The apple tree is one of the most valuable and widespread crops in the world. Currently, about 30 wild species and more than 18,000 varieties are known. The lifespan of cultivated varieties depends on the rootstock and growing conditions. With proper planting and proper care, apple trees grow in the garden for 25-40 years.
Unfortunately, inexperienced gardeners often make mistakes when planting apple tree seedlings, which lead to the death of the tree in the first years of its life. This article describes in detail how to select seedlings, how to prepare a planting hole and properly plant seedlings in spring and autumn.
|
In nature, apple trees live 80-120 years. |
General characteristics of apple trees
- Seedlings. Seedlings of wild apple, Siberian apple or plum-leaved apple trees grown from seeds are used as a rootstock. The resulting seedlings have a deep root system, are tall and large. The varieties grafted onto them can be grown in arid areas with severe lack of moisture.
- Vegetative rootstocks. It is difficult to obtain them, since an apple tree is not a currant and it is extremely difficult for cuttings to take root. Rootstocks have a superficial root system. Varieties on such rootstocks can be grown in places with high groundwater levels, but it is not recommended to plant in regions with strong winds, since the root system is weak and does not hold the tree well in the soil.
The apple tree is a very winter-hardy crop. It can withstand frosts down to -42°C. If the graft does not take root well, it may freeze out, but the rootstock, as a rule, remains and can be re-grafted. Complete freezing of apple trees is a very rare occurrence.
Frost resistance and winter hardiness
Trees start their growing season late and finish it late. Sap flow begins only when the soil in the zone of sucking roots warms up to +8°C. In the middle zone this is the second or third ten days of May (depending on the weather), in the south - the first ten days of May. In autumn, trees take a long time to ripen. In the middle zone, trees often go into winter not quite ready. The apple tree does not have enough months to fully prepare for the cold, so if severe frosts occur in late autumn, the young growth freezes. In general, freezing of apple trees occurs precisely in December, if frosts of -13-15°C or lower occur, and in January-February the trees can withstand the most severe frosts without damage.
Winter thaws are not capable of causing damage to apple trees. Since the main parameter for the beginning of the growing season is the temperature of the soil in the root layer, even the most severe and prolonged thaws cannot awaken the apple tree. However, if severe cold sets in after a thaw, frost holes—longitudinal cracks of different lengths—may appear on the bark.
Soils
The apple tree can grow on any soil except strongly acidic and strongly alkaline. Depending on the climate, it can develop differently on soils of different mechanical composition. Thus, on sandy loam soils in a zone of abundant moisture, the crop feels excellent, and on the same soil, but with a moisture deficiency, it will produce low yields, even taking into account artificial irrigation.
Hydration
Seedling varieties have a powerful root system that goes deep into the soil and is 2 times larger than the crown. They can be grown in arid regions with severe moisture deficiency and deep groundwater.When groundwater occurs at a depth of 1.5-2 m, apple trees are planted on vegetative rootstocks.
Apple trees can withstand even prolonged flooding without visible damage. The crop also tolerates drought without problems. But with a long absence of precipitation, especially in arid areas, the tree begins to shed ovaries and fruits.
Temperature
If a blooming apple tree is exposed to frost, the flower dies. In some years, severe frosts can destroy the entire flower, leading to a complete lack of harvest. Usually frosts occur in stripes and you can notice how in one and the same area there is a large harvest of apples in one part of it, and in another there is a complete absence of them. But frosts are dangerous only during the period of full flowering and for young ovaries. Unopened buds can withstand frosts down to -3°C without damage. Several years ago, when the apple trees had just finished blooming and young ovaries appeared, there was a frost. And it wasn’t that strong, only -1°C, but the apple trees lost 3/4 of their ovaries, and there was practically no harvest.
|
Frosts can destroy the entire apple harvest |
Temperature affects crop ripening. In cool and damp, as well as hot and damp weather, the crop ripens 15-20 days later and fruiting is more extended. In dry and hot summers, the crop ripens faster.
