Blackberries came to us from America, where they were introduced into cultural circulation. It is a close relative of raspberries. In the European part of the country it is found up to the Moscow region, but it forms thickets only in the south: in the Crimea, in the Caucasus. It is not grown on an industrial scale, since there are still no winter-hardy varieties.But in the gardens of amateurs it is often found, because planting and caring for garden blackberries is not particularly difficult and it is quite simple to grow it, especially in the southern regions.
|
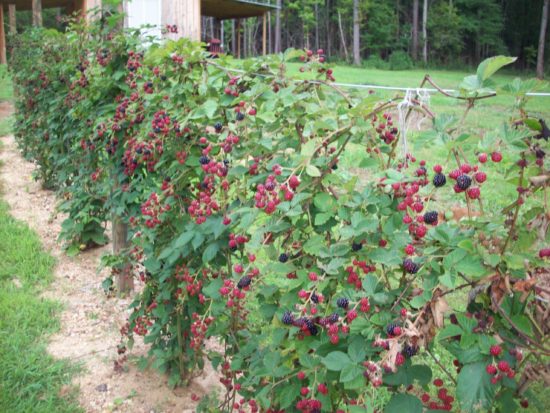
Blackberries ripening in the garden |
| Content:
|
Biological features
Blackberry is a perennial shrub whose shoots have a two-year development cycle. In the first year, the shoot grows to 2.5-4 m. In the second year, it branches, forming fruit branches on which flowers and fruits appear.
The roots are located somewhat deeper than those of raspberries, so the crop is more drought-resistant.
Blackberries are more drought-resistant and less winter-hardy than raspberries. Prefers sunny places or light partial shade, but in the Central region it does not bear fruit in partial shade. Does not grow in the shade. The erect blackberry in the middle zone freezes in winter even with mild frosts; the creeping variety can survive quite severe winters, as it is under the snow.
|
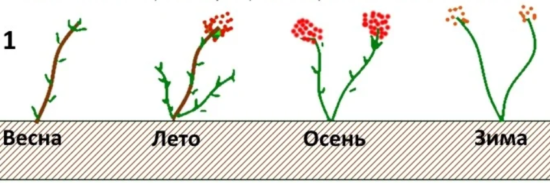
Flowering begins in mid-June, in the middle zone at the end of June. First, flowers bloom in the upper part of the shoot, then in the middle, then in the lower. The berries ripen in the same order. |
Grows well in fertile, moderately acidic soils. It can tolerate light acidification (optimal pH 5 - 6), but does not grow on more acidic soils. It responds very well to fertilizing with nitrogen fertilizers, manure crumbs, and humus. Does not tolerate weeds inside the bush and in the tree trunk.
Garden blackberries tolerate drought well without reducing yield. Does not tolerate flooding and waterlogging.Does not grow in areas with close groundwater.
Blackberries ripen very unevenly, fruiting is spread over 4-6 weeks.
In the southern regions, the first harvest can be obtained at the end of July, in the northern regions - only by the end of August, and the main harvest in mid-September. The shoots also ripen quite late, so sometimes the bush goes into winter with unripe stems and dies even under the snow. The period of active fruiting is 12-13 years.
After the harvest ripens, the two-year shoot dies. Replacement shoots and root shoots appear next to it.
Varieties of blackberries
Varieties of garden blackberries are divided depending on the nature of shoot growth and method of reproduction into:
- erect or bramble;
- creeping or sundew (dewdew);
- remontant varieties.
In the north of the non-chernozem zone, another species is found - princely or polyanica (mamura). A hybrid of glade and raspberry was bred in Finland, but it is not widespread in our gardens.
