Diseases in culture are visible and invisible. Almost all types of cabbage suffer from the same pathogens with a few exceptions. Other cruciferous crops also suffer damage from these harmful objects. This article talks about the main diseases of cabbage and how to treat them.
|
It is easier to prevent any diseases than to spend a long and tedious time treating them. |
Spread of cabbage diseases
Cabbage diseases have a clear geographical distribution. In the north and in the middle zone, the culture is severely affected by clubroot. Phomasis is widespread in the Far East and Siberia, as well as in some areas of the Volga region. In the southern and southeastern regions, cruciferous crops suffer from fusarium. Other diseases are found in all regions.
| Content:
|
Treating clubroot on cabbage
A very widespread disease of cruciferous crops. It affects all types of cabbage, but is extremely rare on Brussels sprouts. Brussels sprouts become infected with clubroot only in highly acidic soils. Also, the disease causes great damage to radishes, turnips, turnips and mustard.
The harmfulness is very high: late and mid-season varieties do not set heads of cabbage, early ones form a loose, small head of cabbage. If the infection is severe, the cabbage dies.
Description of the disease
The causative agent is a pathogenic fungus that persists in the soil for up to 15 years. Initially, the pathogen parasitizes in root hairs, and later in the bark of plant roots. The fungus gets from the soil into plants through root hairs, where it stays for some time. As a result of its vital activity, growths are formed on the roots, which are destroyed under the influence of bacteria and a huge number of zoospores of the pathogen enter the soil.
|
Zoospores do not require a period of rest and germinate in the soil, and once again entering the plant, they continue their destructive activity. |
In open ground, the disease spreads through water currents, soil insects, earthworms, and also through the manure of animals that have fed on affected plants.
Favorable conditions. The disease develops quickly at a temperature of 20-25°C, humidity 75-90% and soil acidity less than 6.5. The development of the pathogen slows down at temperatures below 18°C, and at temperatures below 15°C it completely stops. The development of the disease also stops when soil moisture is below 50% or more than 98%. In addition to cultivated plants of the Brassica family, it also affects its wild representatives: shepherd's purse, rapeseed, and jarutka.
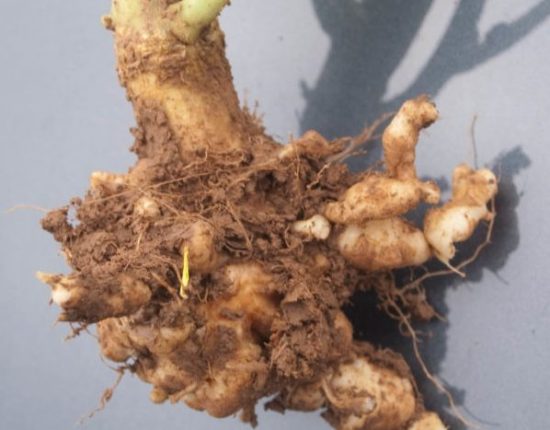
Signs of cabbage being affected by clubroot
Cabbage can get sick even at the seedling stage, but this does not appear outwardly. The seedlings look healthy and well developed. Young plants get sick when using contaminated soil. When seedlings are infected, heads of cabbage do not form.
Plants can also get sick in open ground when they are mature. They begin to lag behind in growth, practically no new leaves are formed, and the heads of cabbage are very loose.
At whatever stage the infection occurs, ugly swellings and growths form on the roots. Plants are severely stunted in growth, the leaves acquire a yellowish tint.
|
Gradually, the growths are destroyed and rot, and the supply of water and nutrients to the above-ground part is disrupted. The affected plant dies. |
The main symptom of clubroot is the wilting of the lower leaves in the heat despite sufficient watering. If the cabbage is sick, this sign appears long before the head of cabbage forms.
Methods to combat clubroot
Clubroot does not develop on neutral and alkaline soils, so the main measure of both control and prevention is soil liming.
If the cabbage has already been planted in a permanent place, then on slightly acidic soils it is watered with lime milk once every 2 weeks (2/3 - 1 cup of dolomite flour per 10 liters of water). If the pH is below 5.5, water with lime once a week, especially if clubroot has previously appeared. Instead of milk of lime, you can use an infusion of ash (1 glass/10 liters of water).