Selection of seedlings
When choosing planting material you should consider:
- fruiting time of varieties;
- crown height;
- with what root system the planting material is sold;
- age of seedlings.
Fruiting dates
There are varieties according to their ripening time.
- Summer. The harvest ripens in July-August and is not stored. The fruits are usually soft, juicy, suitable for immediate consumption and processing.The most common varieties are Medunitsa, Grushovka Moskovskaya, Belyi naliv, etc.
- Autumn. Fruiting period is late August-September. The fruits are hard, but after resting, they acquire softness and aroma. They are stored for 3-5 months. The varieties Melba, Cinnamon Striped, Antonovka, and Borovinka are widely known.
- Winter. Ripen at the end of September-October. Apples are very hard, they can be stored for 6-10 months, and during storage they acquire juiciness and aroma. Varieties: Welsey, Aport, Moscow Winter, etc.
Don't forget to read:
The timing of fruiting is very arbitrary and can shift by 1-3 weeks. It depends on weather conditions. From my own experience, I can say that in warm and humid summers, summer varieties ripen as early as July. In the case of a dry and hot summer, no matter what kind of autumn it is, autumn apples are ready for harvesting only in the first ten days of October.
In addition, the difference between autumn and winter varieties is determined not only by the ripening period of apples, but also by the duration of their storage. For example, the same Antonovka can manifest itself differently in different conditions. Why, in different conditions! Even in the same area, dates fluctuate depending on the weather. In my garden, if the fruits ripen in September, they are stored until mid-January. But there are years when Antonovka ripens only in the first ten days of October, and then it is stored until the end of March.
In the fall, after the harvest, the processes of transformation of substances and preparation of the tissues for winter continue in the tree tissues. In autumn and winter varieties, these processes continue even in December.They don’t have enough months to properly prepare for low temperatures, and most often, even with slight December frosts (-10 - -15°C), they freeze and even freeze out. Summer varieties have much more time to prepare for winter; they have time to ripen the wood and complete metabolic processes, so they are much more resistant to December frosts.
Almost all varieties of apple trees are self-sterile, i.e. cross-pollination is necessary for fruit set. If pollen lands on the pistil of a flower of the same variety, pollination does not occur. For pollination, apple trees of various varieties must be planted on the site.
When planting a garden, they are usually guided by the varietal ratio:
- 10% on summer varieties
- 30-40% for autumn
- 50-60% for winter.
In regions with early and severe winters, winter varieties should be discarded.
Do not miss:
Crown height
The height of the apple tree depends on the rootstock. Apple trees are divided into groups according to their growth strength.
- Vigorous. These are, as a rule, seed stocks (apple seedlings grown from seeds onto which a cultivar is grafted). the roots go deep into the ground, and the height of the crown without pruning reaches 7-8 m. With annual pruning, the height can be kept at 4-5 m. But as soon as pruning is not done, the branches will rush upward, and the tree will not calm down until it reaches its "natural growth" Tall apple trees are planted in areas where the groundwater depth is at least 3.5 m. At a higher depth, the tree loses winter hardiness and eventually dies. It should also be taken into account that such a crown will shade a very large area of the site and will be difficult to work with.
|
Vigorous trees are very durable. |
2. Semi-dwarfs. Grows up to 5 m without pruning.Can be planted in areas with groundwater no higher than 2.5 m.
|
Semi-dwarfs are less durable, living 35-50 years. |
3. Dwarfs. They grow no higher than 2.5 m. Ideal for areas with high groundwater levels (at least 1.5 m). Their yields are low, but due to compact planting, the yield increases.
|
Dwarfs are short-lived, living 15-20 years. |
4. Columnar apple trees. Mostly low-growing, although sometimes medium-growing rootstocks are used. The yield for such a small tree is decent - up to 7-10 kg of fruit per tree.
|
The fruiting period is 8-10 years. Then the fruit branches (rings) die off and fruiting stops. But the apple tree itself can live 30-50 years. |
It should be remembered that without care, an apple tree tends to reach its maximum height, like its wild ancestor. And only pruning allows you to keep it within the required limits. In addition, in nature, an apple tree is a shrub tree. Therefore, varieties grafted onto apple tree seedlings strive to produce several trunks from the base. Only pruning forms the correct standard of the seedling. If formed incorrectly, horns are formed (2-3 trunks coming from the root).