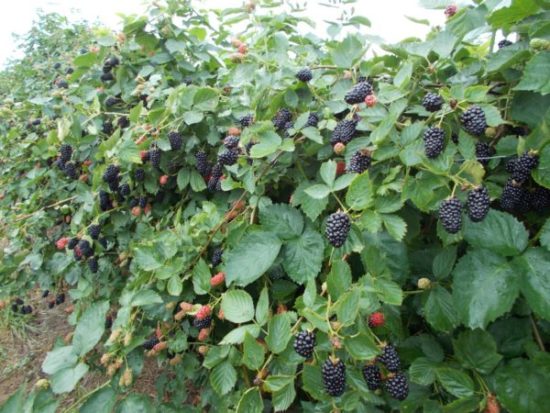
creeping blackberry or dewberry aggressively takes over the territory. Its shoots immediately form roots when they touch the ground. Without care, it forms impenetrable thickets, so it is grown only on a trellis. In the central regions it winters well under a thick layer of snow. In the south, with little or no snow cover, it requires shelter, otherwise it freezes.
|
The berries of the dewberry are larger and tastier than those of the upright varieties, and they are more productive. In addition, varieties without thorns have been developed. |
Erect blackberry or the bramble forms a bush, is more compact, not so aggressive. However, its yield is lower and it ripens later.
|
Cumanica is suitable for growing in a small area. In the south it is more winter-hardy than dewberry. |
Remontant varieties. This blackberry is completely unsuitable for the middle zone. The main zone of its cultivation is the Caucasus, Krasnodar Territory, Crimea, and the Lower Volga region. Forms a low bush (1-1.5 m). The flowers are very large (4-7 cm), bloom continuously from June until frost.
Fruiting occurs on the shoots of the current year. Requires shelter for the winter.
Growing and caring for blackberries
Blackberries are not a crop for active cultivation in the middle zone. For her, the border of cultural cultivation runs along the north of the Chernozem zone.
Landing place
Blackberries, like raspberries, are tolerant of slight acidification of the soil. The crop does not grow on alkaline or strongly acidic soils.
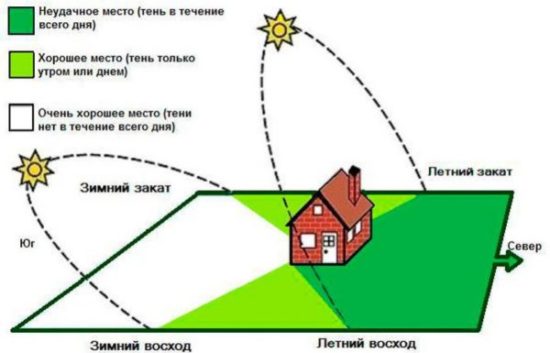
In the middle lane The place for planting blackberries should be the sunniest, so that both the berries and shoots have time to ripen during a short warm period. The growing season of the bush begins at a temperature of +10°C.
If the sun does not illuminate the plot all day, neither the berries nor the shoots will ripen. And those berries that ripen will not have time to accumulate sugars and will be sour.
The place should dry out as quickly as possible in the spring, and during summer showers there should be no stagnation of rainwater.
|
The plot must be protected from cold northern winds. It is desirable that it should not be blown through at all. |
In the southern regions Can be planted in light partial shade. In the shade, young shoots stretch out, shading fruit-bearing ones, develop worse and do not ripen by winter. As a result, they freeze out in winter. Since the young shoots shade the fruiting shoots, the yield decreases.
It is necessary that the place is well soaked during rains, but without prolonged stagnation of water. Then you won’t have to water the plot very often.
Soil preparation
The planting pit is prepared 10-14 days before planting. Its size is 50x50 and depth is 30 cm.10 kg of rotted manure or compost, 3 tbsp. superphosphate and 2 tbsp. potassium sulfate. Chlorine fertilizers are not used, since blackberries do not tolerate chlorine, the planted seedling will wither.
|
Instead of mineral fertilizers, you can use 1 cup of ash per pit. All applied fertilizers are mixed with the soil. |
On carbonate soils, peat is additionally used to acidify the soil, since blackberries do not grow well on alkaline soil. Along with it, microfertilizers with a high content of iron and magnesium are applied, since on such soils the crop is affected by chlorosis due to a lack of these elements.