Maintaining crop rotation. Where there was clubroot (be it cabbage or any other crop from the Cruciferous family), onions, garlic and nightshade crops (tomatoes, potatoes, peppers) are planted in subsequent years. These plants actively suppress clubroot spores, and subsequently there are significantly fewer of them. However, it is better to return the culture to its original place no earlier than after 10 years.
If it is impossible to maintain such a crop rotation on a small plot, then it is better to give up growing cabbage altogether for the next 10 years. You may also have to refrain from sowing radishes and turnips.
If diseased plants are discovered, they are pulled out and immediately burned, and the place where it grew is sprinkled with bleach.
There are currently no chemicals available to treat clubroot.
Disease prevention
Preventive measures include: liming the soil in the fall, using clean soil for seedlings and growing resistant varieties.
Autumn liming of soil for cabbage. The soil for cabbage is limed if its pH is less than 6.5, even for Brussels sprouts, because although they are resistant to clubroot, some specimens can still get sick.
You cannot apply lime and manure at the same time. If it is necessary to do both, then add lime in the fall, and manure in the spring.
|
Lime fertilizers are planted to a depth of 20 cm.Application rates depend on the acidity of the soil and its mechanical composition. |
The speed of action depends on the fertilizer. If you plan to plant cabbage next year, then add fluff. It instantly reduces acidity, but its effect lasts no more than a year. This is what is usually used for cabbage.
Limestone flour reduces acidity for 2 years after application. It is valid for 2-3 years.
The duration of action of dolomite flour is 5 years, but maximum deoxidation is observed starting from the 3rd year.
Lime application rate for soils of various mechanical compositions (kg/100 m2)
| Soil composition | Soil acidity (PH) | ||||
|
4,5 less |
4,6-4,8 | 4,9-5,2 | 5,3-6,0 | 6,1-6,3 | |
| Sandy loam and light loamy | 40 | 35 | 20 | 20 | 35 |
| Medium and heavy loamy | 60 | 55 | 40 | 35 | |
The application rate is always indicated based on ground limestone. To correctly determine the required volume of fertilizer, you need to multiply the dose indicated for ground limestone (see table) by 100 and divide by the percentage of active substance (a.i.) indicated on the package with the fertilizer.
Soils for seedlings. Regardless of whether they are purchased or prepared independently, they must be disinfected. First, pour boiling water over the soil 2 times with an interval of 3 days. Then, 3-4 days before sowing, they spill it with a hot solution of potassium permanganate.
In greenhouses, the soil is usually healthy because the nightshades grown there kill clubroot spores with root secretions. But for your own peace of mind, it is better to flood the greenhouse with boiling water and then a strong solution of potassium permanganate before sowing.
|
If there is nowhere to get boiling water at the dacha in early spring, then watering is done with a very strong burgundy solution of potassium permanganate, and then the bed is spilled with clean water so that the seeds do not burn. |
Cabbage varieties resistant to clubroot
Currently, varieties have been developed that are quite resistant to this disease. From white cabbage varieties:
- late-ripening Kilaton, Ramkila;
- mid-season Tequila, Kilagerb;
- early ripening Kilagreg.
Cauliflower hybrids Clarify and Clapton. From Chinese cabbage there are hybrids Kudesnitsa, Nika, Filippok.
Weeding a cabbage plot is mandatory, especially for cruciferous weeds.
Folk methods of struggle
The main and most effective method is to add ash to the cabbage, both in liquid and dry form.
Checking the ground for clubroot spores. In the spring, early Chinese cabbage is sown on the selected plot. They begin to pull it out with its roots, one plant at a time, from the moment the rosette forms until the head forms. The roots are carefully examined. And if there are no thickenings or growths on any plant, then the soil is free from clubroot spores and any cabbage, as well as other cruciferous vegetables, can be grown on it.
