Rules for feeding an apple orchard
Apple trees are very susceptible to fertilizing. The timely entry into fruiting and the quality of the harvest depend on them. It is very important to feed apple trees in a timely and competent manner in spring, summer and autumn.
| Content:
|
|
What is the best way to feed an apple tree? |
Types of fertilizers for feeding apple trees
To feed apple trees, both organic and mineral fertilizers are used. Trees respond very well to organic matter, but when there is an excess of it, they begin to fatten: they produce a lot of fatty shoots (tops), but practically do not bloom or bear fruit. Organic matter has a beneficial effect not only on tree growth, but also increases soil fertility. The fertilizer has a long shelf life; with a single application, apple trees can receive nutrients from it for 1-2 years.
Mineral fertilizers cause active growth of trees. The effect of mineral water is short-lived: it lasts for 2-3 months, and then the apple trees need feeding again. But we can’t do without it.
Organic fertilizers
|
In autumn it is necessary to feed apple trees with organic fertilizers. |
Manure. This is the best organic fertilizer not only for trees, but also for berry bushes. Semi-rotted manure is applied in the fall for digging. You can, of course, use fresh, but seal it in late autumn, when root growth stops (late October-November).
Horse dung. It is more concentrated than mullein and is used only in its semi-rotted form. They dig in in the fall along the perimeter of the crown.
Pig manure It is not used either fresh or half-rotted. It is very fatty and even its delivery to the roots in the form of a solution can cause the death of young sucking roots. And this leads to a delay in the onset of fruiting in young apple trees or its absence in adults. Young seedlings may even die.
Bird droppings. Also very concentrated.Apply only in late autumn in half the dose.
Peat. This is not a fertilizer, but a deoxidizer. It is used on alkaline soils to deoxidize them every 3-4 years. It is dug in around the perimeter of the tree trunk circle.
Mineral fertilizers
|
Mineral fertilizers must be applied very carefully and strictly according to the instructions. |
Nitrogen
Apple trees are fed with nitrogen in spring and early summer to improve shoot growth. Their dose should not be exceeded, otherwise the shoots will stretch out and ripen for a long time, and eventually freeze out in the winter.
Nitrogen should be given only after the threat of frost has passed (in the south this is mid-May, in the central and northern regions - after June 10). Nitrogen reduces the resistance of apple trees to frost by 1.5°.
If there is no organic matter, then additional nitrogen fertilizers are applied in mid-September for the ripening of young shoots. Autumn nitrogen fertilizing does not cause vigorous growth. Fertilizer is spent on other purposes.
Phosphorus
They are introduced in the second half of summer, when the growth of young roots begins. Phosphorus is not contained in any type of soil in sufficient quantities for cultivated varieties of apple trees, so its use is mandatory. Water-insoluble phosphorus fertilizers are laid out on the soil surface and sprinkled with soil. Phosphorus, even from insoluble granules, penetrates into the zone of sucking roots, but more slowly compared to other elements.
Potash
Potassium fertilizers are necessary for apple trees to ripen shoots and form fruits. Potash fertilizing is done 2 times during the growing season. Potassium is applied for the first time in the spring when the leaves are blooming. The second is done on young non-fruiting apple trees in early August. Feeding fruit-bearing apple trees with potassium fertilizers depends on the variety.It is given during the period of the most intense fruit filling:
- on summer varieties in the first ten days of July;
- in autumn - in mid-August;
- in winter - at the beginning of September (in the south it is possible in the middle of the month).
When applying potassium in September (for winter varieties), it can be combined with nitrogen fertilizers or manure.
Microfertilizers
They are fertilized in a young garden in mid-June, in a fruit-bearing garden at the time of intensive growth of ovaries (2nd decade of June - 1st decade of July, depending on the variety). If the tree at this moment is acutely lacking in microelements, it begins to drop the filling apples one after another.
