How to properly plant and grow privet on a plot and in a city apartment.
| Content:
|
Recently, amateur gardeners have been paying special attention to the appearance of their summer cottages. They want not only to grow vegetables, berries and fruits, but also to decorate their garden or plot of land with beautiful plants and unusual plant compositions. The issue of landscaping is decided by gardeners based on personal preferences - by arranging lawns and flower beds, hedges and rock gardens.

This is what a privet bush looks like
The perennial shrub common privet will help realize many of the plans of experimental gardeners. Our article will tell you how to plant, grow, propagate and use privet in garden design.
Common privet description and features
Common privet is a representative of the genus of plants of the Olive family. The family includes about fifty species of deciduous, semi-evergreen, evergreen shrubs and small trees. Translated from Latin, the name means “to bind,” which indicates the astringent properties of the plant’s bark, and in Russia it is called “wolf berry” or “privet berry” because of the poisonous properties of the fruit.
Common privet is the most popular and unpretentious of all varieties, due to many features:
- grows up to 3 meters in height and width;
- blooms in early summer for 20-25 days;
- not picky about soil, but prefers neutral or slightly alkaline soil;
- resistant to pest attacks and diseases;
- does not require complex care;
- Privet reproduces well in several ways;
- can grow in a polluted and smoky atmosphere, therefore it is actively grown in urban environments;
- drought- and frost-resistant;
- tolerates haircuts well, recovers quickly after it, keeps its shape well;
- per season, the growth of green mass is up to 30 centimeters in height and width (depending on the variety).
- life expectancy - 70 years.
Among the decorative forms one can distinguish pyramidal, weeping, bluish, golden, and golden-variegated. All decorative specimens are less winter-hardy and low-growing, but deserve attention due to their beautiful foliage and are used in the design of low borders (30 cm) or in single plantings.
How privet is used in garden design
- Privet is an excellent plant material for creating low borders in the design of paths, delineating garden zones, and edging large flower beds.
- The ability of the plant to retain its shape well allows you to make figures of various configurations (spherical, pyramidal, cylindrical).
You can even grow a boat like this from privet.
- Used to imitate boulders in a Japanese garden - trimmed karikomi cushions.
Karikomi pillows
- Standard varieties look great in alley plantings.
Standard forms of the plant.
- But traditionally, common privet is used to create a green hedge.
Privet hedge.
Planting privet
The further development of the plants will depend on how the planting of privet seedlings in open ground goes. This process is simple, but requires several mandatory steps:
- Dig up the area for planting shrubs using the bayonet of a shovel;
- Dig planting holes measuring 60x60 and 65 centimeters deep;
- Soak the soil in the hole with water;
- Lay out the bottom with a layer of expanded clay 8 - 15 cm thick;
- Pour a mound of soil, mixing 130 g of nitroammophoska into it;
- Place the seedling on the mound, straighten the roots;
- Fill the hole with soil, but without adding fertilizer;
- It is necessary to keep the soil around the seedlings moist for a month;
- Sprinkle the area around the seedling with a layer of peat 5-8 cm thick.
Planting seedlings.
Privet care
Caring for privet is an equally important step and involves performing standard actions:
- Loosening the soil under plantings to improve air permeability. Loosening is combined with weed removal.
- Mulching soil to protect the roots from overheating and the appearance of weeds. The mulch layer should be at least 5 cm. The soil is mulched at the end of spring, after the soil has sufficiently warmed up, while there is still enough moisture in it.
- Watering infrequent, but plentiful. Each bush is given at least 3 buckets of water per watering, trying to wet the soil to a depth of 0.5 m.
Feeding Privets are carried out in two stages:
- Root feeding is carried out in the spring, after the soil has warmed up (a bucket of humus and a pinch of urea per bush). The fertilizer is distributed around the bush, lightly dug up and watered. To get rid of pests overwintering on the branches of bushes, in early spring the bushes are sprayed with a 5% solution of urea (500 g of fertilizer is diluted in 10 liters of water).
- In the fall, for better wintering (once every 2-3 years), potassium fertilizers are applied at a rate of 15 grams per square meter. m, phosphorus - from 10 to 15 g/sq.m. m. Then the soil is deoxidized with lime (once every 3-4 years). You can replace it with dolomite flour or chalk.
Plant pruning. During the season it is necessary to prune twice: at the end of spring and at the end of summer. For decorative pruning, trellis scissors, a stencil, and twine are used. Two-year-old bushes must be pruned.