Root system
Seedlings come with open and closed root systems.
Open root system
The seedlings were grown in the ground, and for sale they dug up with a clod of earth, the roots are visible. If the roots are too dry, you should not take a seedling. The roots should be moist. When purchasing, you should lightly pull the spine. If it is healthy, it will bend, but if it is rotten, it will easily come off.
|
The root system must be well developed, at least 1/3 of the seedling long. |
Closed root system
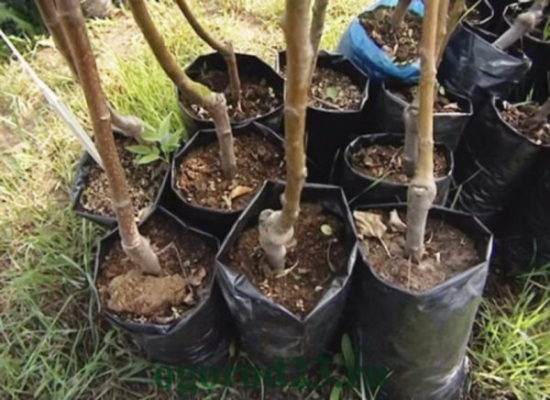
These are seedlings grown in a container. Moreover, the rootstock must be grown in a container, and it must already be grafted onto it.
But often containers sell material that is grown in the ground and then dug up and stuck into the container. To make sure that the tree was actually grown in a container, you need to inspect its bottom. If it was really grown in this way, then young roots will sprout from the drainage holes. If this is dug material, then either nothing sticks out of the holes, or stubs of roots stick out.
|
This planting material can easily be transported and takes root very well. |
Age of seedlings
The younger the age, the better the survival rate. A 2-year-old seedling is considered optimal. It is advisable to take 3-year-olds with a closed root system; The exposed roots of such planting material are already quite powerful, they suffer greatly during digging and the trees do not take root well.
Age can be determined by the number of branches: a one-year-old has none, a 2-year-old has 2-3 branches, the branches extend at an angle of 45-90° from the stem, a 3-year-old has 4-5 branches.
It makes no sense to take seedlings older than 3 years. They take a very long time and are difficult to take root (even grown in a container). Some varieties already produce their first harvest at this age.
Other recommendations for choosing seedlings
They are common to all trees and shrubs.
- Only zoned varieties are purchased. They tolerate local climatic conditions very well. Imported varieties will suffer from climate conditions that do not meet their requirements; the trees may freeze in winter, and their life and fruiting life will be significantly reduced.
- Buy apple trees without leaves. The tree should not have any blossoming leaves. In their presence, water evaporates and the trees suffer from a lack of moisture, and seedlings with an open root system begin to suffer from severe dehydration.
- Carefully inspect the plant. There should be no broken branches. The bark should be intact, without cracks, frost holes, sunburn, or signs of disease.
It is advisable to purchase apple trees from trusted nurseries. Then there is a guarantee that exactly what was purchased will grow. When purchasing at the market and various exhibitions and fairs, there is no such guarantee.
Landing dates
Apple trees have two main planting periods - spring and autumn. It depends on climatic conditions and the condition of the seedlings.
In autumn, apple trees are planted 1-1.5 months before the onset of persistent cold weather. In the middle zone this is the whole of September. In the fall, trees with an open root system are mostly planted, since at this time it is easier to keep the roots moist during transportation. The survival rate of seedlings with an open root system in autumn is much higher than in spring. This is due to the fact that the stem no longer requires many plastic substances for growth and the roots spend growth energy for their own restoration and development.
In spring, mostly seedlings grown in containers are planted. Damage to the roots here is minimal; the root system is already quite developed and is capable of both developing itself and providing the above-ground part with everything necessary. Container apple trees can also be planted in the fall.