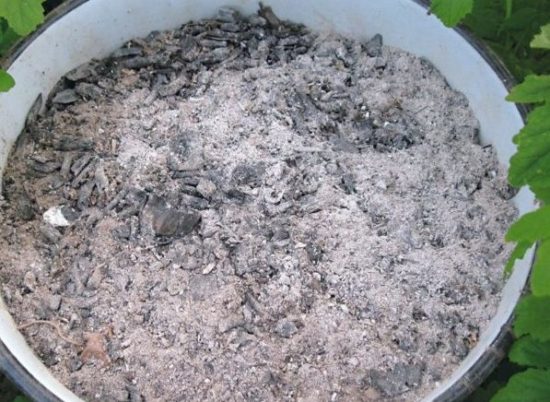
Phosphorus-potassium and microfertilizers can be replaced with ash. It contains phosphorus, potassium, and various microelements in the required quantities. It cannot be used only on alkaline soils, since the ash alkalizes them even more.
|
Ash is an excellent substitute for mineral fertilizers |
The need for apple trees in nutrients
The need for mineral elements in an apple tree depends on the phase of development of the apple tree. When young, she needs the most nitrogen, followed by phosphorus and potassium. Fruit-bearing apple trees have the greatest need for potassium, then nitrogen, and their least need for phosphorus. Regardless of the stage of development, cultivars require microelements. The need for them increases when they enter the fruiting period.
From every m2 nutrition, the tree tolerates 17 g of nitrogen, 7-8 g of phosphorus at a young age and 4-5 g at the fruiting stage. Potassium during the growth period requires 10-13 g, when entering fruiting 20 g.
In addition to macroelements, the apple tree needs microelements:
- iron;
- magnesium;
- calcium;
- boron;
- copper;
- manganese;
- zinc;
- molybdenum.
The rate of fertilizer application is calculated based on the feeding area of the apple tree.On average, a tall fruit-bearing tree has a feeding area of 16-20 m2. For the apple tree season with a feeding area of 20 m2 12 spoons of nitrogen are required (2 spoons per 10 liters of water), 9 spoons of superphosphate and 15 spoons of potassium sulfate.
Microfertilizers are dissolved according to the instructions and sprayed on the leaves. Root feeding with microfertilizers should not be done.
Express method of feeding an apple tree video:
Rules for applying fertilizers
Correct and timely application of fertilizers is the key to tree longevity and high yields.
- The best fertilizer for an apple tree is organic. It contains all the necessary batteries. There is enough nitrogen in organic matter for apple trees. But poor soils may lack some element, most often phosphorus or potassium. Then this element is added to organic matter in the form of mineral fertilizers. You can use ash instead of mineral water; it contains enough phosphorus and potassium and many microelements, but it does not contain nitrogen. Ash can be mixed with humus and compost. But it cannot be applied with fresh and half-rotted manure. In this case, it is sealed separately or liquid fertilizing is carried out.
- Mineral fertilizing should be done very carefully. Most mineral fertilizers acidify the soil. Even trees that initially developed well are suppressed when only mineral fertilizers are used. Mineral water, especially nitrogen fertilizers, causes short-term explosive growth, after which the effect fades away and the tree again experiences a deficiency of nutrients. With organic fertilizing, this effect is not observed. Organic matter not only affects the tree, but also increases soil fertility and improves its structure, which is much more important for fruit trees.It is permissible to use mineral water in the absence of organic matter, but it is impossible to keep the crop on mineral fertilizers alone. They are applied as additional fertilizing during the growing season.
- Feeding should be timely. The best time to apply organic matter is the beginning of October (and potassium-phosphorus fertilizers, if organic matter is not available). Digging in manure allows young roots to absorb some of the nutrients and better prepare for winter. At this time, apple trees experience a severe nitrogen deficiency, and the roots that grow in August-September effectively absorb it.