In order for the crown to grow thick, young shoots are first shortened by half. The next time you trim, shorten it by two-thirds.Because of this, flowering is delayed, but the shoots grow more actively. The crown turns out lush and dense.
Reproduction methods
Cuttings
The most common method of propagating privet is cuttings. The survival rate of this year's planting material is close to 100%.
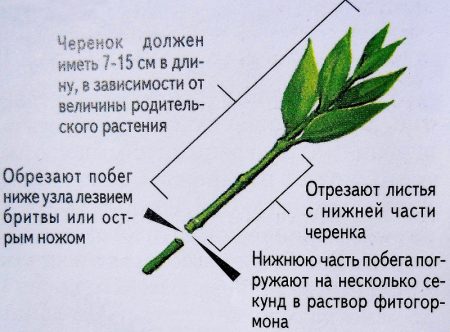
Preparing the cuttings.
You can prepare planting material yourself:
- To prepare cuttings, shoots of the new season will be needed;
- after flowering, cuttings 10–14 cm long are cut;
- the cut is made under the internode, the lower leaves are removed;
- cuttings should be planted in a greenhouse with light shade or by making mini-greenhouses from plastic bottles. The bottles have several holes for ventilation. This will prevent mold from forming on the cuttings;
- after 2 months the cuttings begin to grow and the shelter can be removed;
- the seedlings are left alone until next spring, weeding them regularly;
- Next spring you can plant young bushes in a permanent place.
Reproduction of privet by layering
At the beginning of summer, the lower shoots are pressed to the ground with staples and sprinkled with moist soil on top. The root system is gradually formed in the buried shoots.
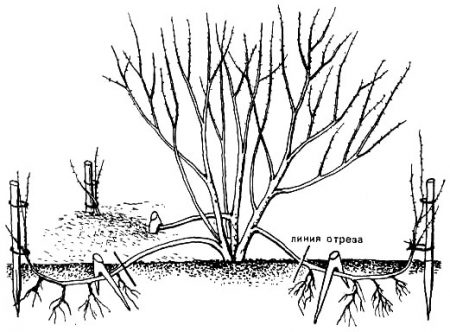
Formation of layering
The next year, the cuttings are separated from the mother bush and transplanted to a permanent place. From one queen cell you can get 10 - 15 layerings.
Seeds
Privet can also be propagated by seed. Specimens at least 5-6 years old are suitable for collecting seeds. The method of planting privet seeds is long (the bushes will become marketable only after 2-3 years) and labor-intensive, despite the fact that about 60% of the seeds germinate. Therefore, this method is more often used for propagating privet on an industrial scale.
Seeds require long-term (6 months) stratification.When planting in autumn, stratification will be natural; when planting in spring, it is necessary to place the seeds mixed with a moist substrate in the refrigerator for 6 months in advance.
Privet hedge
A privet hedge can change the landscape of any garden or park. A green screen can be used to enclose recreation and play areas for children, gazebos, paths and other areas for various purposes.
The main components when creating a green privet fence are planting material and its correct planting:
- the age of the planted plants should be from 3 to 5 years;
- for planting, a trench is dug 0.5 m wide and 0.6 m deep;
- Privet bushes are planted from each other at a distance of 25-30 centimeters.
The following conditions contribute to the formation of a thick and dense crown:
- growing in an open sunny place;
- maintaining optimal humidity;
- presence of neutral soil.
The unpretentiousness of privet, ease of care and the ability to shape it by cutting make this shrub indispensable in organizing green hedges and various shapes in garden design.
Growing and caring for indoor privet
Privet is grown not only as an outdoor plant, but also as an indoor plant. For growing in an apartment or house, evergreen crops with beautiful leaves are used.
They are often formed in the form of mini-trees. The spectacular dark bark looks old even on young branches.
Caring for and creating conditions for the growth and development of privet in a room is somewhat more difficult than for a garden form. The plant has increased requirements for lighting, ambient temperature, and air humidity.
Lighting
Indoor privet loves bright but diffuse lighting.Such lighting should be of the same intensity at all times; this is the key to an attractive appearance of the crop. Artificial illumination does not bring the desired result.
It is preferable to place the plant on southern, south-eastern, south-western window sills. Placement on window sills on the east or west side is permissible in the summer, with the crop moving to the southern window sill in the autumn-winter period.
Temperature
Comfortable temperature for homemade privet is from +15 to +21 degrees.
At higher temperatures, the plant needs increased air humidity. Indoor culture likes to overwinter at a temperature of +10...+12 degrees. Critical temperatures are: +5 degrees - minimum, +15 degrees - maximum.
