Article from the section “Calendar of work for a gardener, gardener, florist”
Your garden: work of the month.
By the beginning of July, fruit trees have finished growing their annual shoots. At this time, watering should be reduced so as not to cause a second wave of growth. In dry, hot weather, you will have to water once every 2 weeks, but in moderate doses. And then loosen the soil and mulch.If you notice shoots still growing in the crown, pinch them.
July work on a strawberry plantation
On a strawberry plantation, remove the runners after harvest if they are not needed for propagation or filling the rows. All excess mustache must be removed from the plantation no later than the beginning of August. Pull out all the weeds at the same time.
Apply complete mineral fertilizer to the cleaned soil: 10-15 g of urea, 40-60 g of superphosphate, 15-20 g of potassium sulfate per 1 linear meter of row spacing.
It is useful to sprinkle humus or compost closer to the bushes. Loosen the soil between the rows to a depth of 10 cm. Lightly hill up the bushes, raking the soil up to the horns for better root formation.
If strawberries have suffered from pests (mites, weevils), you can spray them with fufanon-nova. Against diseases, you can add 30 g of homa (or abiga-pik) or 100 g of colloidal sulfur.
To destroy mites and prevent diseases, it is effective to mow down the affected leaves and tendrils immediately after fruiting. You cannot be late with pruning: the bushes must recover and prepare for winter.
Immediately after mowing and removing the leaves, you should spray the plantation with one of the insecticides (fufanon, actellik, colloidal sulfur or thiovit jet), adding abiga-pik or khom, zircon or agate 25-K. After this, apply complex fertilizers, water and loosen the rows.
If you are leaving leaves, remove the tendrils except those you need for seedlings. The remaining measures are the same as those recommended after mowing the leaves.
Pollinate remontant varieties twice in July with freshly slaked lime or slug ash (20 g per sq. m).
Currant
On currants after the end of the harvest, powdery mildew, anthracnose, and septoriosis may appear.Against American powdery mildew, you can use topaz (2 g) or colloidal sulfur (30 g per 10 liters of water) or thiovit jet (20-30 g). Thiovit jet can also be used on gooseberries, despite the fact that it is also a sulfur preparation.
Raspberries
On raspberries, after harvesting, cut off the fruit-bearing shoots to the ground. Spray fufanon against pests, and abiga-pik or hom against diseases.
Cherry
After harvesting, cherries need to be protected from moniliosis (cut off dried branches, spray the crown with chorus), coccomycosis (the leaves have turned yellow and fallen off) and other fungal diseases (hom), from the cherry slimy sawfly (kinmiks).
Cherries
In July, form a crown of young cherries. Cut branches into a ring, directed towards the inside of the crown, thickening it. Shorten too long annual growths (more than 50 cm). Treat the cuts with garden varnish. For trees that have entered fruiting, cut out the central conductor at a height of 2-2.5 m.
Pear
If pear seedlings grow poorly, check whether the root collar is deep when planting, and whether you are over-moistening the soil.
Plum
The main pest of the plum tree in July is the plum moth, which began to harm it back in June (the first generation), and in the first ten days of July, the caterpillars of the first generation go to pupate under the loose bark, into the cracks of the trunks, into the soil, weave cocoons there and pupate. In 8-10 days (mid-July)
second generation butterflies emerge and lay eggs on the fruits of late varieties. After 4-8 days, caterpillars hatch, damaging the fruits.
Apple tree
Fruit harvest is approaching on summer varieties of apple and pear trees. Do not use chemicals on them. Spray against aphids with infusion of garlic or succinic acid (1 g per 10 liters of water).
For better storage of fruits, spray winter varieties with extrasol (10 ml per 10 liters of water).
Don't forget about pests
Collect carrion every day and spray the trees with fufanon (in mid-July).
Against moniliosis and cluster poriosis, add Khom or Abiga-Pik to the insecticide solution.
The second generation of codling moth also causes damage in July. Damaged carrion should not be left under trees. Clean daily; along with fresh carrion, you will remove a significant part of the codling moth caterpillars from the garden.
Once every 10 days, look through the trapping belts on the apple tree trunks.
To combat the codling moth in summer, it is better to use biological products:
- lepidocide (20-30 g)
- fitoverm (15 g)
- bitoxybacillin (40-80 g)
Their waiting period is from 2 to 5 days. Repeat spraying after 8-10 days.
