Raspberries don't have many diseases. Previously, apart from various chloroses, the crop suffered from few diseases. But in recent years, diseases that previously did not appear every season occur annually.
The main diseases of raspberries are anthracnose, purple spot, and rust. Gray rot is spreading more and more.
|
The higher the agricultural technology, the fewer diseases! |
Raspberry diseases and methods of treating them
| Content:
|
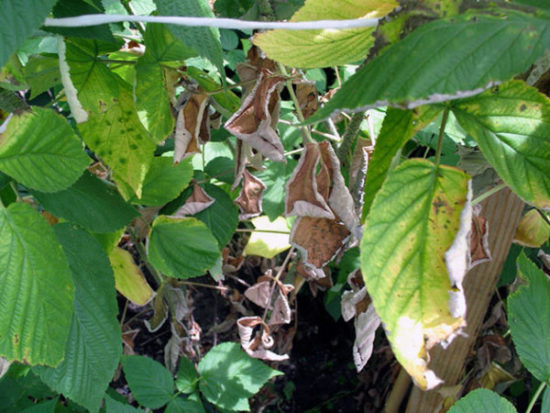
Anthracnose
The most common disease of raspberries. It causes the greatest damage in wet years and in dense plantations. It also spreads in thinned plantings, but more slowly. Without taking protective measures, it can affect a significant part of the bushes. Also, in the middle zone there is a surge in the disease in years with mild winters with frequent thaws.
Description of the pathogen. The causative agent is a pathogenic fungus. Affects stems, leaves and petioles. Preserves on damaged bark and plant debris.
Signs of the disease
The first signs of the disease appear immediately after flowering. On the growing shoots of this year, single spots of gray-white color with a wide purple border appear. Over time, the spots merge and darken. Longitudinal ulcerated stripes of gray color with or without a border are formed. The bark in the affected area dries out and becomes covered with a network of small cracks, and later begins to peel off in separate sections.
In autumn, the bark on the young shoot becomes light gray, and brown spots with blurry edges appear on it. Diseased shoots gradually begin to dry out, the tops droop, and the leaves wither. Such shoots are unsuitable for fruiting next year.
|
The disease begins to appear immediately after raspberry blossoms. |
When leaves are damaged, light small spots with a red-brown border appear on them, located along the veins. Light bordered spots appear on the petioles, pressed into the tissue. The affected tissue on both the leaves and petioles gradually dries out and cracks.
Currently, anthracnose has become much more common on berries than before. Gray-blue spots appear on the fruits, the berries dry out. Mature fruits are separated from the fruit stem along the drupes; severely affected ones are not separated at all. The berries dry out and fall off along with the stalk.
Anthracnose of berries is especially common on remontant raspberries.
How to treat the disease
Fighting anthracnose is easy in hot and dry summers and very difficult in wet and rainy weather.
- Good results are obtained by treating raspberries twice with copper-containing preparations: HOM, Ordan, Oxyx, etc. The treatment is carried out 2 times: before flowering and immediately after it. In hot summers, you can get by with one early spring “blue” treatment. Preparations containing copper sulfate (Bordeaux mixture, Kuproxate, etc.) are somewhat less effective. These preparations are applied three times: before flowering, after picking berries and in the fall (after flowering, raspberries are not sprayed, since copper sulfate is toxic and can remain in the berries).
- Speed Very effective against this disease. Treat 2 times: before and after flowering. The interval between treatments is at least 14 days. When using the drug, even in rainy summers, the disease does not spread.
- Angle. Raspberries are treated for disease before and after flowering and in the fall.
All drugs are quite effective and allow you to completely get rid of the disease in dry summers, and in rainy summers - to significantly reduce its spread and keep it under strict control.
|
Light spots on raspberry leaves indicate anthracnose disease of the plant. |
Mistakes when fighting anthracnose
- The main mistake is that the raspberry plantation is processed in dense plantings.Pesticides do not reach the most difficult places where the pathogen persists. Therefore, first they cut out all diseased, broken and extra shoots, thin out the raspberries, and only then spray them.
