| Content:
|
Pruning raspberries is both simple and difficult at the same time. To prune raspberries correctly, you need to know the plant’s development cycle.
Raspberry life cycle
Regular raspberry varieties are grown in a two-year cycle. In the first year the shoot grows, in the second it bears fruit, after which it dies.
Remontant varieties can produce two harvests per year. They can be grown in either a biennial or annual cycle. It all depends on the wishes of the summer resident and the climate. Pruning of these raspberry varieties depends on the cycle in which they are grown.
|
This is what young and last year's raspberry shoots look like |
Don't forget to read:
Pruning goals
Pruning raspberries is aimed at removing dead, frail, diseased shoots and excess root growth. When carried out correctly, conditions are created for the normal formation of the bush, which leads to increased productivity.
Pruning purposes:
- Removing fruit-bearing shoots. After fruiting, the shoots of the second year of life dry out. So that they do not interfere with the development of young shoots, they are cut out immediately after fruiting.
- Thinning bushes. Raspberries produce a lot of shoots, which thicken the bush. Therefore, excess shoots are cut out.
- Disease prevention and pest protection. Various pests (not only raspberries, but also other crops) live and overwinter in dense bushes and on old dried branches. And under fallen leaves, spores of pathogens that cause plant diseases persist.
- Improving the quality of the crop and its quantity. Proper pruning improves fruiting, increases the size of berries and improves their taste.
And from the point of view of caring for the crop, it is easier to process and harvest when there is no thickening and dry branches.
Pruning depending on the growing method
Raspberries are grown in two ways:
- ribbon, when the bushes are planted in one line; More often, crops are grown in this way along the fence and along the boundaries of the site;
- clump, when raspberries form small groups, often of irregular shape.
|
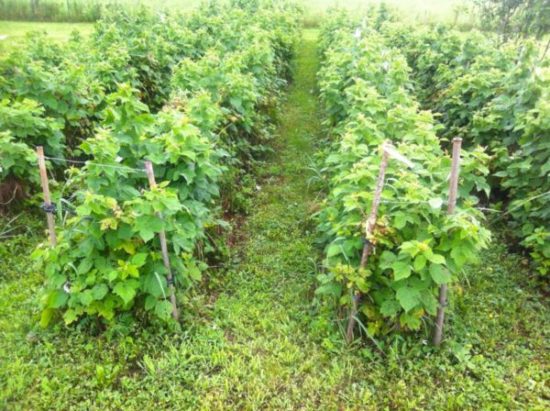
If the rows are not thickened, then the raspberry yield is higher and the berries are larger. Conversely, in dense rows the yield decreases and the berries become smaller. |
Most often, raspberries are grown in dachas in rows. In this case, as few shoots as possible are left, but so that they replace fruit-bearing branches. Replacement shoots are left at a distance of 5-7 cm from each other. They begin to cut them when they reach a height of 20-30 cm. The strongest ones are left. As a result, after harvesting, 4-5 shoots remain in the bush. Fruit-bearing branches are cut out without leaving stumps.
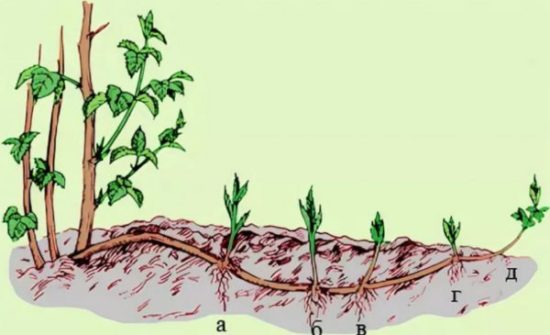
Root shoots, if needed, are left at a distance of 50-100 cm from the mother plant. The shoots located too close are cut out so that they do not thicken the plot, and those that are far away, as a rule, extend beyond the plot and grow in beds or on paths. They not only cut it out, but also cut off the roots extending from the mother plant so that it does not spread beyond the raspberry tree.
|
Replacement shoots differ from root shoots in that they grow directly in the bush next to the old branches, while shoots are formed on horizontal roots, at a distance from the main bush from 20-30 cm to 3 m. |
At Curtain When growing in a bush, 9-12 young shoots are left annually, cutting out all the rest. Young plants in the first 2-3 years do not produce such a number of replacement shoots, so 2-3 shoots are left in the first year, 4-5 shoots the next year, etc. until the bush is capable of producing many shoots and shoots. Old fruit-bearing branches are removed annually. In clumps for the winter, 2-4 extra shoots are left as insurance in case the main ones freeze out. In the spring, if all is well, they are removed.