When planting in spring, apple trees are planted before the leaves bloom. The soil temperature must be at least 7°C.
The survival rate of apple trees with a closed root system is 98%. The reason for the non-survival of a seedling can only be damage to the roots when grown in a container (various rots), or if, instead of a container tree, a seedling dug out of the ground and passed off as a container plant was put in there.
Landing place
Several factors are taken into account.
- At the dacha, for an apple tree, choose a place protected from cold winds. You can plant a tall tree in the shade of the house. Literally in 3-4 years it will outgrow the structure and will not feel shading. Low-growing varieties and columns are planted in fairly bright places, but they can also tolerate partial shade.
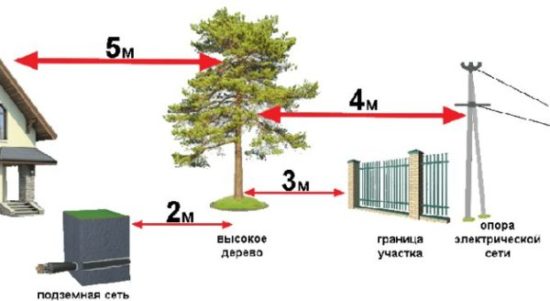
- When planting, you should remember that in just 3-4 years the crown will provide dense shade, so you should not plant apple trees next to the beds or the greenhouse. No garden crops will grow under its crown. Typically, fruit trees are planted along the perimeter of the site, 3-4 meters away from the border.
- The culture grows on any soil except strongly acidic and strongly alkaline. How a crop will grow on soils of different mechanical composition depends on the climate. In arid regions, even on clay soils, the apple tree grows and bears fruit well, but in the middle zone the apple tree will not grow on clay.
- When planting, take into account the occurrence of groundwater. If they are closer than 1.5 m, then hills are poured. And on clay soils, in this case, you should completely abandon planting both apple and pear trees, since after each rain the water will stagnate in the root zone and freeze in winter. And the tree will inevitably die, if not immediately, then in 1-2 years.
- When the site is located on a slope, apple trees are planted in the upper or middle part. The lower part is unsuitable because cold air accumulates there, which is detrimental to flowers and young ovaries.
- If the plot is too large, then several fruit trees of different varieties are planted on it for cross-pollination. In this case, it is better to plant the crop in a row or in a checkerboard pattern, this will leave more unshaded areas, and such planting is better for pollination.
|
You should not plant fruit trees directly under the windows, otherwise in a few years there will be thick shadow here, there will be twilight in the house, and neither flowers nor vegetables will grow under the apple trees. |
The distance between the tree and the fence for tall varieties is at least 5 m. Otherwise, part of the crop will inevitably fall over the fence. For semi-dwarfs and dwarfs, the distance is at least 3 m. The branches should not rest against the fence, and the shadow from it in the first years of growth should not greatly shade the seedlings.
Preparing a site for planting an apple tree
Apple trees are planted either in holes or (if groundwater is high) on hills. Both are prepared in advance. The planting site is prepared if the soil is cultivated. Otherwise, it is cultivated by applying fertilizers and carrying out reclamation measures, if necessary.
Planting pits
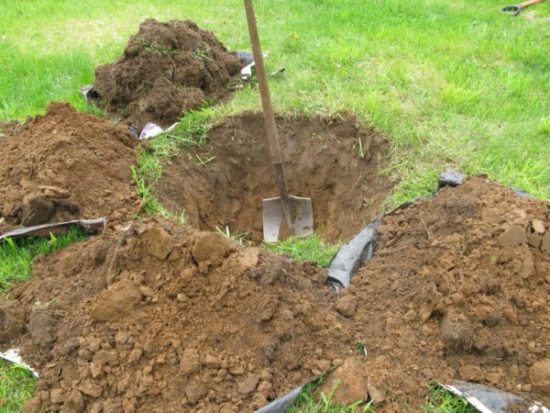
They are prepared six months before the intended planting. If several seedlings are planted, then the distance between tall varieties is 5-6 m, for semi-dwarfs 3-4 m, for dwarfs 2-3 m. For tall apple trees, a hole is made with a diameter of 80 cm and a depth of 60-80 cm, for semi-dwarfs the diameter is about 60 cm, and the depth is 50-60 cm, for dwarfs the diameter is 50 cm, the depth is 30-40 cm. The depth is calculated taking into account the fact that the bottom of the pit is filled and a hill is poured.