For scab and powdery mildew on apple and pear trees, add quick or thiovit jet to the working solution.
Copper-containing preparations can form a net on the fruit.
Feed trees and shrubs
In the second ten days of July, most garden crops begin to lay fruit buds. Take care of the future harvest and feed the trees and shrubs with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers: 20 g of superphosphate and 15 g of potassium sulfate per 1 sq. m. m of tree trunk circle. Apply fertilizer along with watering. In hot, dry weather, water the garden 2 times a month.
If tree branches are actively growing, do a second summer pinch: remove the tops of competitors or break them out in the same way as top shoots. If they are needed to replenish or correct the shape of the crown, these shoots can be pulled back and tied up.
The blackberries have sprouted young shoots. In June you pinched their tops by 4-5 cm.As a result, side shoots began to actively grow. Monitor their growth. Pinch the tops of the shoots, leaving 40 cm.
In July, currants, gooseberries, and raspberries ripen. Pick blackcurrants in a timely manner: overripe berries crack and fall off. In red and white currants, they can remain on the bushes for up to a month if there is no rain.
If you process gooseberries, remove them when they are slightly underripe. When fresh, they are tasty when they become soft and turn the color characteristic of the variety.
After harvesting, water all berry fields and fertilize them with complete mineral fertilizer.
Budding work is carried out in July
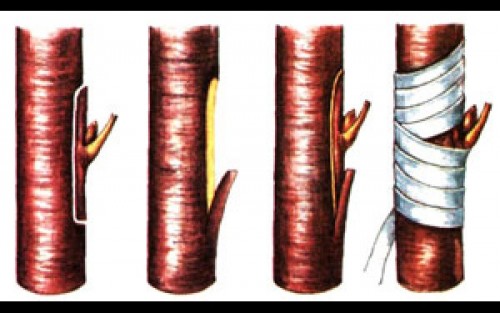
Butt budding - how it's doneAt the end of July, you can start grafting apricots and peaches, but with plums, cherries, pears, and apple trees, this work can be done earlier. Prepare the rootstocks for budding: clean the seedling boles and water generously. The easiest way is budding in the butt. Graft eyes are taken from finger-thick shoots at a distance of 10-15 cm from the base. Carefully remove the leaves and use a sharp knife to cut out the graft eye, surrounded by a small area of bark, in the direction of growth. The length of the shield is about 3 cm, the eye is in the middle. A cut of identical shape is made on the rootstock. Place the peephole with the shield into the cut on the rootstock. They tie the grafting site with film tape, leaving only the bud open. |
Seasonal work in the garden. July.
The season has just started, but it’s already the middle of summer. Procurement chores are added to everyday work in vegetable beds.
It would seem that there is simply no time to look closely at every bush in the garden. But it was not there.Someone will notice that for some reason the leaves on the pepper are turned inside out. Some may be alarmed that the leaves on the cucumbers seem to be nibbled here and there.
And the leaves on the pepper may have simply been blown away by the wind. There are varieties that have leaves on longer petioles than other varieties. That's why they're being rattled. We will not be able to help the plants in such a situation. The leaves of the cucumbers could be damaged by locusts and caterpillars of the cutworm and meadow moth.
I would like to advise meticulous summer residents not to take such a meticulous look at their beds. It’s not the attention itself that’s alarming, but the fact that after every “oh, what happened!” drastic measures follow: spraying the plants with everything that is in the garden medicine cabinet.
It seems that summer residents do this more for their own peace of mind, not taking into account that any spraying with chemical pesticides weakens the plants’ immunity.
Without making a diagnosis, do not handle the sprayer!
Now, especially when we have been harvesting cucumbers and zucchini for a month (and for some more), chopping Chinese and white cabbage from our garden into salads, we use protective equipment with great caution: only those permitted for personal farming and only for a short period of time expectations.
What can harm our beds in July?
There is still a strong likelihood of viral diseases occurring. After a temperature change or rain, dark stripes may appear on the stems of tomatoes. This is already a streak. The infection occurred earlier, and the weather only helped the disease manifest itself.
But the symptoms of diseases vary depending on the viruses that have “settled” in the plants: these can be mosaic yellow leaves on potato or tomato bushes, corrugated leaves on peppers, mosaic leaves and shortened internodes on cucumbers.