Garden blackberries can be planted without any fertilizers, and they can be added later by digging around the perimeter of the bush. The culture will grow without problems in this case too.
When planting in furrows, dig a furrow 10-12 cm deep and apply the same fertilizers. Fertilizers are applied here immediately, since later the bushes will grow, and additional digging can damage the root system.
Planting blackberries in spring
Garden blackberries are an exception to the berry crops. It is planted in the spring, because in the fall, due to the insufficient maturation of the seedlings, they do not take root well and usually freeze out in the winter.
Erect varieties of blackberries are planted at a distance of 90-110 cm from each other, creeping ones - 120-150 cm. Varieties that produce abundant root shoots are planted in a strip along the borders of the site or as individual plants, otherwise, when planted in groups, impenetrable thorny thickets will appear in 2-3 years . Varieties with low shoot-forming ability are planted in stripes along the borders of the site or in groups of 2-4 plants.
The dewberry is immediately tied to a trellis, otherwise the shoot, in contact with the soil, will begin to take root.
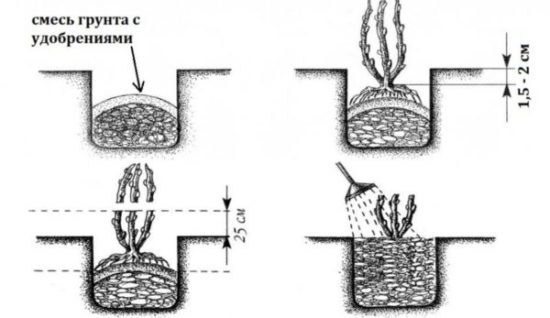
Garden blackberries are planted in early spring before the buds open.Good planting material has 3-4 roots 10-15 cm long or a root lobe of the same length, 1-2 green annual shoots and 1-2 formed buds on the rhizome (from where young shoots will come).
|
The seedling is placed vertically in the planting hole so that it is well lit from all sides, the roots are straightened, directing them in different directions, covered with a layer of 4-6 cm of soil and watered abundantly. |
When planting in furrows, the cuttings are placed at the bottom of the furrow and covered with soil. The bud on the rhizome at the base of the stem should be sprinkled to a depth of 4-5 cm. During early summer frosts, the blackberries are mulched with peat or covered with a double layer of spunbond.
Immediately after planting, the seedlings are watered. In hot and dry weather, watering is repeated after 3-4 days. The irrigation norm is 3-4 liters of water per bush.
You need to plant several different varieties to ensure cross-pollination.
How to care for blackberries
Caring for blackberries depends on the stage of development of the bush.
Seedling care
In the year of planting, a blackberry seedling produces 1-3 young shoots. After this, in the middle zone, the old shoot is cut off near the ground so that the young ones have time to grow and ripen. In the south, the old shoot is left, and it and the new shoots will have time to ripen before frost.
After planting in dry weather, watering is carried out once every 3-5 days for 2-3 months. Then water once every 5-7 days. When it rains, watering is not carried out. Water with warm, settled water.
Blackberries, as a southern crop, do not tolerate cold water well, especially in hot weather, this slows down growth.
The soil under the bushes is kept free of weeds. Blackberries are more demanding than raspberries when it comes to soil cleanliness. Annual weeds slow down the growth and ripening of shoots, and perennial weeds, especially cowgrass and wheatgrass, can suppress the growth of a bush.Therefore, the soil is regularly loosened, weeds and soil crust are removed after watering and rain. Loosening is done to a depth of 4-6 cm; if you loosen deeply, you can damage the roots. In autumn, the ground under the bushes is hoeed to a depth of 7-9 cm, carefully selecting the roots of the weeds.
|
Instead of loosening the bushes, you can mulch with straw, peat-humus crumbs, and leaf litter. On highly alkaline soils, use pine litter, as it acidifies the soil. |
Along the perimeter of the bush at a distance of 0.4-0.6 m you can sow green manure: oilseed radish, white mustard, but in no case cereals. Oats and rye drown out wheatgrass, but create a very dense turf, depriving the seedlings of sufficient access to oxygen. The culture requires clean, loose soil.