When digging a hole, the top fertile layer is folded in one direction, the lower, less fertile layer in the other. The apple tree has its own roots, which go deep into the ground. The gardener’s task is to try to ensure that some of them grow in a horizontal direction. To do this, broken bricks, stones, rotted sawdust, and branches are placed at the bottom of the pit. If groundwater is close, then the drainage layer is made large enough (15-20 cm).
|
Preparing the planting hole |
Next, prepare the soil. To the soil from the bottom of the pit add 2-3 buckets of semi-rotted or rotted manure, humus or compost, 1 kg of ash and 1 kg of complex fertilizers, mix everything thoroughly. Additionally, on highly alkaline soils, add 1 bucket of peat to the mixture, on very acidic soils - 300 g of fluff. Fertile soil sold in stores is undesirable. Usually this is peat from a nearby swamp or, in general, soil from a greenhouse farm, which has served its purpose and is thrown out of the greenhouses.
The soil mixture is also prepared six months in advance, thoroughly mixed again and the hole is filled with it again. The top fertile layer is poured down, and the bottom layer, now enriched with manure and fertilizers, is poured on top. The pit is covered with covering material to prevent weeds from growing in it.
Planting seedlings on hills:
planting hills
Planting apple trees on hills is carried out either in the case of close groundwater, or if water stagnates in the area for a long time after melting snow and rain.
Hills are poured with a height of 80-100 cm and a diameter of 1-1.2 m. They are prepared a year before planting. Initially, drainage is laid on the soil: broken bricks, slate, cut branches, boards, pieces of plaster, etc. The height of the drainage is at least 30 cm, it is covered with earth. Next, sand, sawdust, and wood shavings are poured in so that the water does not stagnate in the root zone. Everything is covered with fertile soil and manure.
The next layer is cardboard, newspapers, torn into pieces, dry leaves. Next, make a soil mixture from manure/humus, ash, fertilizers and pour it on top. Instead of pouring soil, you can make a compost heap, periodically watering it with Compostin or Radiance for better rotting.A hill, whether composted or earthen, will settle by 2/3 over the winter, so in the fall it should be at least 1.4 m, and in the spring it needs to be filled up. A month before planting, fertile soil is brought onto the hill and dug up.
|
The hill itself is covered with boards, slate, paving slabs, etc., so that the earth does not fall off. |
It should be taken into account that bulk hills freeze in winter. Therefore, they are usually done under the protection of buildings, fences or plantings (so that it is not blown by the winds), leaving the required distance from them. Over the coming years the hill should expand.
Do not miss:
Preparation of seedlings
Seedlings with open and closed root systems are prepared for planting differently.
Open root system
Before transportation, the roots are dipped in a clay mash or placed in a bucket of water for 2-5 minutes. Then they are wrapped in newspapers and film on top of them. The branches are tied so that they do not break. If there are leaves, they are torn off. If planting is not planned immediately, then store them in the same form, periodically wetting the roots with water.
Immediately before planting, apple trees are placed in water for 1.5-2 hours, Kornevin is added to the water. There is no need to keep it in water longer, since the plastic substances are washed out and it is more difficult for the tree to take root. If the roots are dry, they are kept in water for 4-6 hours. Seedlings with dried roots are not planted: they do not take root well, often freeze out in the first winter, and if not, the trees are severely retarded in growth.
Before planting, remove broken branches and damaged roots.
Closed root system
When transporting, the branches are tied to avoid breakage.Before planting, tear off all the leaves, if any, and water them with water to make it easier to remove the seedling from the container.
Planting apple trees
Planting apple trees with closed and open root systems is significantly different. Before planting, stakes 2-2.2 m long are prepared.