- In the southern regions, raspberries and grapes cannot be placed together, since if one of the crops is affected, the disease will certainly spread to the second.
Disease prevention
Cleaning up plant residues. Planting only proven planting material. Timely thinning of plantings, cutting and burning of diseased shoots.
|
When raspberries are infected with anthracnose, the berries dry out and crumble |
Modern raspberry varieties are much more resistant to the disease.
These include red-fruited: Balm, Companion, Creed, Illusion, Sun, Ruby, etc. Of the old red varieties, Barnaulskaya is very stable.
From yellow-fruited plants: Yellow Spirina, Yellow Pineapple, Yellow Giant.
From black-fruited varieties: Cumberland, New Logan.
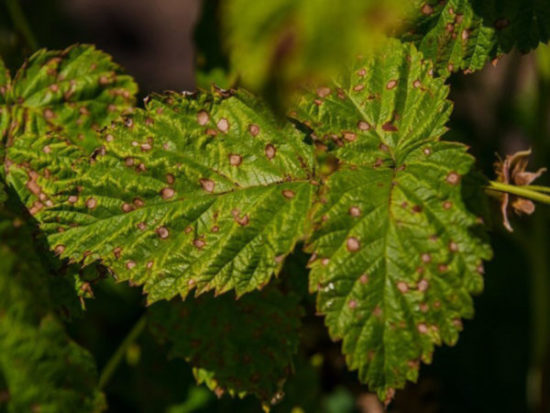
Purple spot or Didimella
The disease is spread very unevenly across Russia. The regions of Siberia suffer the most from it. When widespread, purple spot damages up to 30% of plantings. It is rare in the European part of the country. Remontant varieties suffer more than regular raspberries.
Pathogen - pathogenic fungus. Affects stems and leaves. Preserved in soil, bark and plant debris.
Signs of the disease
Annual growing shoots are affected. Small purple spots appear at the base of the stems and where the petioles attach. They quickly increase in size, spread upward and to the sides, and ring the stem. The affected stem dries out and the bark cracks.The disease penetrates deep into the stem, affecting the cambium and wood. Because of this, the stems become brittle and break easily.
|
The disease penetrates deep into the stem, affecting the cambium and wood. Because of this, the stems become brittle and break easily. |
Brown spots with a yellow border of irregular triangular shape appear on the leaves. They are located along the edge of the sheet.
On annual shoots, the infection appears in early June. On the shoots of the second year it appears in the spring. The buds on the stems do not bloom, and it dries out, starting from the top.
Purple spotting is often confused with gall midge infestation. Purple spots also appear at the site where the larva penetrates the stem and at the site of its feeding, which can easily be confused with Didimella. But, if this is a gall midge infection, then the surface will be uneven, there will be thickenings, compactions, and ridges, whereas with a fungal infection, the affected surface will be smooth.
Control measures
Copper preparations significantly reduce the spread of the disease. Treatment of raspberries against disease is carried out 3 times: early in the spring before the leaves bloom, after harvesting and in the fall.
Preparations based on propiconazole are also used (Prognoz, Profi, Agrolekar, etc.). Raspberries are sprayed at the same time as with copper-containing pesticides.
Didimella is very stubborn; it can be completely cured with chemicals. difficult means. But you can keep it under control.
Folk remedies to fight the disease
The method is very old, but extremely effective. Suitable only for traditional raspberries on a two-year cycle. Not suitable for remontant varieties.
The crop should be grown in two plots, the distance between which is at least 30-50 m.Usually in a dacha, semi-shrubs are grown along the edges on both sides of the plot. On one side this year in the spring, all raspberry stems are completely cut out at the root. There are no stems left on the plot and, accordingly, no harvest. Raspberries produce only young shoots that grow all summer. In the fall, cut out all the excess growth that thickens the plot.

Didimella on raspberry leaves |
On the other side of the site, all growing young shoots are cut down to the ground. All the energy of the raspberry is spent on forming the crop; the shoots are not allowed to develop. In the fall, all fruit-bearing shoots are completely cut out. Only the root system goes away before winter. The soil is mulched with manure or peat manure crumbs to a depth of 5-7 cm.
