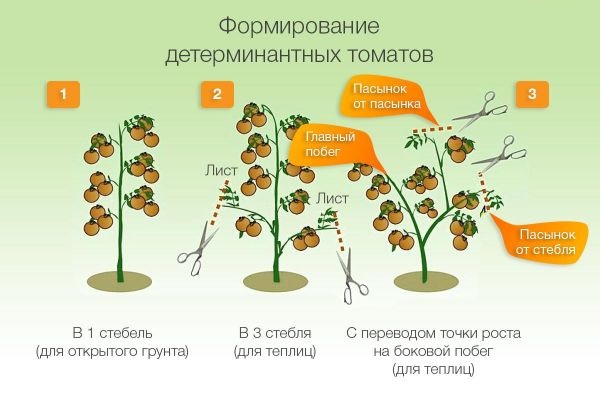
What is tomato formation?
Forming tomatoes is the regular removal of shoots and leaves to obtain maximum yield. Without this, it is impossible to get a full harvest in our country, even in the south. Untimely pruning of shoots and leaves leads to crushing of tomatoes, early disease with late blight and rot.
The formation of tomatoes in a greenhouse and open ground varies greatly depending on the region where the crop is grown and the variety.
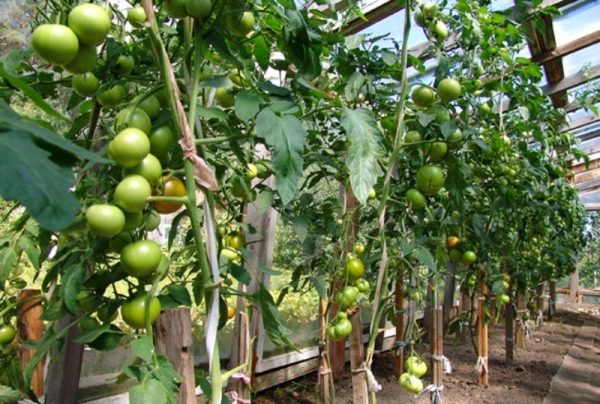
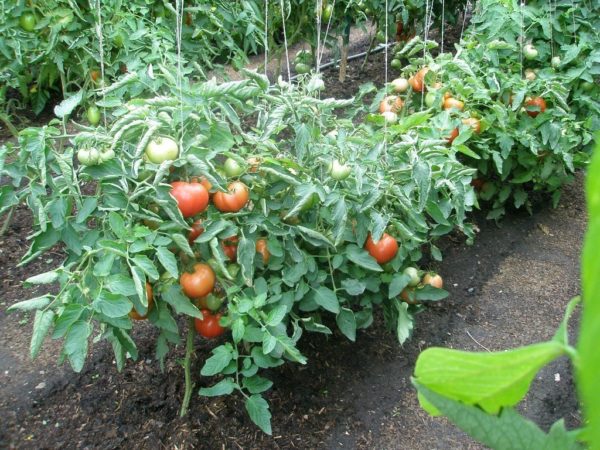
Tomatoes are formed both in the greenhouse and in the ground throughout the growing season. Properly carried out measures improve ventilation in plantings (especially in greenhouses), promote uniform lighting and good pollination of flowers.
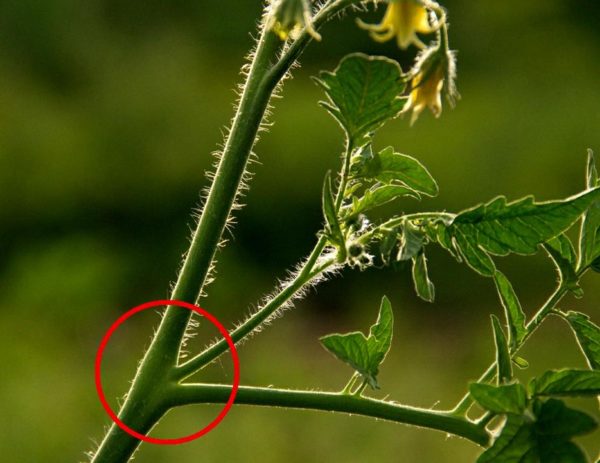
Tomato bushes begin to form when stepsons appear in the leaf axils. In some varieties they appear during the seedling period. But in most cases, young shoots appear 7-10 days after planting the seedlings.
