, leads to severe elongation and thinning of plants. |
Subsequent feedings are carried out after 12-14 days. Seedlings of late and mid-season varieties are fed 3-4 times before planting in the ground. For early ripening varieties, 1 or maximum two feedings are enough. For hybrids, the amount of fertilizing is increased by 2 for each type of seedling.
If the land is purchased, then it is sufficiently filled with fertilizers and fertilizing is not carried out when growing tomatoes on such soils. The exception is hybrids. They consume nutrients more intensively and before planting it is necessary to carry out 1-2 feedings, no matter in what soil they are grown.
Caring for seedlings after picking
After picking, the seedlings are placed on the windowsills as freely as possible. If she is cramped, then she develops poorly. In densely spaced seedlings, the illumination decreases and they stretch out.
- 2 weeks before planting tomatoes, they are hardened off
- To do this, seedlings are taken out to the balcony or open air even on cold days (temperature not lower than 11-12 °C)
- At night the temperature is reduced to 13-15°C.
- To harden hybrids, the temperature should be 2-3°C higher, it is gradually lowered.
|
To harden, pots with hybrids are first placed next to the glass itself, where the temperature is always lower. After a few days, if the batteries are regulated, they are closed for a few hours; if they are not adjustable, then open a balcony or window. At the final stage of hardening, the hybrid seedlings are taken out to the balcony for the whole day. |
If the tomato seedlings cannot be taken out onto the balcony, then they are sprayed daily with cold water to harden them.
Main reasons for failure
- Tomato seedlings are very stretched. There are several reasons: not enough light, early planting, excess nitrogen fertilizers.
- Seedlings always stretch out when there is insufficient light. It needs to be illuminated. If this is not possible, then place a mirror or foil behind the seedlings, then the illumination of the tomatoes increases greatly and they stretch less.
- No need feed the tomatoes nitrogen, this causes rapid growth of the tops, and in low light conditions (and there is always not enough light indoors, no matter how much you light the seedlings) they become very elongated.
- Sowing seeds too early. Even normally developing seedlings stretch out when sown early. After 60-70 days, the plants become cramped in pots and containers, they need to develop further, and in conditions of limited food space and cramped conditions on the windowsill, they have one way out - to grow upwards.
- All these factors, both individually and together, cause the seedlings to stretch. Tomatoes stretch even more if excessive watering and high temperature of seedlings are added.
- The seeds don't germinate. If the seed is of good quality, then there are no seedlings due to low soil temperature. This is especially important for hybrids.They germinate at a temperature of 28-30°C. Therefore, to speed up the emergence of seedlings, containers with sown tomatoes are placed on a battery.
- Tomatoes don't grow well. They are too cold. For varietal tomatoes, a temperature of 18-20° is required for normal growth, for hybrids - 22-23°C. Hybrids can grow at 20°C, but more slowly and, accordingly, will begin to bear fruit later.
- Yellowing of leaves.
- Leaves of tomatoes grown in close quarters usually turn yellow. When the seedlings are large, there is not enough light on a cramped windowsill, and the plants shed excess leaves. In such conditions, all attention is paid to the top of the stem; the bushes try to outgrow their competitors in order to have more comfortable conditions. When the leaves turn yellow, the seedlings are spaced more freely and the air temperature is reduced.
- If the leaves are small, turn yellow, but the veins remain green or slightly reddish, this is a lack of nitrogen. Feed with complete mineral fertilizer. There is no need to feed nitrogen alone, otherwise the tomatoes will stretch.
- Limitation of power supply area. The tomatoes are already cramped in the container, the roots have entwined the entire earthen ball and further growth stops. Transplant the seedlings into a larger pot.
- Leaf curl. Sudden and significant changes in temperature. When growing tomatoes, you need to avoid sudden increases in air temperature. The feeding area of the seedlings is limited, and the roots cannot support all the leaves in hot weather. The same thing happens during a sudden cold snap, but this is much less common at home.
- Blackleg. Common disease of tomato seedlings. Affects all types of plants. The disease spreads rapidly and can destroy entire seedlings in a short time.The stem at the soil level turns black, becomes thinner, dries out, and the plant falls and dies. Infected plants are removed immediately. The soil is watered with a pink solution of potassium permanganate, Fitosporin, Alirin. After this, the tomatoes do not need to be watered for a week; the soil should dry out.
Growing seedlings at home is a troublesome task, but otherwise reap a good harvest will not succeed, especially in the northern regions and the middle zone.













 (70 ratings, average: 4,31 out of 5)
(70 ratings, average: 4,31 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
Very useful article. The preparatory processes are described in detail. For beginners in this matter everything will be clear and understandable. I recently read a similar article, the article also turned out to be useful, read it if you are interested in this topic, the more information the better.