The next year, on one side of the plot, the raspberries bear fruit, but the shoots are cut out. On the other side, shoots grow that will produce a harvest next year.
This method allows you to get rid of many crop diseases, including purple spot, anthracnose, rust, etc.
Prevention
Planting relatively resistant varieties: Vera, Barnaulskaya, Amurchanka's Daughter, Kirzhach, Kolokolchik. They are only slightly affected. There are no absolutely resistant varieties.
The Prelest variety is very susceptible to purple spotting.
The remaining methods of prevention are traditional: removing plant debris, removing diseased shoots, thinning the plot.
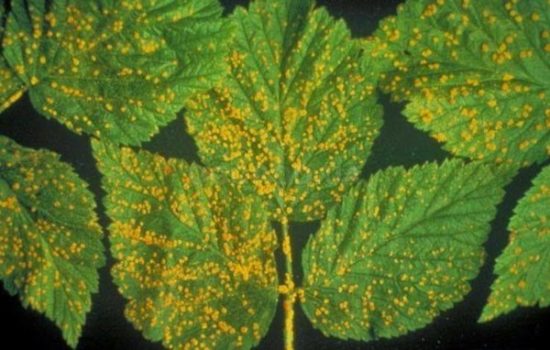
Rust
Pathogen - pathogenic fungus. Overwinters on plant debris. Signs of the disease appear in the spring, and then they only increase.
Signs of the disease
Affects leaves and young shoots of the current year. Yellow-orange, small, slightly convex spots appear on the shoots and on the upper side of young leaves.After 2-3 weeks (depending on the weather), orange spots appear on the underside - this is the first summer sporulation of the fungus. At the beginning of autumn, these spots darken on the lower side, and the second (winter) sporulation occurs. Affected leaves drop prematurely.
Ulcers appear on the shoots, which later merge and form cracks. Diseased shoots die.
|
Rust is not that common. Usually wild raspberry thickets are infected with it, and it comes to the site with seedlings brought from the forest. |
Methods for treating rust
Rust is highly treatable.
- With minor damage, Pseudobacterin gives excellent results. Spray when signs of disease appear on the upper and lower sides. You can process raspberries 5 days before harvesting, since the biological product is not dangerous to humans.
- Speed Depending on the degree of damage, 1-3 treatments are done. During the ripening period, treatment is carried out 15-20 days before harvesting the berries. The last treatment is done in September when winter spores of the fungus appear.
- In case of severe damage, the raspberry plant is treated with copper preparations three times.
In autumn, raspberries are mulched with manure.
Folk remedies for rust control
The most popular is to use 3 tbsp soda solution. l. per 10 liters of water and adding liquid soap as an adhesive. Apply when the first signs of the disease appear. If the damage is significant, they proceed to spraying with pesticides.
Prevention
Varieties such as Krasa Rossii, Novosti Kuzmina, Hercules, and Patricia are practically not affected by the disease.
Old varieties that are not resistant to the disease: Vera, Cascade.
Other preventive measures: cleaning up plant debris, removing diseased leaves and shoots, thinning plantings.
Gray rot
In recent years, raspberries have suffered from gray mold more often than before. In warm but damp summers, only the fruits become sick. In cold and rainy summers, the disease can also appear on the leaves.
|
Gray rot on raspberries |
Pathogen - a pathogenic fungus that overwinters in the ground and on plant debris. It affects not only raspberries, but also strawberries, pears, apple trees, cucumbers, eggplants, etc.
Signs of the disease
Gray-brown spots appear on the berries, which very quickly spread throughout the entire berry. It dries out and becomes covered with a gray fluffy cottony coating. In high humidity, the berries rot, and in drought they mummify.
It appears on leaves very rarely in very rainy and cold summers. Gray spots with a fluffy cotton coating appear. Mainly the lower leaves are affected. They are selectively affected.
How to treat the disease
Pesticides are alternated because the pathogen quickly develops resistance to the chemicals.
- The most effective drug is Euparen. When using it, raspberries practically do not get sick. It cannot be mixed with other pesticides. The period of protective action in the absence of precipitation is 10-14 days. During the season, 2-3 treatments can be carried out, the last one 15-20 days before harvest.