Northern regions
These include the northwestern regions, the middle zone and some regions included in the central black earth region.
Formation of plants in open ground
Early-fruiting ultradeterminate and determinate tomatoes are grown in open ground.
Ultradeterminate varieties are low-growing and early-fruiting. They form 2-3 fruit clusters on the main stem, after which a flower cluster forms at the top, and their upward growth stops. Almost the entire harvest is on the side shoots, so these tomatoes do not shoot.
Each shoot emerging from the leaf axil is allowed to grow and develop into a full-fledged stem. The stepsons on the stepsons are also not removed, since over the summer they turn into full-fledged stems and bear fruit. But, since ultradets branch weakly, the bush turns out to be sparse. Sometimes on a shoot that has grown into a stem there are no new stepsons. In open ground, the branching of a tomato bush depends on the weather.
As the brushes are tied, the lower leaves of the ultradeets are removed. There should be no leaves under the brush. To prevent the bush from falling apart, it is tied to a support.
Determinate varieties in the middle zone they are also grown in open ground. The bushes of these tomatoes are taller than ultradeets, but their growth is also limited. 4-5 fruit clusters are formed on the plant, and then it is crowned, that is, a flower cluster that completes growth appears at the top.
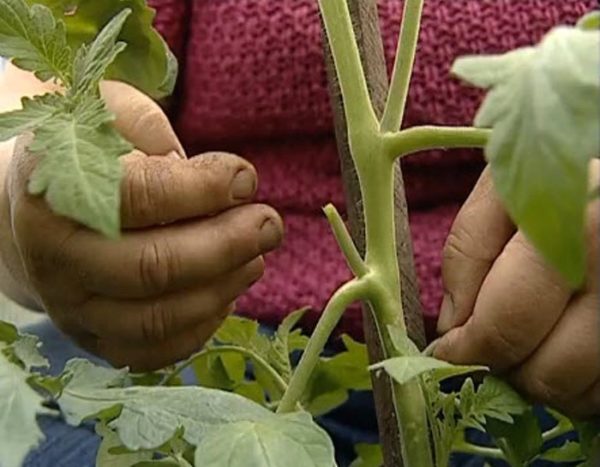
Children are grown in 2-3 stems. The most powerful stepson is left under the first flower brush, the rest are plucked out. Next, the young shoots are left under the 2nd and, if the summer is hot, 3rd tassels. But in cold, rainy summers, it is enough to leave only one shoot. In such weather, tomatoes fall ill with late blight early, and on multi-stemmed bushes the entire crop is lost, whereas when grown with 2 stems, the tomatoes have time to ripen.
After planting the seedlings in the ground, their lower leaves are cut off, then 1-2 leaves are removed every week. By the time the brush is tied, all the leaves under it should be cut off. On the left stepsons, the leaves are also cut off as they grow. All excess shoots, both on the main stem and on the side ones, are removed when they reach a size of 10-15 cm.
If one of them was not cut in time and has already formed into a stem, it is still removed, since it delays the ripening of the crop. Strongly overgrown bushes and stems, which have fallen under the weight of fruits, are tied to a support. Each stem can be tied to a separate peg.
Neither leaves nor fruits should be allowed to come into contact with the ground.