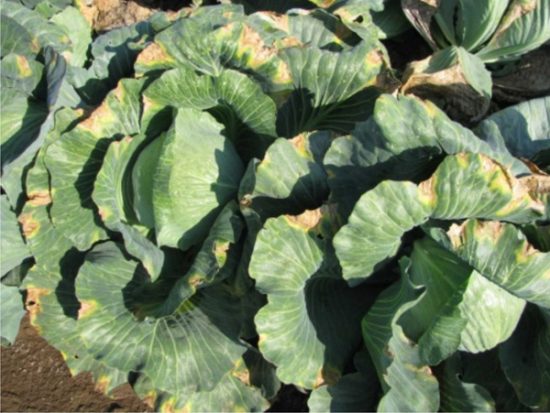
Fomoz (dry rot)
The disease affects cabbage, both adult plants and seeds, and seedlings, as well as turnips, radishes, turnips, and wild cruciferous plants. Phoma develops especially strongly in open ground in damp, hot summers on white cabbage. Other types of cabbage also get sick, but the harmfulness here is less. It is more common in the southern regions of Siberia, in the northern regions - in hot and damp years.
Description of the disease
The causative agent is a pathogenic fungus that overwinters in the soil, on plant debris, and can survive in seeds. It gets inside the plant through microdamages. It is spread by wind, insect pests, with rain and irrigation water, and on gardener's clothing. Can be stored in soil for up to 7 years.
Signs of defeat. On cabbage, the stem and leaves are affected.On seedlings, the disease resembles a “black leg”: the stems are covered with small black spots, black specks appear on the cotyledons and true leaves, and the seedlings die.
The very first sign is the purple-lilac color of the leaves, which is uncharacteristic for the variety, and this is not at all a sign of phosphorus starvation, as in nightshades. The spots appear a little later.
In adult plants, yellow and brown spots with black dots framed by a dark border appear on the leaves; gray spots appear on the stems.
|
15-20 days after the onset of the disease, the lower leaves may fall off. The spots on the stem gradually grow, the tissue is destroyed, it becomes rotten and breaks. |
On the testes, fungal spores enter the seeds and they become unusable. Affected pods become stained and dry out. The diseased queen cell is completely destroyed.
The disease may appear during storage. First, the upper and then the inner leaves become covered with brown spots, the head of cabbage becomes rotten and dries out.
Treatment of the disease
The seedlings cannot be saved. Adult cabbage can be cured at the earliest stage of the disease.
- All diseased plants are removed from the seedlings, the rest are watered with a strong solution of potassium permanganate and the leaves are sprayed with a pink solution. The plants are transferred to a cold room, and the windows or doors in the greenhouse are left open.
- Spraying the crop with Maxim. It is used mainly for treating seeds, but in exceptional cases it can be sprayed on vegetative plants. 20 ml of the drug is dissolved in 1 liter of water and sprayed onto the leaves of the crop. After 7 days, the cabbage is watered with clean water from above so that the remaining preparation does not get into the head of cabbage.
- At an early stage, they are treated with copper-containing preparations.
- Treatment with biological products Trichodermin or Fitolavin.
All treatments are carried out on the leaves and stem. After 7 days, the leaves are washed with water from a hose to remove any remaining chemicals. 2 weeks after the first treatment, spray again. After a week, the plants are also washed.
|
Cabbage affected by Phoma during winter storage. |
There is advice to use sulfur preparations to combat Phoma. They can be used only at the beginning of the growing season, until the harvest is formed. In the second half of the growing season, sulfur is not used, since the smell is partially retained and the products become unsuitable for food.
Prevention of Phomasis
- If the cabbage is sick with Phoma, then cruciferous plants are planted in this area after 5-7 years.
- Disinfection of seeds before sowing in hot water at 45-48°C or in a strong solution of potassium permanganate at the same temperature. You can etch them with the drug Maxim.
- Regular weeding of the plot, both around the perimeter and between the plants. Cruciferous crops are removed especially carefully.
- Growing resistant varieties. There are no completely resistant varieties; there are those that are less affected than others; for white cabbage these are Aggressor, Regent.
Folk remedies
To prevent Phoma, cabbage is sprayed with an infusion of onion peels. 200 g of husk is poured with boiling water, left for 24 hours, filtered and sprayed.
Protecting cabbage from mucous bacteriosis
A bacterial disease that is widespread. It affects many vegetable crops, not only cruciferous ones. The damage from the defeat is significant. Cabbage can get sick at all stages of the growing season, as well as during storage.