It is better to remove single diseased plants, and spray the rest every 7-10 days. milk-iodine solution (liter of skim milk or skim milk + 11 drops of iodine per 9 liters of water).
Foliar feeding with microelements and spraying with phytoavalanche will also play a protective role. But let’s not get our hopes up that the disease will go away: There are no drugs against viruses.
All we can do is ease its course and prevent the plants from dying. If the disease appears en masse, there is no point in removing the affected plants: we continue to care for them in order to get at least some harvest.
The influence of weather on the development of diseases
What diseases and pests of vegetable crops will be added to the list in July depends on the weather. Hot, dry weather will “multiply” mites and thrips, and therefore regular spraying of cucumbers, zucchini, and eggplants with phytoverm will remain in effect.
Rains and high air humidity can provoke the development of peronosporosis and late blight. Alternaria blight may appear on plants weakened by the virus.
With these diseases, it is no longer possible to postpone treatment with chemical fungicides.
With late blight, watery spots initially appear on the tips and along the periphery of the lower leaves, which soon become necrotic and die. Under favorable conditions, the disease quickly covers all leaves and growing fruits.
Temperatures above 26 degrees and dry air inhibit the development of the disease.We must remember this so as not to treat tomatoes with copper-containing preparations in the middle of summer, when the heat is over thirty degrees.
Temperatures within 18-20 degrees, the presence of drops of dew, rain or irrigation water on the leaves for 8-9 hours are favorable conditions for the development of peronosporosis, or downy mildew, on cucumbers.
Watery spots limited by leaf veins quickly turn yellow, then become necrotic and crack. Diseased leaves curl down along the central vein and dry out. Under favorable conditions, cucumbers can die within a few days.
Alternaria spot can develop on tomatoes in greenhouses with high air humidity. Growing dark brown spots may appear on leaves, stems, and fruits.
To prevent late blight and alternaria on tomatoes, cucumbers, as well as in case of weak development of these diseases, spraying with the biological fungicide phytosporin-M is used.
If plants need urgent help, spraying with abiga-pik (50 g per 10 liters of water) will be more effective, but this fungicide is not used on plants at harvest time, since it has a waiting period of 20 days.
Powdery mildew on carrots
In July, it is quite possible for powdery mildew to develop on carrots. A gray-white coating appears on the petioles and leaves of diseased plants. If measures are not taken, the leaves will turn brown and dry out, and the root crops, not receiving nutrition, will stop developing and become stringy.
The disease develops in damp, warm conditions. Therefore, it is very important to thin out the carrots so that they are better ventilated, loosen or mulch the rows.
It is better to dig up early carrots with formed root crops at the first signs of disease, carefully wash the root crops, dry them and put them in the refrigerator. Late varieties of carrots and carrots sown in June should be processed quickly, because There is still a long way to go before cleaning.
You can read: «What to do if powdery mildew appears on carrots«
Leaf parsley, leaf celery, sorrel, if any spots appear on them, are completely cut off, fed with complex fertilizer or organic infusion, watered, i.e., we stimulate the rapid regrowth of young leaves.
Summer menu for garden beds
While paying great attention to the fight against pests and diseases of vegetable crops, do not forget that the main thing now is different. We must strive to ensure that the plants are comfortable even in the most unfavorable weather.
Plants become vulnerable to diseases after suffering stress:
- temperature changes
- hot dry weather
- untimely watering, etc.
Make sure that the soil in the beds does not dry out. Loosen the soil and mulch with organic matter to create more favorable conditions for plant roots.
Regular foliar feeding with complex fertilizers with microelements, humates, and bishal will help vegetable crops grow actively and bear fruit. Such “feeding” is especially necessary during stressful periods, when plant roots do not absorb nutrients from the soil well.
During the period of fruit formation, it is advisable to regularly feed tomatoes and peppers with calcium nitrate on the leaves in order to reduce yield losses from blossom end rot (a tablespoon of calcium nitrate per bucket of water).
There may be enough calcium in the soil, but in hot weather it is practically not absorbed by plants, and it cannot move from leaves to fruits, like some other nutrients.
Foliar phosphorus fertilizing will help tomato fruits ripen faster. We make an extract from 1-2 tablespoons of superphosphate: pour in a liter of hot water, leave for a day, stirring, remove from the sediment and add to a bucket of water.