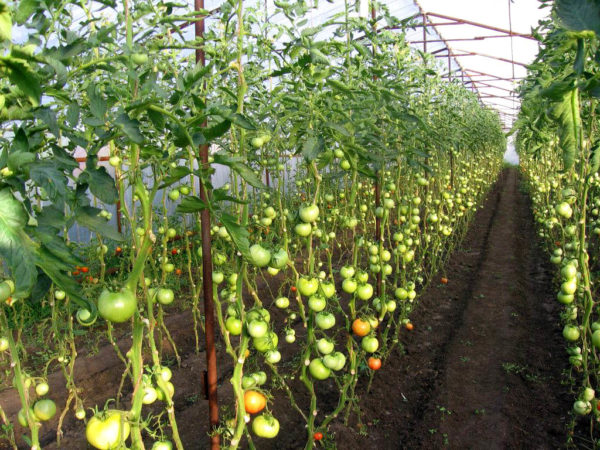
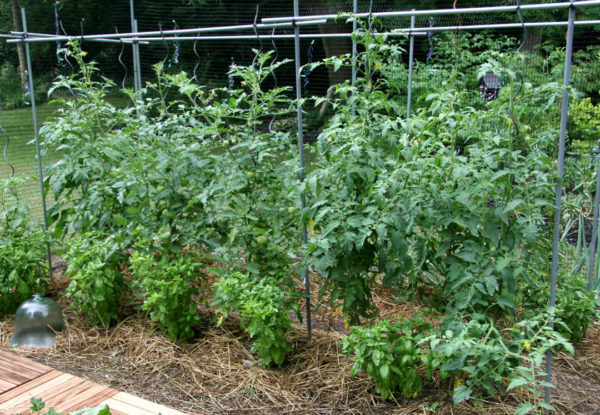
Formation of tomatoes in a greenhouse
In the northern part of the country, all varieties of tomatoes are grown indoors, including ultra-determinate and determinate varieties. But mainly indeterminate and semi-determinate tomatoes are grown in greenhouses.
Ultrachildren and children in protected conditions form in the same way as on the street. Determinate varieties in the greenhouse produce 3-4 stems.Here, tomatoes can be kept on the bushes until they are fully ripe, if there is no risk of disease.
Indeterminate tomatoes They produce the largest and most delicious fruits, but they begin to bear fruit late, so in central Russia they cannot be harvested in full.
Indeterminate varieties
Indets in the greenhouse they lead strictly to one stem; with a larger number of them, the plant is rejuvenated, flowering and fruiting are delayed, and this leads to a shortage of harvest, and more often to its complete absence.

Tomatoes grown in 1 stem
After planting the seedlings, as soon as the tomatoes take root, they begin to cut off their lower leaves: 1-2 leaves every 5-7 days. The leaves should not touch the ground; if they are too long and cannot be cut off yet, they are shortened by 1/3-1/2 of the length, and the rest is removed next time. They cut it so that a stump of 1.5-2 cm remains, then the wound quickly heals, and the stump itself gradually dries out and falls off. With this pruning, the risk of infection is minimal.
Pinching in the greenhouse is very active: 2-5 shoots appear from one axil. They are removed as they appear. When the stepson grows to 10-15 cm, it is cut off, leaving a stump of 2 cm, then no new shoots will appear in this bosom. Removing young shoots too early (less than 8 cm long) leads to intensive growth of 2-3 stepsons in the same place.
You need to remove foliage and young shoots throughout the growing season. If the stepson has managed to grow into a new stem, then it is better to cut it out, since it will not have time to produce a harvest, but will only delay its maturation on the main stem.
When the tomatoes reach the ceiling of the greenhouse, they are thrown over the trellis and sent down, continuing to pinch. If the greenhouse is large, then the plant can be placed along the trellis.At the beginning of August, the top is cut off, thereby stopping growth and directing all efforts to ripening the fruits.
If the tomato bushes are formed correctly, there should be no leaves under all the bunched trusses. In fact, by the beginning of August, tomatoes appear to be a whip, with several fruit clusters hanging on it.
Semi-determinate varieties
Semi-determinant varieties in the middle zone and to the north are also grown only in a greenhouse. These tomatoes are quite tall, they form 4-6 clusters, and then they can end at any moment, which is impossible to predict. Half-children can be either early, middle or late. If the variety is early or medium, in a greenhouse it can be grown in 2 or even 3 stems, if late, then in 1-2.
After planting the seedlings, all emerging young shoots are plucked out weekly and the lower leaves are cut off. The first stepson can be left under the second or third brush. As it grows, all the stepsons on the new shoot are cut off. When the first brush is formed, the leaves on it are also removed. On the central stem, if it is not completed, after the 5th brush another stepson is left, forming it into a stem. But if the summer is cold, then the third stem will be superfluous.