With this method of cultivation, you need to carefully monitor the condition of the plantings, since raspberries in clumps tend to form thickets, as a result of which the berries become very small. They become as small as those of forest raspberries, but at the same time they do not acquire either the taste or aroma of their forest counterpart. On the contrary, in thickened clumps, cultivated raspberries lose their taste.
How to properly prune raspberry seedlings when planting
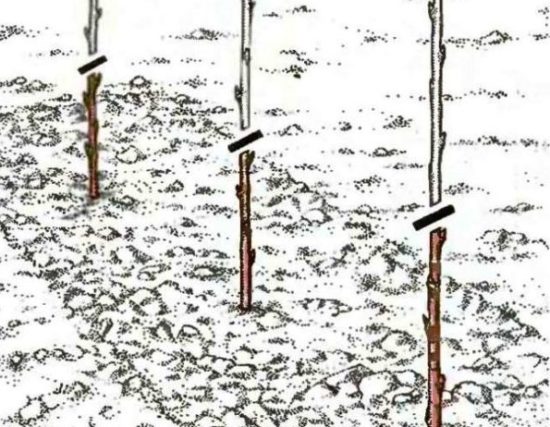
Pruning raspberry seedlings depends on climatic conditions. When planting in autumn, well-ripened seedlings are not pruned. But if they are still semi-green, then cut off the crown by 10-15-25 cm (depending on the height of the seedling and its maturity). The event is held in late autumn, when the air temperature drops to +7°C.
|
When planting raspberry seedlings, you need to cut off the crown, then they are better accepted. |
When planting in spring, the seedling is shortened by 20-25 cm. And if there are several stems, the excess ones are cut to the ground, leaving one of the strongest shoots. Seedlings planted in autumn and spring are also shortened by 15-25 cm. This stimulates stem branching and increases productivity.
Forming and pruning raspberries of traditional varieties
You need to prune raspberries several times a season.The degree and scale of pruning depend on the growth phase and the condition of the plantings.
Spring pruning
Spring pruning of raspberries is carried out during bud break. They inspect the plot. Before pruning, raise the raspberries if they were bent down for the winter, remove the mulch and last year's plant residues.
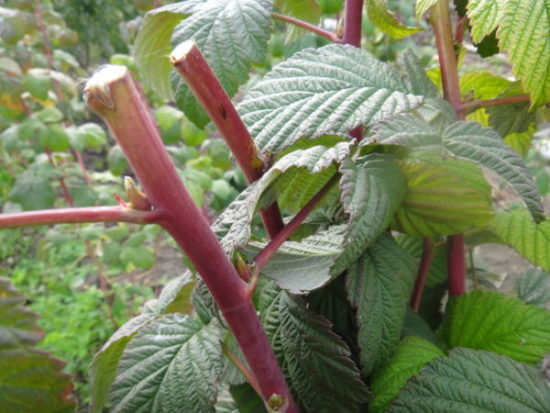
If swelling appears on the branches, they are immediately removed and burned. Frozen, damaged, non-blooming shoots are cut out at the root. Often the tops of raspberries that are not bent down for the winter freeze. In spring they look dry, their buds are either absent or do not bloom. Such tops are cut off to the first living bud.
If the raspberries have overwintered well, then remove the excess safety shoots that were left before the winter. If last summer the tops of the green shoots were pinched, now side branches have grown on each stem. They are also pinched at 15-20 cm. As a result, further branching occurs, and the shoot takes on the appearance of a small standard tree.
After pruning, raspberries are fed with nitrogen fertilizers, manure or humates.
|
Scheme for double pruning raspberries |
How to prune raspberries in spring Video:
Early summer pruning
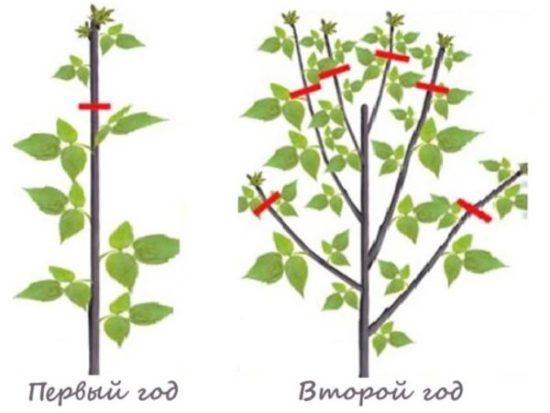
The first summer pruning of raspberries is carried out in late May-early June (in the southern regions, early May). Pruning is carried out only on young shoots. When they reach a height of 0.8-1 m, the top of the head is pinched to 15-25 cm. As a result, branching begins and 1-3 lateral branches grow at the top, which will also bear fruit next year.
|
After trimming the tops of raspberries, side shoots begin to grow from the axils of the leaves. |
Remove frail growth, as well as excess shoots that thicken the plot.On one linear or square meter (depending on how you grow it), 10-12 shoots are left.