If you want to harvest from a cucumber bed for a long time, feed them every ten days so that the vines continue to grow. There will be no growth, and there will be no new ovaries.
For 10 liters of water, take a teaspoon of urea, potassium sulfate, add 0.5 liters of mullein infusion or green grass. You can do it easier - dissolve a tablespoon of complex water-soluble fertilizer in a bucket of water.
And harvest as often as possible, do not let the cucumbers outgrow. Even one giant cucumber can slow down the development of other fruits on the plant.
You can read: » 5 proven ways to feed cucumbers«
The same fertilizer is suitable for zucchini and pumpkin, but the proportion of organic infusion for them can be increased to a liter.
For other vegetable crops, avoid nitrogen fertilizing so as not to provoke the development of diseases and the accumulation of nitrates. Feed carrots and beets with potassium sulfate (a tablespoon per bucket of water).
We water according to the weather
Pay special attention to watering. It is important to carry it out taking into account the weather, and not the watering schedule. On hot days, when intense evaporation occurs, it may be necessary to water more often than twice a week; during hot hours, light watering should be carried out to reduce the temperature and increase the air humidity around the plants.
On cooler days, you need to moderate your “watering fervor”.Excess water, displacing air from the soil, disrupts the physiological processes of plants; they look depressed, although, as it seems to us, they have enough of everything: water, nutrition, and our care.
We remove one, sow the other
In July we are preparing to dig up garlic, early varieties of onions planted with sets, and family onions, having stopped watering two weeks before. This must be done so that the bulbs ripen well. Well-ripened onions are easily pulled out of the ground.
Harvesting garlic
We dig up the garlic when the leaves turn yellow, the arrows straighten and the “shirts” tear on them. You can dig up a few heads for testing. It is better to dig with a pitchfork so as not to inadvertently damage the heads.
You cannot keep garlic in the ground until the heads begin to fall apart into cloves. This garlic will not be stored. It’s better to hurry up a little with digging than to be late.
The garlic, without cutting the tops, is dried in a well-ventilated area, spread out in one layer or tied into braids and hung.
Properly removing onions
If the heads of the onion do not appear from the ground, we will loosen it a little. This is necessary so that the bulbs ripen better and the neck becomes thinner. Such onions will be stored better.
We cut off the tops not immediately after digging, but after drying. Avoid the recommended drying in the open sun. The upper juicy scales will get burned in direct sun.
You've probably had to peel bulbs with brownish, juicy scales that can later rot. These are the negative consequences of improper drying of onions - in the open sun.
Cabbage can give an additional harvest
We will also harvest other vegetables in July: early varieties of white cabbage, cauliflower, broccoli, early carrots.Having carefully cut the harvest of white cabbage and broccoli, water it, feed it with organic infusion and wait for the second harvest.
From the cut white cabbage, we will later remove the small heads that appeared from the axils, leaving 1-2 of the largest ones so that they will give us an additional harvest.
We release the broccoli “into the wild”, but make sure that the inflorescences that form from the side buds do not outgrow or bloom (we cut them off regularly).
After cutting off the cauliflower heads, we immediately pull out the stalks, chop them and put them in compost. It makes no sense to expect a second harvest from cauliflower.
The vacated area can be sown with green manure. It is better if it is not mustard, which is of the same family as cabbage and is affected by the same pests (for example, cruciferous flea beetle).
For summer sowing of green manure, phacelia and oats are suitable. You can also get a second harvest of vegetables by sowing early ripening bush beans after cabbage. It will produce a harvest and improve the soil.
We dig up the carrots, wash them, dry them, put them in plastic bags and put them in the refrigerator. There is no point in keeping heavy root vegetables in the garden: they will not gain any flavor, but will only become coarser.
We will fill the bed with compost or good humus and sow early varieties of cabbage (cauliflower, broccoli) there. After sowing, mulch the soil surface with grass, and after germination, “powder” it with wood ash to repel cruciferous pests.
If there is no need for repeated sowings, let the soil rest under green manure. But in any case, we don’t leave the garden bed to become overgrown with weeds or, even worse, to fry in the sun.
The bed from which the peas or beans have been removed can be left for planting strawberries.Legumes are considered good predecessors of this berry crop.
At the end of July, you can sow daikon and kohlrabi cabbage for the autumn table and winter preparations. You can choose a site for them after legumes, potatoes, early carrots, onions, and garlic. Let's think in advance about the area for planting garlic.
