To obtain an ultra-early harvest of cucumbers, they are planted in warm beds. At this time, the weather is still cool and there is no point in sowing crop seeds in cold soil. A warm bed significantly speeds up the production of greens; without it, you can wait until mid-June for the start of the season. In the north, cucumbers are grown in warm beds in the summer.
| Content:
|

Growing cucumbers in warm beds
Advantages and disadvantages of warm beds
Warm beds have a number of advantages over conventional ones.
- The ability to sow seeds and plant seedlings two weeks ahead of schedule and obtain a very early harvest of finished products.
- The number of feedings is reduced, since a sufficient amount of organic matter has already been added to the planting and will be gradually used throughout the growing season. If manure was added to the garden bed in large quantities, then you can not feed it with organic matter at all, but only add potassium, magnesium and microelements.
- The roots of cucumbers are always warm, so the plants can more easily tolerate unfavorable conditions.
- After harvesting plant residues, there is no need to apply organic fertilizers. Next year, crops that require high soil fertility can be planted here.
- Significant reduction in labor and material costs for growing crops.
Despite all the advantages, warm beds also have significant disadvantages.
- Accumulation of nitrates in green vegetables. This is very difficult to prevent because large amounts of available nitrogen are found in the soil. Increasing doses of potassium and magnesium, as a counterbalance to nitrates, is not the best solution in this case. Under such conditions, they do not completely eliminate nitrate accumulation.
- In a very warm spring, plants may burn. This is especially true for the southern regions.
- Arranging a warm garden bed is not an easy task.
In general, this growing method has more advantages than disadvantages. In summer, cucumbers are not planted in such beds. You can plant greens on it, and closer to autumn, when the summer heat subsides, you can cultivate cucumbers again.
What is a warm bed?
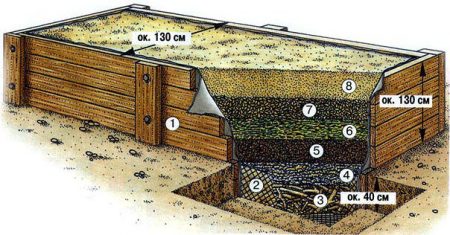
Essentially, this is a layer cake, the main component of which, the “filling” so to speak, is organic matter. In addition to it, the composition includes sawdust, plant and food residues, peat and fertile soil.
Arranging a warm bed
As a result of the chemical reaction between the components, a large amount of heat is released, the soil is always warm, which allows the crop to be planted 15-20 days ahead of schedule.
It is advisable to maintain the sequence of layers:
- wood debris (branches, chips, boards);
- plant residues (various peelings, banana skins, onion peels, etc.), tops, leaves;
- manure or compost;
- fertile land.
But most often, not all components are included in the garden bed. The main component - manure or compost - must be present, as it provides the greatest amount of heat.
Slowly rotting components (sawdust, branches, boards) go to the very bottom. They decompose over several years and the effect of their transformation appears after 3-4 years. What is subject to rapid decomposition (kitchen waste, tops) goes to the middle; rots in 2-3 years. Manure decomposes during the 1st season and goes up.
Thus, different layers begin to release heat over several years, and the exploitation of warm ridges is possible for several seasons even without the addition of manure in subsequent years.
3 types of warm beds
For cucumbers, you can make a sunken, raised, or at ground level bed.
Option 1. sunken bed
Particularly suitable for growing cucumbers in dry regions of the country. Always located below soil level, service life 3-5 years. More suitable for open ground than greenhouses.

Setting up a warm sunken bed for cucumbers.
Advantages.
- Saving time, effort and money.To create such a bed, no additional materials are required.
- It retains moisture better than other types of beds.
- Does not require annual digging.
Flaws.
- During heavy rainfall or intensive watering, it is washed away by water.
- Usually, water stagnates in such beds, and this leads to rotting of the roots.
- Crawling pests easily reach the plants.
- If the structure is made in the shade, then it is not warmed up enough by the sun. Cucumbers will suffer due to poor soil heating.
- Cucumbers suffer greatly from late spring and early summer frosts.
In the middle zone they are practically not used due to their low efficiency in this climate, since cucumbers in such beds often freeze during frosts.
Option 2. raised bed
Suitable for the middle zone and northern regions. It is raised relative to ground level, service life is 3-5 years. Suitable for open ground. In the north, such beds are also built in greenhouses.

Raised beds in open ground.
Advantages.
- Well warmed up by the sun.
- Cucumbers are less likely to suffer from frost.
- The water does not stagnate.
- Convenient to weed and water.
- Crawling soil pests cannot enter the garden bed.
- It can be built in any place that is not suitable for a buried or surface bed.
- With proper care, the harvest of early and late cucumbers is good.
Flaws.
- Requires significant physical and material costs.
- Requires frequent watering as the soil dries out quickly.
- In summer, the soil warms up very much, so when grown in hot weather in summer, cucumbers can burn.
A raised bed is ideal for early and late harvests of cucumbers in northern and central regions.
Option 3. At ground level
The simplest type of warm beds, this option is easy to do with your own hands. Can be used both in the greenhouse and outdoors. The bed is raised 3-5 cm above the ground surface. Service life 1-2 years.

Beds at ground level.
Advantages.
- Very easy and quick to do.
- Does not require investment.
- Good yield of cucumbers.
- In the cold summer in the middle zone, cucumbers grow well in such beds.
Flaws.
- When watering and raining, the edges of the bed are washed away, causing it to lose nutrients.
- Requires edge reinforcement.
- Soil pests freely enter plants.
- It loses its shape very quickly, so it needs to be trimmed or re-done every year.
Most summer residents use just such beds for growing cucumbers and other crops.
Construction of warm beds
All three types of warm beds can be arranged both in the greenhouse and outside.
Recessed warm beds in a greenhouse
If it is done in a greenhouse, then its width corresponds to the width of the greenhouse bed. All greenhouse ridges have sides on the sides, so to place the insulation, soil from the ridges is selected at a depth of 50-60 cm (2 shovels).