- It is better to fertilize apple trees little by little; you should not immediately apply concentrated fertilizing. The tree trunk circle is divided into 3-4 parts and organic matter is added annually to only one part of the circle. This technique is very effective. Roots cut when digging fertilizer are quickly restored and entwine organic matter from all sides. When fertilizer is applied evenly along the entire perimeter of the crown, the cut roots take much longer to recover, and this is a great stress for the tree. In addition, fragmentary annual application of organic matter prevents fattening of the apple tree, when the fruit-bearing tree stops bearing fruit and begins to intensively grow shoots over several years.
Organic matter is not introduced into the tree trunk circle, but, if possible, along the edge of the crown projection. This is where the largest number of sucking roots are located.
Feeding a young garden
Feeding seedlings depends on the type of soil. On chernozems, if all the necessary fertilizers were applied during planting, they do not need to be applied the next year. On poor soils, fertilizing is required. When planting seedlings in the fall for the next year, liquid organic root feeding is applied at the beginning of summer.A shovel of manure is filled with 15-20 liters of water and left for 12-14 days. 1 liter of infusion is diluted in 10 liters of water and watered. On very poor soils, simple superphosphate is added to the manure infusion. Fertilizer consumption rate:
- for an annual seedling, 2 buckets of solution and superphosphate at the rate of 2 tbsp. l. for 10 liters of water;
- for a two-year-old seedling, 3 buckets of solution, the rate of superphosphate is the same;
- for a three-year-old tree, 4 buckets of solution and the same dose of superphosphate.
In the absence of organic matter, it is replaced with nitrogen fertilizers. For 10 liters of water, take 2 tbsp for an annual tree. l. fertilizers, for a two-year-old 3, for a three-year-old 4 tbsp. l. on a bucket of water.
When planting seedlings in spring, the first fertilizing is carried out the following year.
Seedlings are not treated with microfertilizers. Although adding ash in addition to manure, especially on poor soils, has a very good effect on the development of a young tree.
How to feed young apple trees
Young, but not yet fruiting apple trees, feed 1-2 times per season. If organic matter was added in the fall, then fertilizers are applied in early August, when active root growth begins. Apple trees require potassium and phosphorus at this time.
|
The best feeding is an infusion of ash. 4-5 glasses of ash are infused in 10 liters of water for 24-48 hours. 1 glass of infusion is diluted in 10 liters of water and watered. The consumption rate is 4-5 buckets per apple tree. |
This fertilizing should not be carried out on alkaline soils, since ash alkalizes the soil, and this inhibits the growth of fruit trees.
In the absence of ash, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are used with the addition of microfertilizers. 2 tbsp. l. superphosphate (preferably simple, since it dissolves better in water) and 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate (micropreparations are added according to instructions) per 10 liters of water.The consumption rate is 6-8 buckets per tree.
If there are no soluble fertilizers (well, or water at the dacha, anything can happen), then dry fertilizing is carried out. Take a complex fertilizer containing phosphorus and potassium with the addition of microelements. A furrow 8-10 cm deep is made along the perimeter of the crown, fertilizer is poured there and covered with earth. Over time, with watering or precipitation, it will reach the depth of the sucking roots. For feeding, 3 tbsp is enough. l. superphosphate and 1 tbsp. l. potassium It is not sealed along the entire perimeter, but like organic matter in some part under the crown.
|
Nitrogen and potassium fertilizers are used as a substitute for organic matter in the spring. For 10 liters of water take 2 tbsp. l. nitrogen fertilizer (urea, ammonium sulfate, etc.) and 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate. The solution consumption rate is 4-5 buckets per tree. |
If organic matter was not added in the fall, then additionally in spring it is necessary to do one more feeding. At this time, either manure is applied in half the dose, and the rest is applied in the fall, or, in its absence, mineral water is used. The spring norm for half-rotted manure is 3-4 buckets per tree. It is dug in half a spade's length.