The following are considered good predecessors of this culture:
- peas
- cabbage
- potato
- roots
To ensure that the bed chosen for garlic does not remain empty until October, it can be sown with green manure so that it can be dug up in September.
If you don’t yet know how to use green manure to improve the soil on your site, then you will probably be interested in reading the article “Siderata. You’ve been imprisoned, but what next?”
And in mid-summer you can replant potatoes
We dig up potatoes planted in April and sow the area with green manure or, having improved the soil with compost and humus, sow cucumbers to start preserving in late summer-autumn, when the heat subsides.
If there is space and seed tubers, we plant potatoes. After planting, it is advisable to mulch the surface of the bed with grass in order to create more humid and cooler (as far as possible in the July heat) conditions for the germination of tubers.
Such a bed can be watered by sprinkling before emergence without fear of crust formation. By mulching we protect potatoes even after germination.
No waste, only organic
Carrot, pea, bean tops, cabbage leaves (it would be nice to chop them up a little with a shovel) are placed in compost, sprinkled with soil and watered so that it all rots faster and turns into good organic fertilizer.
You can also use special biological preparations for quickly preparing compost.
What flower growers need to take care of in July
Your flower garden: work of the month.
Faded plants, so that they remain beautiful until the end of the season, and next year please us with even more abundant flowering, require our attention.
We cut off faded peduncles and flowers, feed the plants with phosphorus-potassium or complex fertilizers (at the roots and along the leaves). During stressful periods (changes in weather, intense heat), we will help the plants maintain immunity: we will sprinkle them with solutions of humates, microelements, and HB-101.
We make sure that no traces of pests or diseases appear on the leaves and stems. Be sure to trim (if you have not done so before) faded carpet plants (aubrietta, carnations, etc.).
They will give fresh shoots, and neat thick curtains will delight you until late autumn. We do not leave wilted inflorescences on more vigorous perennials. Having cut off the flower stalks of the delphiniums, we will definitely wait for them to bloom again.
By carefully trimming the stems of faded lilies at one level, we will create a green background for other plants. By removing the wilting baskets of gatsanias and calendulas, which set the seeds of snapdragon inflorescences, we not only restore the beauty of flower beds, but also extend the flowering period of plants.
If you do this regularly, everything will not take as long as it might seem.
Don't forget to sow new flowers
Some flowers that reproduce by self-sowing:
- oriental poppy
- aquilegia
- feverfew
- Eschsolzia
- Nigela
- calendula, etc.
You can leave a few seed pods - let them scatter; the seedlings can always be removed or transplanted into a flower garden.
And here are the seeds of biennials:
- bell medium
- pansies
- Turkish cloves
- daisy
you'll have to assemble it yourself. You can sow them right away to expect flowering next season.
True, it is difficult to get seedlings in hot weather. But if you choose a site for a nursery in a semi-shaded place, cover it with non-woven material on arches, you can count on success.
Sowing biennials in the second half of summer saves us a whole season. Just don’t forget about the seedlings: water and feed them on time, be sure to thin out the dense shoots so that the “youth” grow strong and strong.
It is already difficult to care for the soil among overgrown perennials: with a hoe you can damage the roots and break off the stems. Therefore, having loosened the soil shallowly where this is still possible, we mulch the open areas.
While caring for your favorite plants, take time to admire them. They will become even more beautiful from your admiring glances.
And also prepare the colors and smells of summer for winter. The most suitable day is July 7th.
It was on the night of Ivan Kupala that our grandmothers collected herbs for amulets. The bouquets were illuminated in the church and hung in the house. It is believed that medicinal plants are especially healing on this day.
Well, why don’t we prepare lemon balm, oregano, and thyme for the winter? And just in case, go to your fern at night: suddenly it will bloom!
A fairy tale is a fairy tale, but for every summer resident there is some truth in it: to find the treasure pointed to by a blooming fern, you don’t have to go far, you have already created this treasure with your own hands, in your garden, growing beautiful plants.
Other articles from this section:
- Seasonal work for gardeners and gardeners in August.
- Seasonal work for gardeners and gardeners in September
- Seasonal work for gardeners and gardeners in October.
- Seasonal work for gardeners and gardeners in November.














 (6 ratings, average: 4,67 out of 5)
(6 ratings, average: 4,67 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.