We make a warm bed in a greenhouse.
- The greenhouse usually has very good drainage, so branches and sawdust are not used. Kitchen waste - leaves, husks, tops - is immediately poured into the bottom.
- The next layer is organic matter - humus, compost or manure. You can also apply fresh manure (except chicken manure) under the cucumbers, but it generates a lot of heat and such a bed is prepared in the fall.
- If fresh manure is introduced, then it is covered with a 7-10 cm layer of soil on top. If compost or half-rotted manure is used, it is mixed with the soil and is not incorporated into the soil.
- The finished beds are watered with hot water and covered with black film.Boiling water starts the fermentation process, as a result of which a large amount of heat is released.
- After 2-3 days in You can plant cucumbers in the greenhouse.
Warm ridges in open ground
The process of arranging ridges on the street is slightly different from the greenhouse version.
- Dig a trench 60 cm deep and 1.5-1.8 m wide. The width should not be too large, since wide ridges make it difficult to care for cucumbers.
- Branches, boards, and sawdust are laid at the bottom of the trench. These materials create excellent drainage, preventing water from stagnating in the borage. The height of the layer is about 20 cm, but if the soil on the site is sandy, then it is made 10 cm.
- Next comes a layer of plant residues: leaves, straw, hay, and tops are covered. This layer should be 10 cm.
- Then everything is covered with compost or manure with a layer of 10 cm.
- The biofuel is covered with earth on top. The bed should be buried 7-10 cm into the ground.
- The finished “pie” is carefully poured with boiling water and covered with black film.
Cucumbers can be planted after 5-7 days.
Raised ridges
Their construction is the same both in the greenhouse and on the street.
- First, a box is assembled from scrap materials (boards, slate, pipes, etc.). The width of the box is no more than 1.5 m, the height is from 30 to 100 cm. Usually the box is made 60-80 cm high. Such a bed is easier to care for than a very high or low one.
- A layer of plant residues is immediately laid out at the bottom of the box. Wooden materials are used only in the case of clay soil on ridges no more than 35 cm high.
- Apply manure or compost.
- The top is covered with earth.
- Water the ridges with hot water and cover with film.
- After 4-6 days, the beds are ready for sowing cucumber seeds.
The largest layer should be a layer of plant and kitchen residues. The thickness of the manure layer should not exceed 10-12 cm. If there is a lot of manure, too much heat will be generated and the cucumbers will burn. The top layer of soil should be about 10 cm, then it warms up fairly evenly.

Warm beds in open ground.
Such ridges are the warmest. They can be used for a long time, but it is undesirable to dig up and mix manure with soil, otherwise their service life will be reduced.
Ridges at ground level
These are the most common ridges for growing cucumbers. It is very easy to build.
- Mark the size of the future borage. The width of such ridges should not exceed 1 m.
- The earth is dug up on the bayonet of a shovel.
- Apply 1 bucket of manure and 2 buckets of compost per 1 m onto the dug up ground.2.
- The organic matter is leveled with a rake. The soil is no longer dug up, since it is impossible to mix and cover biofuel with soil on such ridges. When repeated digging and mixing of layers, the heat generation is greatly reduced and the effect of the ridges disappears. There are no plant residues that generate additional heat, so the soil warms up more slowly than in other types of warm ridges.
- The finished bed is watered with hot water and covered with film.
Cucumbers can be planted after 7-10 days.
Warm beds without manure
If there is no manure, no compost, no straw, no sawdust at the dacha, then a warm bed can be made from plant residues and kitchen waste. They can be either raised or recessed. Surface ridges cannot be made this way.
- The box or trench is filled with plant and kitchen scraps.
- The layers are carefully compacted or, if possible, compressed. Otherwise, when watering, the grass will settle and the roots of the cucumbers will end up on the surface of the soil. And this most often leads to the death of plants.
- The grass is covered with a 10 cm layer of soil on top.
- Pour hot water over and cover with film.
- Since such beds warm up more slowly than manure beds, cucumbers are planted after 10 days.
Grass beds are suitable for late summer and autumn cucumber harvests. They are also suitable for early planting, but in early spring there is nowhere to get such an amount of grass, and there is not enough kitchen waste to arrange it. To obtain early cucumbers, they can be used from the 2nd year.
Time frame for the construction of warm ridges
All preparatory work - digging trenches and putting together a frame - is best done in the fall. At this time, the main dacha concerns have already moved away, and attention can be paid to other matters. It is advisable to fill finished structures immediately before planting cucumbers, that is, in early spring. But some people have been stuffing them since the fall. You can do this, but in the spring you need careful and abundant watering with boiling water to start the fermentation processes and release heat. In open ground in spring, watering is carried out twice.
If warm ridges remain from last year, then they are also poured with boiling water and covered with black film. The process of the beginning of heat release and soil warming is determined by touch. The soil in the garden bed should be warm, unlike the rest of the soil, which has not yet warmed up.

Various options for warm beds.
Cucumbers are grown using biofuel in the same way as in a regular garden bed. A special feature is the reduction in the rate and amount of organic fertilizing, and if a sufficient amount of manure is applied, then organic fertilizing is not done at all. The application of mineral fertilizers, which include microelements, remains unchanged - once every 7-10 days.
Continuation of the topic:
- How to grow cucumbers on a windowsill in winter.
- The most common diseases of cucumbers and their treatment
- How to deal with cucumber pests
- How and why to shape cucumbers
- Growing bell peppers indoors

 (6 ratings, average: 4,67 out of 5)
(6 ratings, average: 4,67 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.