Open root system
|
When planting seedlings with an open root system, it is recommended to soak them in water for 1.5 - 2 hours |
It is imperative to tie the apple tree to a peg, otherwise the wind, even not very strong, can tilt or even completely twist the roots out of the loose soil. Seedlings on dwarf rootstocks, which have a weak root system, are even tied to three stakes for more reliable fixation.
The root collar is not buried; it should always be 2-4 cm above the soil. Roots are the most sensitive part of the plant to temperature changes. Therefore, when the stem is buried or placed too high, trees lose frost resistance. In addition, when the neck of dwarf and weak-growing varieties is deepened, they lose their short stature and begin to grow upward strongly. When the neck becomes too deep, the trunk begins to rot and the tree dies.
The root collar is where the brown root meets the greenish stem.It is located 4-5 cm above the first root branch and 5-7 cm below the grafting site.
Beginning gardeners often confuse the root collar and the cut of the thorn from the rootstock. It should be remembered that it is always 4-6 cm below the thorn!
If at first it is difficult to understand where this root collar is located, then the apple tree is planted a little higher, and then, after looking closely, it is easy to add soil.
|
After planting, the soil is lightly trampled down, but not too much; the roots need access to air. Planted trees are watered. A hole with a radius of 25-30 cm is made around the trunk, along the perimeter of which an earthen roller is made. The seedling is tied to pegs. |
Closed root system
In the prepared area, dig a hole the size of the container. A peg is driven into the edge of the hole where the tree will be tied. Before planting, the seedling is watered. The container is cut on the side and the seedling is removed. They lower it into the hole and fill the voids with earth. Plant it at the same level as when it grew in the container. A hole with a roller is also formed around it and watered. After planting, it is tied to a peg.
The trees are always tied to a support at the top of the trunk.
Care after landing
- In dry weather, they are watered regularly. The rate of watering depends on the type of soil. The main indicator is dry soil, which crumbles into powder in your hands. During dry autumn, trees are watered once a week, and 3 weeks before the onset of cold weather, water-recharging watering is done, increasing the water consumption rate by 2 times. In rainy weather, seedlings are not watered.
- The soil in the tree trunk circle will settle and is regularly replenished.
- After planting, the trees are regularly shaken up and down so that the soil is compacted and the tree stands stable in the soil.
- In cold regions where winter comes early, during autumn planting the trunk of the seedling is sprinkled to a depth of 20-30 cm to prevent freezing. Early in spring, the soil is removed, freeing the root collar.
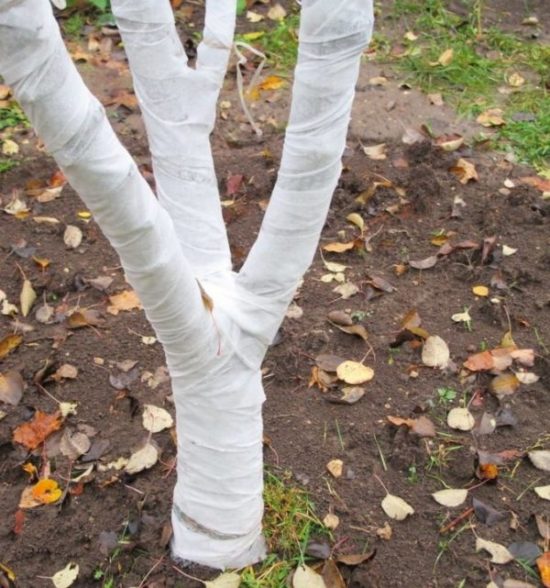
- In spring, the stem of a young tree is wrapped in rags to prevent sunburn. When a stable positive temperature is established and mature apple trees bloom, the rags are removed. Older trees are whitewashed to protect them from burns. But young seedlings cannot be whitened, as this will cause the bark to age and give small cracks.
-
I had such an unpleasant situation. Three-year-old apple and pear trees were whitened at the very beginning of spring, and after 2 months, when the whitening had more or less disappeared, it was discovered that the previously smooth bark turned out to be rough and full of small cracks, especially in the lower part of the trunk. The six-year-old trees that were whitened at the same time were fine, but their bark was rougher.