In the first 2 years, fertilizers are not applied, since the crop has enough of what was applied during planting.
Caring for a fruit-bearing plantation
A fruiting bush should consist of 4-5 strong shoots of the second year and 5-6 young green shoots. In the south, stronger bushes contain 5-7 biennial shoots and 7-8 replacement shoots. An extra young shoot is left just in case one suddenly dies. They get rid of it in the spring, cutting out the weakest and poorly overwintered.
Watering
In the south, during the berry-filling period, blackberries are watered once every 5 days if the weather is dry. During drought, watering is increased to 2 times a week. If it rains and soaks the soil well, then watering is not necessary.
|
During the period of intensive shoot growth, water once a week. Watering norm for young bushes is 5-7 l, for bushes older than 3 years 10 l. |
In the northern regions, if there is no rain for more than 14 days, blackberries are watered. In hot and humid summers, watering is not necessary. Short summer showers, as a rule, do not wet the soil, so regular watering is carried out once every 2 weeks.The water must be at least 17°C. Cold water greatly slows down the growth of shoots and the ripening of berries, which in the north can lead to a significant reduction in yield.
Garden strawberries have the greatest need for water during the ripening period.
Weeding
The berry harvest depends very much on the cleanliness of the soil. Weeds compete with crops for nutrients. And since the rhizomes and roots of blackberries are in the same soil layer with the roots of weeds, especially perennials, they experience a lack of nutrition. Therefore, the soil is hoeed 5-7 times per season to a depth of 10-12 cm, and under the bush itself it is loosened to 4-6 cm, weeding out all the weeds. When growing blackberries in strips, the row spacing is also weeded and loosened.
Blackberry feeding
An adult fruit-bearing bush needs fertilizers, both organic and mineral. Organics cannot completely replace complex mineral fertilizers. Their regular application is the key to a high yield.
|
During the season, 4-5 feedings are carried out, alternating organic and mineral water. Blackberries most of all need nitrogen, so it is applied every time with the exception of the last autumn feeding. |
- 1st feedingand in the initial growing season. Rotted manure is dug in around the perimeter of the bush (1 bucket per bush). At the same time, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied, preferably in liquid form.
- 2nd feeding during the period of budding and flowering. At this time, the crop most often lacks iron and magnesium. The lack of iron is especially pronounced on alkaline soils, magnesium - on acidic soils. With a lack gland chlorosis of the upper leaves appears. They turn yellow, but the veins remain green. In case of shortage magnesium The leaves of the middle tier turn yellow, mostly closer to the top, but not the top ones. Both tissues and veins turn yellow. Microfertilizers containing iron and magnesium are applied (Kalimag, iron chelate, Agricola). At the same time, water with humates or nitrogen fertilizers (urea, ammonium sulfate) and ash infusion.
- 3rd feeding when pouring berries. Add microfertilizers or ash. In the southern regions, use a watering can of humates or nitrogen fertilizer. In the north, nitrogen fertilizers are not used during this period. They cause strong growth of shoots, which definitely will not have time to ripen before the cold weather, and feed them with ash.
- 4th feeding after harvest. In the central region it is the last (in terms of timing it is approximately the beginning of September). Phosphorus (30 g of superphosphate per bush) and potassium fertilizers (40 g per bush) are applied. It is better to apply dry to a depth of 10-12 cm. If necessary, use deoxidizers (lime, ash) or alkalizers (pine litter, peat). In the northern regions, manure is buried around the perimeter of the bush. In the southern regions they feed with ash and humates.