How to properly do summer video trimming:
Basic trimming
The main pruning is done in late summer-early autumn. In spring and summer, the event is held as needed.
This pruning is carried out after harvesting, usually in early to mid-August. In the south, deadlines may shift by 1-2 weeks. Fruit-bearing shoots that no longer bear berries are cut out.
The branches that bear fruit have brown bark (young annual shoots are green), there are practically no thorns on them, and in many varieties the leaves begin to turn yellow immediately after fruiting. Old branches break easily (young ones bend easily, but do not break).
Cut the shoots to the ground, leaving no stumps. If they are branched and cling to surrounding branches, then in order not to damage the young shoots, first cut out the upper part of 20-30 cm, and then remove the rest.
|
After harvesting, old shoots are immediately cut out |
Next, the young shoots are examined. If it is normal and well developed, then it is left until autumn. Damaged and diseased branches are cut out. If brown-violet spots suddenly appear on the stems, they are urgently removed and burned. Most likely this is a defeat by gall midges, the most dangerous pest of raspberries, which can destroy the entire plot.
All! This completes the main pruning of the raspberry tree.
After pruning, raspberries are fed with nitrogen fertilizers (urea, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate), infusion of green fertilizer or infusion of manure.
Autumn pruning
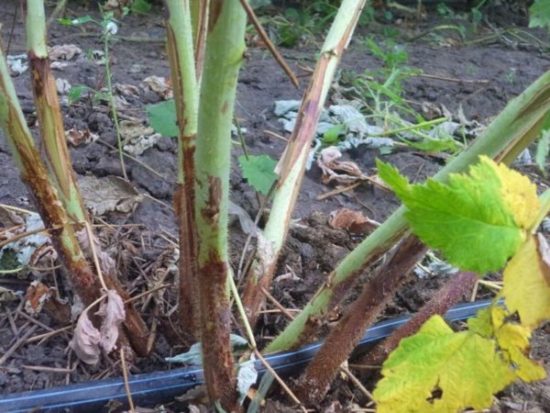
Autumn pruning of raspberries is carried out in early to mid-October. In the southern regions, the deadlines are postponed by 2 weeks. Inspect the young shoots.By winter, the branches ripen and acquire brown-red coloring If the branch has not matured, it remains green. It is cut out because in winter it will freeze anyway. Often the tips of the shoots remain immature. They are cut to the mature part (with brown bark).
|
For the winter, leave 2-3 extra shoots when growing in rows and 3-5 stems when growing in clumps, in case the main ones freeze. Cut out all unnecessary, weak, thin, diseased and immature branches. |
Pruning remontant raspberries
Remontant raspberries produce crops on one-year-old shoots, and if they are left for the next year, they will bear fruit again. But it is impossible to achieve continuous fruiting throughout the season.
Advantages and disadvantages of remontant raspberries
| Advantages | Flaws |
| Fruiting on annual shoots | Not suitable for growing in regions with early onset of cold weather |
| You can get two harvests per season | Often, even in the middle zone, the crop does not have time to fully ripen |
| Fruits when there are no more pests | The taste of the berries is very mediocre, without aroma |
| Sick significantly less | Modern varieties produce few shoots; the entire development cycle is aimed at fruiting. It is difficult to obtain seedlings |
| Does not require chemical treatments against pests and diseases, therefore the harvest is environmentally friendly | More demanding on nutrition, soil and air humidity, heat, lighting |
| Most varieties are low-growing, no more than 1.3 m | |
| The period for obtaining fresh berries is significantly longer (provided that ordinary raspberries are still growing on the site) | |
| The berries hang on the bushes for a long time, do not fall off or rot |
Because of its very mediocre taste, some summer residents refuse to grow it, although the yield of rem is higher.Moreover, not only the autumn harvest has low taste, but also the summer harvest, since due to the rapid growth of the berries, they do not have time to accumulate sugars even under favorable conditions. However, they do not have to be consumed fresh. They are good for processing: for jam, for yoghurts and simply in dry form.
Do not miss:
Growing methods
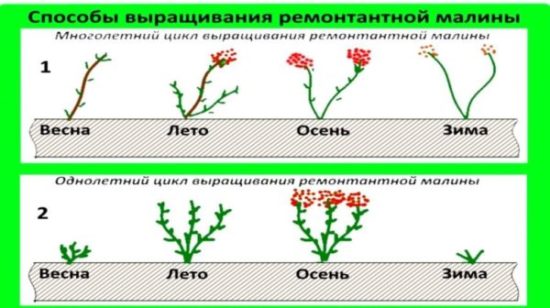
Remontant raspberries are grown in both annual and biennial cycles.