Overwintering at elevated air temperatures leads to the shedding of leaves. The plant will not die, but it will be difficult to restore its decorative appearance.
Taking homemade privet outdoors has a positive effect on preserving its appearance. The plant can be kept outdoors from April to October. Without air walks, indoor privet loses its decorative effect.
Watering and air humidity
The soil should not be allowed to dry out. This causes leaves to fall. In summer, privet is watered frequently, keeping the soil moderately moist. Or the best watering tactic for a house plant is to immerse the pot and the plant in water. The signal for the watering procedure is the drying of the top layer of soil.
In winter, the soil must be moistened in the traditional way, avoiding waterlogging. But complete drying of the earthen clod is unacceptable even in winter. The water temperature should be room temperature.
To maintain the required air humidity, place a container with privet in a tray filled with wet expanded clay, and also use regular spraying.
During flowering, spraying should be abandoned.
Top dressing for indoor privet
To ensure that the mini-plant has the strength to maintain its foliage, fertilizers are applied all year round. During the winter season, privet is fertilized once a month, and during the active growing season - 2 times a month.
For fertilizing, specialized fertilizers for bonsai or complex fertilizers are suitable, the dosage of which should be halved compared to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Trimming
Pruning is a major part of home privet care. It is necessary depending on the speed of shoot growth. Therefore, pruning may be necessary more than once a year.
The stem of a privet bonsai can be formed all year round by wrapping wire around adult branches and the trunk, even in winter.
Transplanting domestic privet
Young specimens need to be replanted once every 2 years, adult plants - after the soil is completely filled with roots.

It's time to prepare this plant for replanting.
At home, mini-privet is planted in peculiar pots and bowls - characterized by the fact that their diameter is twice or more the height. Privet bonsai prefers containers made of natural materials with large holes to ensure adequate water drainage.
Any universal substrate consisting of peat, turf soil, humus and river sand is suitable for planting homemade privet.
When transplanting into a new container, the bonsai roots are trimmed, which prevents the plant from growing excessively, and the dimensions of the container are not changed or slightly increased if the plants are young.The bottom of the bowl is covered with coarse fraction drainage.
Possible problems when growing privet bonsai
Basically, problems arise due to improper plant care:
- the appearance of brown spots on the leaves due to the use of cold water for irrigation;
- the appearance of yellowness on the leaves due to excessive fertilizing, due to direct sunlight, due to dry air;
- wrinkling, wilting and falling of leaves due to drying out of the soil, heat, due to elevated temperatures during the winter period.
Diseases and pests
Privet is not susceptible to disease, but with high acidity it suffers from gray spotting or powdery mildew. High acidity is indicated by weeds growing under the plant: plantain, woodlice or horsetail.
To combat the manifestations of these diseases, it is necessary to adjust the conditions of plant maintenance and add lime to the soil in the fall.
Pests also rarely bother privet.
Possible insect pests can be: spider mites, scale insects, aphids.
Treating plants twice with complex insecticides will help get rid of the scourge.
The most famous types of privet
In addition to common privet, several other varieties deserve attention.
Oval-leaved or Californian
- Fast-growing, densely leafy shrub.
- Height - 1 meter.
- The flowers have an unpleasant aroma.
Round-leaved
- An evergreen shrub with rounded leaves.
- Creamy white flowers are a good honey plant.
- The plant grows on any soil, but is afraid of frost, so it must be planted in areas protected from cold winds and covered for the winter.
Tupolifolia
Deciduous, slow-growing (annual growth - 10-15 cm) shrub, growing in cultivation to a maximum of 3 m in height, up to 2 m in width. It has a wide spreading crown with horizontal and slightly hanging branches.
It is characterized by heat resistance, resistance to air pollution, wind resistance, and undemanding soil conditions.
Brilliant
- A fast-growing, heat-loving evergreen shrub or tree up to 3 meters high.
- When the frost is -15 degrees, the plant requires shelter.
- The leaves are large, shiny, rich green.
- The flowers are collected in paniculate loose clusters up to 18 cm long, with a pleasant aroma.
- Flowering lasts for three months.
Golden
- The semi-evergreen plant surprises with its bright color, especially in winter.
- Tolerates drafts and air pollution well.
- The leaves are 6 cm long, oval in shape. The middle of the leaves is green and the edges are golden yellow.
- To preserve its decorative properties, it is necessary to grow in sunny places.
















 (2 ratings, average: 4,00 out of 5)
(2 ratings, average: 4,00 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush.Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush.Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.