- 5th feeding It is held in the south in late autumn, when the growing season ends. Manure is dug in around the perimeter of the bush if it was not applied in the spring. Potassium-phosphorus fertilizers are also dug in.
How to trim blackberries
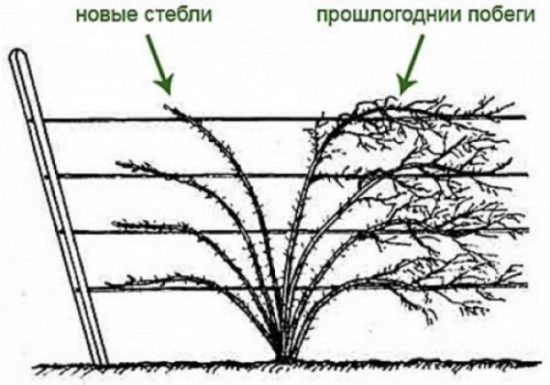
Blackberries are pruned in autumn and spring. In the fall, after harvesting, old fruit-bearing shoots, as well as diseased and pest-affected ones, are cut out. Remove excess root growth. Pruning is carried out at soil level, leaving no stumps.
|
The fruit-bearing shoots are cut out at the root in the fall. |
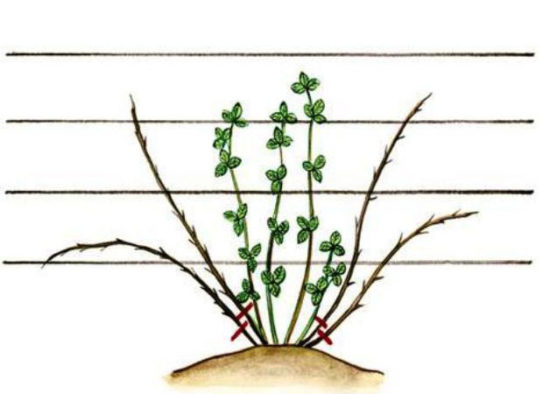
The main pruning is carried out in mid-May (for the middle zone at the end of the month). For brambles, 3-4 replacement shoots are left, for dewberries, 5-7.
The optimal number of shoots in a bush is 5-7; if more, the bush becomes thicker, shading and, as a result, the yield decreases.
The distance between adjacent shoots should be 8-10 cm.
At the end of July, all weak growth is removed. In addition, at the end of May and at the end of September (in the middle zone at the end of June and at the end of August), the tops of young shoots are cut off. As a result, the stems thicken, which promotes the formation of more flower buds. The first time, green shoots are shortened to a length of 0.8-0.9 cm. The second time, they are shortened by almost half so that they have time to ripen better before frost.
In July, to stimulate further fruiting, the tops of fruiting shoots are pinched. The main fruiting of blackberries occurs on the side branches, and pinching stimulates their formation. Shorten the tops by 20-25 cm.
Repairing blackberry
It bears fruit either on this year's shoots, or produces 2 harvests on both biennial and annual shoots.
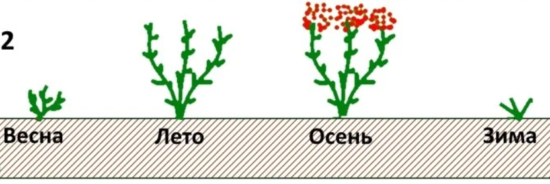
To obtain one harvest, blackberries are completely mowed down to the roots in the fall. Only the roots and rhizomes overwinter. In the spring, young shoots appear, which, when they reach 1 m in height, are shortened by 20-30 cm. As a result, abundant fruiting begins on them in the same year. The berries are juicy, large and there are more of them than on ordinary summer blackberries. Fruiting begins later (in mid-late July) and lasts until late autumn.
|
Formation of a remontant blackberry bush for one harvest |
To obtain a summer and autumn harvest, green shoots are cut by 3/4 in the fall, leaving 30-40 cm above the ground. This blackberry behaves like ordinary varieties, bearing fruit on the shoots of the second year. At the same time, the root shoots are allowed to develop.In mid-May, weak branches are removed, the rest are cut off by 1/3. Such shoots will grow over the summer and begin to bear fruit at the end of August.
|
Forming a bush for two harvests (everything is exactly the same as with remontant raspberries) |
Remontant varieties of blackberries are not intended for growing in the middle zone.