Description of the disease
The causative agent is bacteria that persist on plant debris and in water bodies. The pathogen enters the plant through microdamages that occur during plot care and harvesting for storage. It is carried by insects, rain, and irrigation water. Plants get sick especially often against the background of increased doses of nitrogen in fertilizing.
Terms of distribution. It spreads strongly in humid and hot weather (temperature 25-30°C and humidity more than 90%). Particularly favorable conditions arise when there is heavy dew.
Signs of disease on cabbage. The first signs appear during the harvest period. There are two possible onset of the disease.
1st. The outer leaves and the stump at their base rot, become covered with mucus and emit a strong unpleasant odor. Gradually, rot spreads from the covering leaves to the entire head of cabbage, and it completely rots. The affected leaves fall off the stump. When the bacteriosis reaches the stump, it softens and the plant dies.
2nd. The disease begins with a stump, which becomes creamy and then gray in color, softens and breaks. The head of cabbage falls and rots.
|
Bacteriosis on cauliflower |
On cauliflower and broccoli, bacteriosis begins from the stem of the inflorescence or from the upper covering leaves. The lower leaves and petioles do not rot. The head rots completely, but the cabbage itself remains intact. However, it is unsuitable for further cultivation. Plants are pulled out and burned. In very hot and humid weather, rot can spread to the leaf petioles at the base of the stem.
When storing cabbage, the disease appears if the temperature in the storage is too high.
Methods for treating mucous bacteriosis
- Spraying with Phytolavin.The stump is treated especially carefully at the place where the first covering leaves are attached to it.
- Treatment with other biological products: Trichoderma, Pseudobacterin, Gamair, Sporbacterin. Spray from below at the place where the covering leaves attach to the stump.
- In storage, when a disease appears, the temperature is reduced, and the cabbage is sprinkled with biological preparation powder (Trichoderma, Pseudobacterin, etc.) or a thick layer of ash.
If possible, cauliflower should be sprayed where the inflorescences attach to the stem. You may have to break off a few of the top leaves to do this. At the initial stage, the disease on cabbage can be treated well.
Disease prevention
Some varieties of white cabbage are somewhat more resistant to the disease, even with severe damage. These include Amtrak, Ammon, Monarch, Kazachok.
Plots and storage areas must be cleared of plant debris. During the growing season, pest control is carried out. After each rain, the soil on the plot must be loosened.
If sick plants appear, then reduce the dose of nitrogen in the fertilizing, while simultaneously increasing the dose of microelements and potassium.
|
Dusting cabbage with ash to prevent bacteriosis |
Folk remedies
Ash dusting is used. But it is not the upper leaves, head or inflorescence (for cauliflower) that need to be dusted, but the lower part of the stalk and in the places where the lower leaves are attached to it. Instead of ash, you can use tobacco dust.
To prevent the substance from being washed off by rain, add a few drops of liquid soap to it. After dusting, water strictly at the root, being careful not to wash off the protective layer. The dose is repeated every 7 days throughout the growing season.
When storing, it is better to dust with tobacco dust, since it is easier to wash off and does not stain the product.
How is vascular bacteriosis treated?
Affects conducting vessels of all types of cabbage and other cruciferous crops. Distributed everywhere. It can appear at any period of plant development - from seedlings to seed formation. When the disease spreads strongly, the yield is significantly reduced.
|
Yellow spots on cabbage leaves are a sure sign of a disease. |
Description of the disease
The causative agent is bacteria that overwinter on plant residues of cruciferous crops and remain in the seeds. The pathogen remains viable for 2 years.
Favorable conditions. The pathogen actively develops with frequent rains and temperatures of 25-30°C. At 20-22°C, signs of the disease do not appear, but as soon as the temperature rises, the signs appear again. Weather with hot days and cold nights is especially favorable for the development of the disease. In such weather the disease spreads very strongly.
The pathogen enters the plant through microdamage, as well as during heavy rains through the stomata. In open ground it is spread by insects, wind, water, and on the gardener’s clothes.
Signs of the disease
On seedlings, yellowing of the edges of the cotyledon leaves is observed. The plant begins to lag in growth, becomes distorted and eventually dies.