- With an annual crop, the harvest ripens in late summer-early autumn. This method is unacceptable for regions with early and cool autumn, since the berries do not have time to ripen, the raspberries go into winter with green fruits and freeze (however, this is not so scary, since only the root system of remontants overwinters). Growing in an annual cycle is well suited for the southern regions, where the autumn is long and warm. The harvest has time to fully ripen, and the crop can be properly prepared for winter.
- In a two-year cycle, fruiting occurs both in summer and autumn, on both annual and biennial shoots. Raspberries produce a decent harvest, but autumn fruiting occurs somewhat later. In a two-year cycle, rhemas are grown only in the south.
In an annual crop, rhema can be grown slightly further north than in a two-year crop. This is due to the fact that fruiting in the annual cycle occurs somewhat earlier and most of the crop has time to ripen. The shorter the variety, the earlier it begins to bear fruit.
|
Second harvest of remontant raspberries |
Pruning remontant raspberries for a one-year growing cycle
After planting in the spring, the tops of the rem are pinched, as a result it branches and the yield increases.But in the central regions, pinching is not done, since branching also takes some time, and the timing of fruiting shifts. And this is unacceptable, since the harvest does not have time to ripen.
They normalize the growth, cutting out the excess so that the plot does not thicken. Remontant raspberries do not produce very many replacement shoots, but they still exist. And since they are not needed in the one-year cycle, they are cut out. In the fall, after harvesting, remontant raspberries are pruned at the root.
During the winter, the annual cycle rhems do not have any shoots left. Only the root overwinters! This eliminates the problem of winter hardiness of the crop; there is nothing to freeze out.
In the spring, young shoots grow from the root and the cycle repeats.
|
When growing remontant raspberries for 1 harvest, all shoots are cut off at the root and in winter the bed remains completely empty. Just stumps. |
In regions with little snowy winters, annual fruit-bearing shoots are not pruned in the fall, but rather done in early spring. A technique is used to retain snow and prevent freezing of the root system.
Also, shoots are cut out in spring in regions with warm winters. Because if you remove fruit-bearing branches before the top layer of soil freezes, rhemes may begin to germinate, which will have a very adverse effect on their winter hardiness.
Pruning remontant raspberries for 1 and 2 harvests:
What is a two-year cycle of growing remontant raspberries?
A two-year cycle means that you can get two harvests per season: the first is summer, as on ordinary raspberries on the shoots of the second year, the second is autumn on the green shoots of this year. But this method is used only in the south. Summer fruiting weakens the crop and delays the start of ripening of the autumn harvest.
In the central regions, the autumn harvest does not ripen at all under such conditions.
It is more advisable to grow rems only as an annual crop for fruiting in late August-early September, and obtain a summer harvest from traditional varieties.
Also, it should be taken into account that closer to autumn the amount of precipitation increases and humidity rises in most regions. In the middle zone this is almost imperceptible, but in the south the autumn harvest is much larger than the summer one.
Don't forget to read:
Pruning remontant raspberries of a two-year cycle
Pruning remontant raspberries when grown for 2 harvests, it is very similar to pruning regular raspberries. After the annual shoots bear fruit, they are left for the winter. In the spring, the tops of overwintered shoots are cut off. As a result, they begin to produce side branches (laterals), on which the summer harvest ripens in July.
Simultaneously with summer fruiting, young shoots and replacement shoots grow. After harvesting, cut out the old branches and thin out the root shoots, leaving 7-9 shoots per 1 linear meter. They will produce the fall harvest in September. After fruiting, they are either left as is for the winter or the tops of the shoots are cut off by 10-20 cm in the fall. Then the cycle is repeated.
|
Scheme for pruning remontant raspberries for 1 and 2 harvests |
It should be remembered that in a two-year cycle, the autumn harvest ripens 2 weeks later (in the middle zone at the end of September), does not have time to fully ripen and dies. In addition, it is less than the summer one and less than what it could be when raspberries are grown in an annual cycle.
Feeding remontant raspberries for a two-year cycle
Since the yield of rem is higher than that of ordinary raspberries, they tolerate more nutrients compared to traditional varieties. And when grown in a two-year cycle, the removal of substances increases 3-4 times. In order to somehow compensate for the deficiency of elements, raspberries are fed after the summer harvest. Most of all, it needs nitrogen, so organic matter (preferably in liquid form) or nitrogen fertilizers are added. Consumption rate of manure infusion 4 l/m2, nitrogen fertilizers 3-5 l per m2.
Conclusion
Raspberry pruning is a must. Without it, culture grows wild, thickens and becomes smaller. But you need to understand when, how and what kind of pruning to do. Activities carried out incorrectly, without understanding the timing and cycle of cultural development, will not bring the desired effect.









 CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.