Features of autumn planting
The planting hole is prepared 1-2 days before planting or immediately before it. Dimensions 50x50, depth 40 cm. Phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are added to the prepared planting hole: 1 cup; It is better that it contains microelements, but always without nitrogen. Nitrogen is not needed for blackberries at this time. Instead of mineral water, you can add 2/3 cup of ash. Pour out a bucket of water and plant the cutting.
When planting blackberries in the fall, it is not advisable to add organic matter directly into the hole. Various pests overwinter there and can damage the roots. It is applied for general digging in 1-1.5 months at the rate of 10-15 kg/m2.
Planting is carried out at an angle in the direction where they will be bent for the winter (when planting in spring, the seedling is placed straight).
When planting a seedling with an open root system, the buds on the rhizome should face upward. When planting with the buds down in the spring, young shoots will appear much later, and the growth will be much weaker. Blackberries, unlike other berries, do not need to be covered heavily with soil, otherwise in the spring the young shoots will not be able to reach ground level and will die, followed by the death of the seedling.
|
The shoot is not pruned. When cold weather sets in, the seedlings are covered. Place a plastic vegetable box over them, and cover the top with spunbond, rags or film. |
Sprinkle the roots with a layer of 4-5 cm, but do not cover the stem itself with soil. The seedling should be in a hole 3-5 cm deep.This is done so that next spring, when young shoots appear, soil can be added to the roots. Then they will be deeper and will not be dried out by drought.
The timing of planting blackberry seedlings in the middle zone is the whole of September, in the south - mid-October. In any case, planting should be carried out 10 days before the onset of cold weather.
Trellis and garter of shoots
Typically, there are 3 methods of gartering blackberries on a trellis:
- fan;
- weave;
- incline.
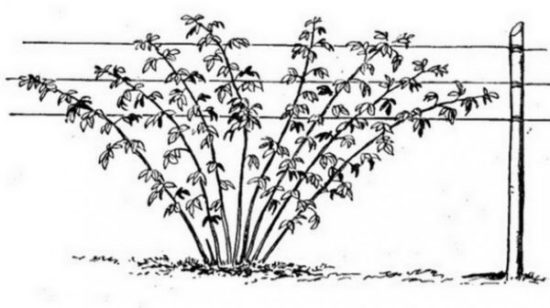
Fan method. Fruiting shoots are tied with a fan to the lower wires in the trellis, the distance between the branches is 20-25 cm. Annual shoots are also tied with a fan to the top wire.
|
Fan garter shoots |
Weave. Fruiting shoots are intertwined with the 1st and 2nd tiers of the trellis, annual shoots are tied to the upper tier without interlacing.
|
If the trellis is low, then you can use the method of intertwining shoots |
Incline. Can be one-sided or two-sided:
- one-sided - fruiting shoots are tilted to one side and each is tied to a separate wire. One-year-old shoots are tilted in the other direction and tied, also, each separately;
Inclined garter method
- double-sided - fruiting shoots are tilted in different directions and each is tied to a separate wire. Annual shoots are tied to the upper tier of the trellis without tilting.
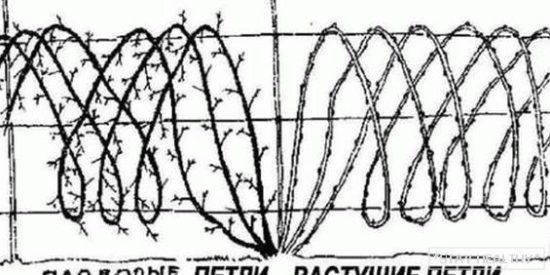
In addition to tying a trellis to a trellis, blackberries can be tied without support (except for the creeping variety):
- all the shoots of the bush are collected together and tied at the top;
- The bush is divided in half, half of the shoots are connected at the tops with the same half of another bush, forming arches.