The main thing when forming half-children is not to pluck out all the stepsons. The plant may suddenly stop growing and then the yield losses will be very large.
Southern regions
In the south, ultra-determinate and determinate varieties are practically not grown, since their yield is small and the fruits are small.
How to form bushes in open ground
Almost all varieties of tomatoes in the south are grown in open ground. Indets even on the street give a full harvest.
Indeterminate varieties grown in 2, 3 and even 4 stems.The formation of tomatoes in open ground begins with regular, once every 5 days, pruning of the lower leaves. If the weather is rainy, then those leaves that touch the ground, but which have not yet reached their turn, are shortened by 1/3. The main thing is that there is no contact with the soil, otherwise early diseases of rot and late blight cannot be avoided.
The first stepson can be left already under the first brush. If the plant is weak and elongated, then remove all the stepsons up to the 2nd cluster. The remaining shoot is formed into a full-fledged stem, gradually removing its lower leaves and emerging stepsons. After 4-5 leaves, the next shoot is left, forming it in the same way.
The third stepson is left 4-5 leaves from the second. Forming into new stems, these shoots greatly rejuvenate the plant, requiring additional nutrition. Therefore, you need to regularly hill up tomatoes, stimulating the formation of new roots.
When the stem near the soil acquires a greenish-gray color and pimples appear on it, it means the plant is ready to grow a root system and needs to be earthed up.
After tying 5-7 clusters on the side shoots, they are pinched, stimulating the growth of the main stem. Without pinching, it is very difficult for tomatoes to feed all the shoots, so the fruits are crushed and there is a shortage of yield. The stepsons on the side stems are plucked out. If they are left to grow a new stem, the main one will be severely suppressed and will eventually die.
During hot and dry summers at the end of July, another stepson can be left at the top of the main stem. If the autumn is warm, it will produce a harvest in late September-early October. Of course, the tomatoes will not be as large and sweet as summer ones, but the harvest will be good.The top of the last “autumn” stepson is pinched after 3-6 brushes (depending on the weather).
Semi-determinant The varieties are very productive and in the southern regions the crop is rationed. Tomatoes are growing sparingly, leaving the first shoot under the first brush. The second shoot is left after the third brush. Then you can leave after the fifth brush, if there is one. The side stems are also not particularly plucked by the stepchildren; they are left after the 2nd, 4th, 6th (if any) brushes. This bush is enough to get a high yield of tomatoes.
Leaves are cut as usual every 5 days. They are removed on the side stems in the same way as on the main stem. There should be no leaves under the formed brushes.
Determinate and ultra-determinant varieties in the south are not planted, only the leaves are removed as needed.
Protected ground
In the southern regions, tomatoes are practically not grown in greenhouses; they are very hot there. In closed ground, either an early or late harvest is obtained. Main varieties - semi-children. In greenhouses they are formed in the same way as in open ground, but leaving stepsons through each leaf. In order for the roots to cope with such a load, the plants are regularly hilled.
Leaves are removed every 5 days. The bush should consist of shoots with established and flowering clusters and 2-3 leaves at the top of each stem.
If the plant can no longer cope with the load, the fruits are crushed or the foliage changes color and begins to wither (a sign that the above-ground part is developing to the detriment of the underground), the newly appearing stepsons are removed. If this is not enough, cut out 2-3 shoots that are not yet bearing fruit.
If this does not help, then remove all the bleached tomatoes, remove all the stepsons and the young stem, which has no more than 2 tassels.If there are no results, the plant is thrown away; it has completed its growing season and will no longer bear fruit.
Sometimes in the south, in a greenhouse, they plant determinant tomatoes. They are not taken care of at all. Their growing season is short. Fewer stepsons appear on young stems than on the main stem. The growth of side shoots depends on the development of the root system. The stronger it is, the more there are. But in children, in comparison with indets and semi-children, stepson formation is much weaker. The main attention is paid to trimming the leaves.
In the south, tomatoes grow better outside than in a greenhouse, so there is no need to create difficulties for yourself by growing them in protected soil.












 (5 ratings, average: 4,60 out of 5)
(5 ratings, average: 4,60 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush.Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush.Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.