Feeding calendar for a young garden
- Main. Autumn application of organic matter.
- Additional. After the leaves bloom, either manure or mineral fertilizers are applied (if organic matter was not applied in the fall).
- Main. In August, they are fed with phosphorus-potassium fertilizers with the addition of microelements.
Feeding fruit-bearing apple trees
Fruiting apple trees require more fertilizer than a young orchard. Their timely application reduces the phenomenon of periodicity of fruiting.
Autumn feeding
Basic feeding is still the autumn application of organic matter. The application rate depends on the variety:
- for low-growing varieties, 4 buckets of manure are enough;
- for medium-sized children 5-7 buckets;
- for tall people 8-10 buckets.
The timing of application depends on the timing of fruiting. For summer varieties it can be applied at the beginning of September, for autumn varieties - at the end of September, for winter varieties - after harvesting (usually the end of October).
If there is no organic matter in the fall, no mineral water needs to be added. It will no longer be absorbed by the roots and will only be washed into the lower soil horizons.
Spring feeding of apple trees
This is carried out even if manure has been applied since the fall. It is done during the leaf blooming period. At this time, trees are in dire need of nitrogen, and the need for potassium is also high. Top dressing can be both root and foliar.
It is best to feed with infusion of manure. A shovel of fresh manure is filled with 20 liters of water and left for at least 12-14 days, stirring regularly. 1 liter of the prepared solution is diluted in 10 liters of water and fed to fruit trees. Consumption rate of the solution for one fruit-bearing apple tree with a feeding area of 20 m22 16-18 buckets. But the effect of edge feeding should be taken into account. If along the perimeter of the crown there are beds with vegetables that are regularly fed, then the dose of feeding is reduced to 10-12 buckets.
When applying manure in the fall, you can feed it with mineral water in the spring. During a wet spring, the granules are laid out around the perimeter of the crown, embedded shallowly in the soil. If the spring is dry, then the apple trees are treated with a solution of nutrients. For foliar treatment, the dose of fertilizer is reduced. For 10 liters 3 tbsp is required. l. urea and 0.5 tbsp. l. (level spoon) potassium sulfate. The resulting solution is sprayed onto the leaves of the apple tree.
Feeding with microfertilizers
It is carried out in mid-late June at the time of the beginning of intensive growth of the ovaries.With a lack of microelements at this time, a large number of ovaries fall off, and the taste of the rest deteriorates. Treatment is carried out either with an infusion of ash or with microfertilizers containing microelements in chelated form.
The apple tree is sprayed with the working solution in cloudy weather or in the evening. The concentration of the solution for foliar treatment should be 10 times weaker.
Of the ready-made microfertilizers, the most suitable are Uniflor-micro, Biopolimik complex, Microflor for gardening, berry and ornamental plants, etc.
Don't forget to read:
How to care for young apple trees in spring, summer and autumn ⇒
Late summer feeding
It is carried out in August, at this time fruiting apple trees require a large amount of potassium. 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate is diluted in 10 liters of water. Water the trees along the perimeter of the crown. On poor soils, you can add 0.5 tbsp superphosphate to potassium. l.
Feeding calendar for a fruit-bearing garden
- Main. Autumn application of organic matter.
- Additional. After the leaves bloom.
- Main. Treatment with microelements regardless of whether the apple trees bear fruit this year or not.
- Additional late summer in years of intensive fruiting.
Don't forget to read:
How to care for fruit-bearing apple trees throughout the year ⇒
How to feed columnar apple trees
Columnar apple trees are fed 4 times per season. Despite the small size of the batteries, they carry a lot.
- First feeding done during bud break. At this time, trees need nitrogen. 2 tbsp. l. nitrogen fertilizer is dissolved in 10 liters of water. One tree requires 7-10 liters of solution.
- 2nd fertilizing is carried out after flowering. For 10 liters of water take 2 tbsp. l. nitrogen and 1 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate.Colon trees need a lot of potassium sulfate, because despite the small size of the trees themselves, they have fairly high yields, so potassium is needed in large quantities.