With such a garter, the yield is reduced, especially in the northern regions.The shoots are illuminated unevenly, the ripening of the berries is delayed, sugars do not accumulate in them and they are sour. In the southern regions, such a garter is acceptable, especially if the blackberries are not shaded by anything.
Simultaneously with the garter, the tops are cut off by 12-14 cm. This promotes active branching and increased yield.
Blackberry propagation
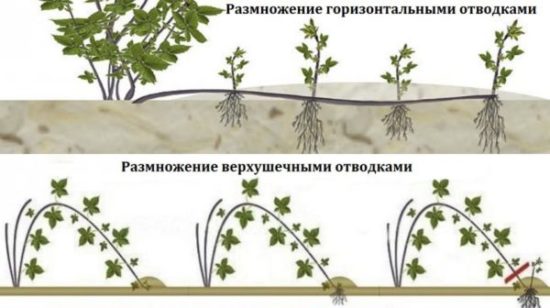
The main methods of propagating the crop are by digging in the tops and cuttings.
Digging in the tops of heads
The method is excellent for creeping varieties of blackberries that do not produce root shoots. As soon as it touches the ground, it begins to take root. It is also used for brambles.
It is better to root in containers to obtain a seedling with a closed root system; planting material with an open root system takes root much worse when planted in a permanent place. It is necessary to bend down the tops in the middle zone at the end of July, in the south - mid-late August.
Small holes are dug near the bush, where containers with a hole at the bottom, filled with fertile soil, are placed. The green tops of annual shoots 30-35 cm long are wiped off from the leaves so that they do not rot in the ground, bent into a container and completely covered with fertile soil with a layer of 10-12 cm. The container and the ground around it are moistened. The upper buds begin to take root; no care other than watering is required. Rooting lasts 30-35 days.
|
When young seedlings appear, the top is cut off from the mother plant. The next year, the containers are dug up and the young seedlings are placed in the right place. |
Layerings. Tops 25-30 cm long are cleared of leaves, bent to the ground and 3-4 buds are covered with soil in a layer of 10-12 cm. 3-4 upper buds with leaves are left above the ground.After 30-40 days, the cuttings take root and produce shoots, which this year do not reach the soil surface.
The next year, 3-4 young shoots (their number is equal to the number of sprinkled buds) sprout. At a height of 10-15 cm, they are dug up and planted in a permanent place.
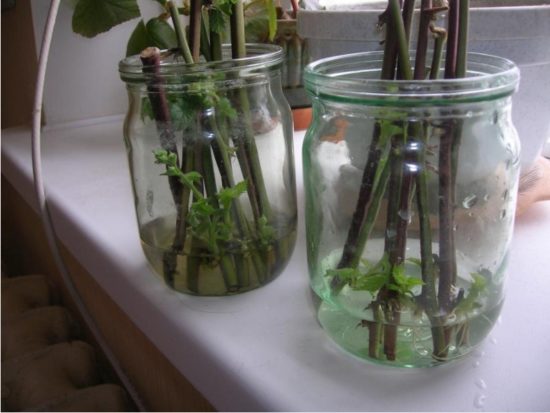
Propagation by cuttings
Also, usually used for dewberries. The most convenient time to take cuttings is during summer pruning of blackberries. After trimming the tops, single-bud green cuttings are cut from them. The upper third of the shoot, except for the 2 uppermost buds, is suitable for cuttings.