- Speed Spraying before and after flowering with an interval of no more than 14 days.
- Pollination by fluff after the petals fall. Raspberries are processed in dry weather.
- Copper-containing drugs. Ineffective, but still reduces the incidence of bushes. Treatment is carried out in early spring with “blue” spraying of the garden, as well as immediately after flowering.
- Biological products Alirin B or Planriz. Raspberries are treated immediately after flowering. When the prevalence is low, they do well.
|
Gray mold is a persistent disease. It will not be possible to cure it completely. When the first signs appear, even on other crops, treatment is immediately carried out, not only for raspberries, but also for all plants susceptible to the disease. No folk remedies are inappropriate here. |
Prevention
Treatment of raspberry plantations with Fitosporin every 7-10 days throughout the growing season. Cleaning up plant residues. Collecting and burning diseased berries.
You cannot pick wet berries; they are not stored even for a short time and are immediately affected by gray rot.
Raspberry Curl
Symptoms appear on shoots of the second year. There are no signs of disease on this year's shoots. Remontant varieties get sick less often.
Pathogen - Raspberry ringspot virus. It gets into areas with contaminated planting material. Spread by insects feeding on leaf sap.
|
Raspberry Curl |
Signs of the disease
The leaves acquire a dark green color, become hard, wrinkled, and their edges curl downward. By autumn, the leaves turn bronze and the veins become glassy. On the affected shoots, even before signs appear on the leaves, the flowers are deformed, do not set, and if they do set, the berries are small, sour, and dry. The shoots are shortened, their tops dry out for no apparent reason.
Ways to fight
There are no chemical treatments for the disease. Diseased bushes are dug up and burned. Control of raspberry pests, spraying of plantings with insecticides during the period of their activity.
Physiological chlorosis of leaves
Raspberry condition associated with unfavorable weather conditions or lack of nutrients. Not a disease!
Leaf chlorosis is often confused with various diseases and pesticides are used. But if you are not sure that this is a disease, you need to take a closer look at the manifestations. If there are no convex or depressed spots with a border, the leaves do not dry out or wither, then the first step is to carry out agrotechnical measures. If they do not help, and signs of illness appear, then chemicals are used.
Chlorosis occurs for various reasons:
- high soil moisture combined with cool weather;
- highly alkaline soil reaction;
- highly acidic soils;
- watering with cold water;
- lack of nitrogen or magnesium.
When the cause is eliminated, chlorosis also disappears.
Control measures
With high soil moisture and incessant rains, the soil under the plantings is regularly loosened. If necessary, drainage grooves are made.
Strongly alkaline and strongly acidic soil reaction. To quickly bring the pH to an acceptable value, the subshrub is watered with peat extract (in alkaline soil) and physiologically acidic fertilizers are applied: urea, ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate, ammophos, superphosphate. For acidic soil, water with ash extract, lime milk, add lime, and use fertilizers with an alkaline reaction: sodium, potassium and calcium nitrate.
|
Raspberry leaf chlorosis is often confused with the disease |
Watering with cold water. Raspberries should only be watered with warm water heated by the sun. If this is not possible, water with settled water, and not with water fresh from the well.
Lack of nitrogen. Raspberries are nitrophilic and need a lot of nitrogen. With its deficiency, the leaves become smaller and become light green with a yellowish tint.Fertilize with nitrogen fertilizers or manure.
For magnesium deficiency the leaves begin to turn yellow from the middle to the edges. They fertilize with Kalimag.
Don't forget to read:
Technology for planting and caring for raspberries in a summer cottage ⇒
Conclusion
Raspberries are quite resistant to diseases, and they do not get sick every summer. But if the disease appears, then it will be for the next few years. It is difficult to completely cure a culture; one disease is replaced by another. Therefore, it is necessary to initially carry out preventive measures and monitor the quality of planting material, since almost all diseases appear initially with seedlings.










 (3 ratings, average: 4,67 out of 5)
(3 ratings, average: 4,67 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.