On a mature plant, the first sign is that the edges of the leaves turn yellow and the veins become dark (this is called black reticulation). When cutting a petiole, stem or stump, a darkened vascular ring is visible. The edges of the leaves gradually turn brown and dry, the leaf itself withers and dies. Gradually, the disease affects leaves higher up the stem.As a result, plants are stunted, produce small, loose heads, or have poorly formed heads.
|
During storage, mucous bacteriosis often joins vascular bacteriosis and the crop rots. |
How is the disease treated?
For treatment, cabbage is treated with biological products.
- Spraying the plot with Fitolavin. You can spray cabbage with the same preparation, since the infection often penetrates through the roots.
- Spraying and watering with Trichodermin. But you need to remember that the treatment must be done in warm weather (temperature at least 20°C), since the Trichoderma fungus is inactive in the cold.
- Watering and spraying with Planriz.
The use of traditional fungicides (HOM, Maxim, Previkur, etc.) against bacterial diseases is ineffective, since these drugs do not suppress bacteria.
Prevention
- Treating seeds before planting.
- Thorough cleaning of plant residues.
- Maintaining crop rotation. It is not advisable to grow any other cruciferous crops after cabbage. The return time for cabbage (or other cruciferous crops) to the same place is 2 years.
- Thorough weeding of the plot.
- Removal of wild cruciferous crops within a 100 m radius.
- Pest control.
- In storage facilities, the storage temperature is not allowed to increase.
Prevention of the disease is very effective. Strict implementation of preventive measures allows you to avoid infection.
Traditional methods of treatment
Since the causative agent is bacteria, all kinds of burning substances have a good effect on them.
- 20 drops of brilliant green are diluted in 2 liters of water and sprayed over the cabbage leaves.
- 15 drops of iodine/2 liters of water. Spraying leaves.
- Watering plants with a pink solution of potassium permanganate.
When the first signs of the disease appear, they switch to biological products.
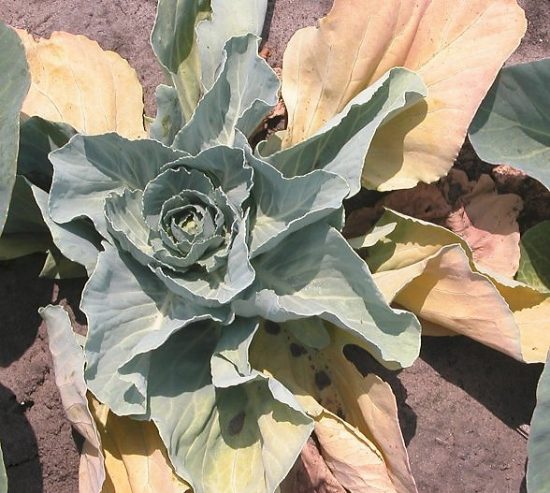
Downy mildew or peronosporosis
The disease mainly affects seedlings, but can also appear in open ground on adult plants. Greenhouse seedlings often get sick. Seedlings grown at home are usually not affected by powdery mildew. The disease also appears on white cabbage in the second year of cultivation (during the formation of seeds). The disease can sometimes appear on individual adult plants, but it does not cause significant harm to them.
|
Pictured is downy mildew or peronosporosis Among the cruciferous vegetables, cabbage and radishes suffer from powdery mildew. |
Description of the disease
The causative agent is a pathogenic fungus that overwinters on plant debris and seeds. Remains viable for 6 years.
Favorable conditions - relatively cool and damp weather. At temperatures above 25°C, the development of the disease stops. Spreads by wind, irrigation and rainwater.
Signs of defeat
On seedlings, blurry yellow spots form on the upper side of the cotyledons and true leaves, and a white coating appears on the lower side, which eventually turns gray. The leaves gradually turn yellow and die. In advanced cases, the mycelium of the parasite penetrates the vascular system of the plant, as a result, darkened vessels are visible on the cut.
If the disease appears during the period of seed formation, it affects the pods and seeds. Gray-brown depressed spots appear on the pods, which gradually turn gray. The pods are puny with underdeveloped seeds. The seeds are unsuitable for use and are destroyed.
After planting in the ground, the disease stops and may even disappear completely, since the cabbage in the garden is much better ventilated.But in wet weather the signs may reappear.
|
On the leaves of adult plants, the spots are reddish-brown on the upper side, and brown with a grayish coating on the lower side. |
How to treat the disease
Cabbage downy mildew is quite persistent, but it can be cured. During the seedling period it causes the greatest damage. Some plants die. At this time, chemicals can be used to combat the disease.