- 3 times Apple trees are sprayed with microfertilizers at the end of June, when the ovaries are growing intensively.
- 4 times add nutrients in mid-July. For 10 liters of water take 0.5 tbsp. l. superphosphate and 0.5 tbsp. l. potassium sulfate. Apple trees are watered along the perimeter of the crown.
From mid-July, all fertilizing is stopped, as winter hardiness of apple trees decreases due to the high concentration of nutrients in the soil.
|
Colonies also need manure. But it is introduced in late autumn, when the trees have gone into winter dormancy. Otherwise, it will provoke new growth of shoots, the tree will not prepare for winter and will freeze. For one apple tree, you need to apply 2-3 buckets of manure around the perimeter of the crown. The perimeter of the crown of the columns is the trunk circle. Application deadline is late October-early November. |
Feeding calendar for columnar apple trees
- Main. Add organic matter in the first half of November.
- Additional spring nitrogen, if manure was not applied in the fall.
- Mandatory. Treatment with microelements at the beginning of intensive growth of ovaries.
- Mandatory. Phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are given in mid-July.
How to feed columnar apple trees:
Lack of nutrition
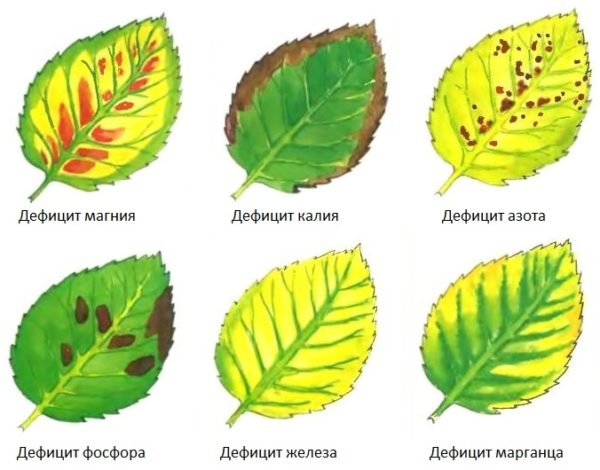
A lack of nutrients always appears on the leaves of an apple tree. A deficiency of any macronutrient (NPK) is typical for certain types of soil. The lack of microelements is felt by cultivated varieties in almost all types of soils.
Nitrogen deficiency
The leaves become smaller and lighter, acquiring a yellowish-green tint. Very few fruit buds are laid, which is why the yield of fruit-bearing apple trees is low.The lack of the element manifests itself in the first half of the growing season.
Nitrogen can be added only in the first half of summer. To achieve a quick effect, spray with a urea solution. 1 tbsp. l. urea is diluted in 10 liters of water and treated in the evening. But urea gives a short-term effect. For a longer effect, the tree is fed with an infusion of manure: 2 cups of infusion per 10 liters of water. Consumption rate: 2-3 buckets for a young apple tree, 4-6 buckets of fertilizer for a fruit-bearing apple tree.
Root feeding is applied only after abundant watering of the apple tree around the perimeter of the crown.
Do not miss:
Potassium deficiency
The edges of the leaves curl upward, forming a boat. Often a brown border appears along the edges - a marginal burn. With a slight deficiency of potassium, the leaves become curled and the internodes are shortened. With a severe deficiency, the apple tree lays many small fruit buds, but it discards most of the ovaries, and the remaining fruits are very small. With potassium deficiency, the overall winter hardiness of the tree decreases. Deficiency of the element is observed in highly carbonate or highly acidic soils.
To eliminate the deficiency, the apple tree is sprayed with a solution of potassium sulfate: 0.5 tbsp. l. (level spoon) fertilizer per 10 liters of water. You can water a tree with the same solution: 1-2 buckets of solution for a young apple tree, 3-5 buckets for a fruit-bearing one.