The cutting consists of part of the stem, bud and leaf. Under the bud, at a distance of 3 cm, a cut is made at an angle of 20-30°. The cuttings are rooted in separate containers (seedling containers can be used). The soil must be fertile. The containers are placed in a greenhouse. For rooting, cuttings require a humidity of 97-100%. Therefore, the greenhouse is not cross-ventilated; only the windows or door are opened on one side. To increase the humidity in the greenhouse, water the ground and path. The soil in containers should be moist.
|
Blackberry cuttings can also be germinated in water, as in the photo. |
Cuttings take root in 30-35 days. They are covered for the winter, and in the spring they are grown to 10-15 cm and planted in a permanent place.
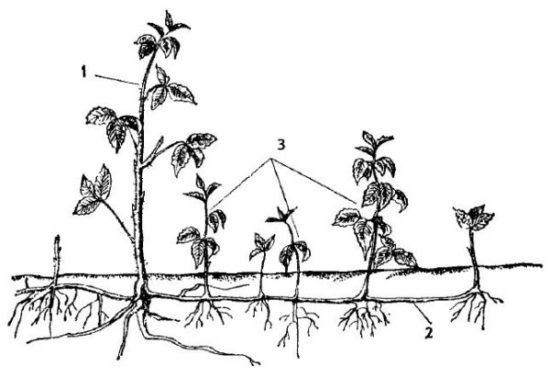
Reproduction by offspring
Drupes are usually propagated. It produces a lot of root shoots, their number depends on the variety and care. To obtain planting material, choose healthy, abundantly fruiting bushes with large, tasty berries.
|
Young offspring are dug up in May-June with a clod of earth, when their height is 10-15 cm and transplanted to a permanent place. |
They can be left until autumn, and at the end of August they can be dug up and planted in a permanent place. When planting in autumn, the top is cut off, leaving a total shoot length of 30 cm.
Preparing for winter
Blackberries must be covered. In the middle zone, after harvesting at the end of September and beginning of October, when it is still warm and the shoots have not fully matured and have not shed their leaves, they are bent under a brick or hook. In the south this is mid to late October. The shoots should not be completely woody, otherwise when they become woody they become brittle and break easily. In mid-October (in the south at the end of October and beginning of November), before the onset of stable cold weather, the bushes are covered with straw, sawdust, leaves or just earth.
|
Under cover, blackberries overwinter well even in the north. |
Blackberries are opened in the spring, when the temperature reaches above zero at night (the middle zone is the middle of the second ten days of May). After opening the crop, it is immediately covered with spunbond so that in the north it does not freeze during frosts, and in the south it does not dry out in the sun. When leaves appear on the shoots, the culture is finally opened. But in the northern regions, during summer frosts, it is still necessary to cover it with spunbond at night.
Don't forget to read:
New, productive (up to 20-30 kg per bush), thornless varieties of blackberries ⇒
Conclusion
If you create the right microclimate for garden blackberries, they are more unpretentious than raspberries and are less affected by diseases and pests. Now there are thornless varieties, which are much easier to care for. Varieties have also been bred that winter well in northern regions and produce quite sweet berries, despite the insufficient number of sunny days.












 (5 ratings, average: 4,20 out of 5)
(5 ratings, average: 4,20 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
Caring for garden blackberries consists of regular watering, loosening the soil, weeding (if for some reason you have not mulched the area), fertilizing, as well as taking preventive or, if necessary, therapeutic measures to combat diseases and pests and, in addition all of the above, in pruning and shaping bushes. As you can see, planting and caring for blackberries is labor-intensive and requires special knowledge, so take our advice seriously.
I have been growing blackberries without thorns for ten years, if not more. I remember my husband brought it from a business trip (from Moscow). At first I tried not to cover it for the winter, but during the cold winter, the entire above-ground part froze. But then I started from the roots - I had to breed it almost from scratch. It reproduces itself from the root with new shoots, which I dig up and give to my friends. And for the winter I bend it carefully (it is not as flexible as a grapevine) and cover it with roofing felt and boards.