- For the winter, the seedlings are covered with rags to protect them from rodents.
- After planting, pruning is carried out. When planting in autumn, it is done in early spring before sap flow begins. Since the roots were damaged during digging and planting, their transport function decreases and they are unable to provide the above-ground part with the necessary amount of water. Skeletal branches are shortened by 1/4-1/2 the length, excess branches are removed by cutting into a ring. Branches located lower on the trunk and having a large angle of departure grow more slowly. Branches that grow higher up the trunk and extend at a sharper angle grow faster. When pruning, it is necessary to balance the growth of branches, so the upper branches are trimmed more strongly, and the lower ones no more than 1/4. All shoots are pruned above the bud (except for pruning to the ring).
When planting in the spring, if the seedlings have taken root, they will certainly produce leaves, which are removed to prevent excessive evaporation of water. When planting in autumn, the survival rate of the seedling can only be judged in the spring.
Features of autumn planting

All leaves on the seedling are removed after planting. The seedling is watered with a solution of growth stimulants (Heteroauxin, Kornevin, etc.). For greater stability, they are also tied to a support, and in regions with strong winds, to three at once.
|
In the spring, as soon as the snow melts, the soil is removed, exposing the root collar. Also, to protect against frost, the seedling can be covered for the winter. It is covered on top with a light, breathable fabric, and early in the spring it is removed.
Do not miss:
Digging up seedlings until spring
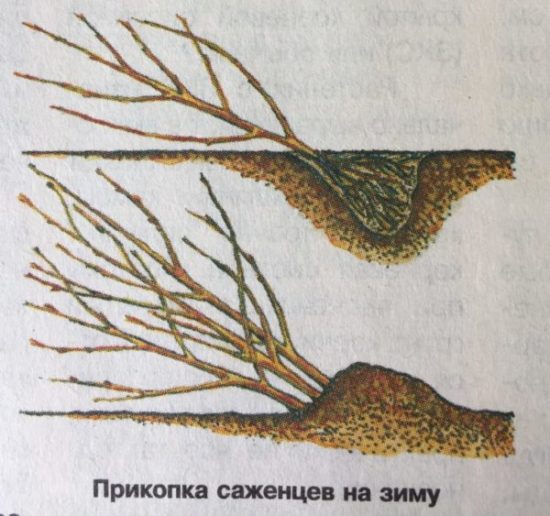
Prikopka
Apple trees are buried in a place protected from cold winds. The digging area is dug immediately before placing the seedlings.1 bucket of humus or compost is added to the ground; on sandy soils, 1 bucket of peat is added; on clay soils, a bucket of sand is added. Dig a trench 50 cm wide, 40-60 cm deep and length depending on the number of seedlings. Lay the plants obliquely, cover 1/4 of the trench with a layer and water. When the water is absorbed, the trees continue to be covered with earth and are buried 20-25 cm above the root collar.
|
Before planting in the spring, the roots are inspected very carefully, removing dry, rotten, broken ones. |
After the snow melts, the trees are dug up and checked for safety. Using a knife, cut small pieces of bark from the branches and a section of the root at the base. If the cut of the root is light brown and the wood on the branch is light green, then the seedlings are healthy, have wintered well and can be planted. If the sections are dark brown, the seedlings are damaged or dead.
Don't forget to read:
How to care for young apple trees in spring, summer and autumn ⇒
Cold storage
The roots of the apple tree die at temperatures of -6 - -12°C, and the crown can withstand frosts of -35 - -42°C without problems (depending on the variety). Therefore, seedlings are stored in a room where the temperature ranges from +1 to -4°C. At higher temperatures, the buds on the branches begin to swell, using the remaining plastic substances, and the seedlings are severely depleted. And without access to light, apple trees in an active state quickly die.
When storing, the roots should always be slightly moistened. To do this, they are wrapped in any breathable material and moistened as needed.
















 CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.