- When the first signs appear, the seedlings are treated with copper-containing preparations (HOM, Oxyx, Ordan, etc.).
- Spraying seedlings with Topaz or Topsin.
- Processing by Revus.
- Pollination of plants with ground sulfur, 5-7 g per m2. Pollination is also carried out on the underside of the leaf.
If downy mildew appears on an adult plant, then it cannot be treated with chemicals. In this case, biological products are used: Trichoderma, Pseudobacterin, Gamair, Vitaplan. Spray the plants on the leaves.
Prevention
All seeds are disinfected before sowing. They are kept in a light pink solution of potassium permanganate, the temperature of which is 50°C for 30 minutes, then washed with clean water.
The greenhouse maintains normal humidity and is ventilated regularly.
Maintaining crop rotation.
Folk remedies
Treatment with a pink solution of potassium permanganate.
Pollination of seedlings and adult plants with ash at the rate of 50 g/m2. Pollination is carried out from both the upper and lower sides. Re-pollinate the cabbage after 7 days.
Fighting fusarium
The disease is highly prevalent in the south and southeast of the country. It is practically not found in the northern regions. It affects seedlings and newly planted plants. Fusarium is very dangerous. The death of seedlings reaches 20-30%.
|
Cabbage infected with fusarium |
Description of the disease
The causative agent is a pathogenic fungus that persists in the soil and on plant debris for 3-5 years. Penetrates into the plant through microdamages on the roots, spreads through conductive vessels and interferes with the flow of water and nutrients in the plant.
Favorable conditions. Hot weather with sharp fluctuations in humidity contributes to the spread of the disease. Sharp changes between day and night temperatures are especially favorable for the progression of the pathogen. The optimal soil temperature for the development of the fungus is 18-22°C.
Signs of disease on cabbage
In seedlings or newly planted plants, the leaves become yellow-green and wilt. Yellowness can spread to the entire leaf, or maybe only to part of it. As a result, the leaf grows unevenly: growth in the green zone is stronger than in the yellow zone.
A cross section of the petiole shows a bunch of affected brown vessels. The plant withers over time and the affected leaves fall off. If the disease continues until the formation of heads of cabbage, then the covering leaves may completely fall off and only one small bare head of cabbage remains on the stump.
|
Very often, with fusarium, one-sided yellowing of the leaves is observed, on the other side they are normal. When the disease spreads severely, the cabbage dies. |
Treatment of fusarium
It is very difficult to cope with fusarium. You can temporarily stop the development of the disease.
- In the earliest period of development of the disease, biological products Baktofit and Pseudobacterin are used for treatment. Water at the roots every 7-10 days.
- Watering with Previkur Energy. Treatment is carried out once every 7 days.
- Bayleton. Spray seedlings and newly planted plants.When forming a crop, you cannot spray cabbage.
- Maksim. Seedlings and young plants are sprayed and watered at the root. When the crop is set, only watering is carried out.
Severely wilted plants are pulled out and burned; it is useless to treat them.
Prevention
- Optimization of the irrigation regime. You cannot first dry out the soil and then immediately pour in a large amount of water; this is the most favorable condition for the development of fusarium. Uniform watering is the best prevention.
- To increase the crop's resistance to all diseases, including fusarium, young plants are sprayed with Immunocytitis.
- Growing resistant varieties. Now there are a lot of them.
- White cabbage: Kilagerb, Kilajek, Cambria, Doubler, Decurion, Devotor, Tacoma, Amon, Zenith, Paradox, Valentina, Kolobok, Krumont.
- Colored: Alpha, Guarantee, Moscow Cannery.
- Broccoli: Fiesta.
- Brussels: Franklin.
- Kohlrabi: Vienna white 1350.
Crop rotation as a preventive measure is ineffective, since the disease affects many garden and wild plants.
Folk remedies
For preventive purposes, water the crop with a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
These are the main diseases of cabbage. Outdoor crops are also affected by other diseases, but they are not so common.















 (13 ratings, average: 4,23 out of 5)
(13 ratings, average: 4,23 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.