Ash perfectly compensates for the deficiency of potassium (and phosphorus, and microelements). Cultivated varieties are either watered with an infusion of ash, or applied dry around the perimeter of the crown, followed by abundant watering.
Potassium deficiency rarely occurs on its own; most often it occurs in conjunction with a lack of nitrogen. Therefore, to correct the situation, nitrogen fertilizers are added to the potassium sulfate solution or ash.
Phosphorus deficiency
The leaves stretch vertically upward, acquire a bronzed-olive tint, with a violet or reddish tint on the petioles and along the edges of the veins. Gradually the leaves turn black and dry out. Flowering and fruit ripening are greatly delayed. The foliage is crushed, the root system develops poorly, and with severe deficiency, young roots are practically not formed. Phosphorus deficiency is very common in poor soils.
If there is a lack of phosphorus, it is better to do root feeding and only in case of acute phosphorus starvation, when the leaves begin to turn black, foliar feeding, since with a severe deficiency the element will not be absorbed by the roots. For 10 liters of water 1 tbsp. l. simple superphosphate. A young apple tree requires 1-2 buckets of solution, and a fruit-bearing one requires 4-5 buckets. Or water it with infusion of ash.
To quickly replenish phosphorus deficiency, use potassium monophosphate (20 g/10 l). But this is if the leaves have already begun to dry out.
After any phosphorus feeding, manure or complex fertilizers are applied under the tree 2 weeks later.
Don't forget to read:
7 main apple tree diseases, their treatment and prevention ⇒
Iron deficiency
The leaves are light green, with severe deficiency they turn yellow, the veins remain green. The apple tree bears fruit poorly.
Spray with a solution of microfertilizers (Aquadron-micro, Uniflor, Ferovit). As a last resort, you can feed it with iron sulfate. The drug is taken at the tip of a knife and dissolved in 10 liters of water, the consumption rate for a young tree is 1 bucket, for a fruit-bearing tree 3 buckets.
Sometimes nails are driven into the trunk to compensate for iron deficiency. I had to do this once. The apple tree showed all the signs of iron deficiency. In addition, it had not bear fruit for 4 years. I had to hammer about 5 nails into the trunk, and then it bore fruit constantly.All signs of element deficiency disappeared. But this is rather an exception and the deficiency of the element can be eliminated in this way only on a very mature apple tree.
Don't forget to read:
Magnesium deficiency
The veins remain green, and the leaf itself becomes yellowish, reddish or purple in color. Already in the summer, the leaves fall from below. The tree loses its winter hardiness and freezes heavily in winter (young apple trees can even freeze out completely). A lack of magnesium is observed in light acidic soils, as well as with an excess of potassium.
Trees are sprayed with micropreparations containing magnesium. Stop potassium supplements. When adding potassium, magnesium is also added at the same time; there is a drug called Kalimag containing both elements.
Do not miss:
Calcium deficiency
The upper part of the young leaves curls, the leaves themselves turn white, the young shoots thicken, and their growth stops. With severe deficiency, the growing point on young shoots dies. Often found on acidic soils.
To eliminate a deficiency, acidity is first checked. If necessary, deoxidize the soil by adding lime fertilizers. If the soil is not too acidic, then the apple tree can be watered with calcium sulfate.
A deficiency of any element can be confused with the onset of the disease; their symptoms are very similar. Therefore, before treating the apple tree, it should be fed. And only if the symptoms do not disappear, but increase, treatment begins.
On carbonate soils there is often a deficiency of manganese, boron, and zinc. On light soddy-podzolic soils - phosphorus, potassium, magnesium, sulfur. In peatlands there is often a deficiency of potassium, manganese, and boron.The deficiency of all microelements can be easily corrected by treatment with preparations containing microelements or ash. But apple trees, as a rule, do not experience a lack of copper, at least among those summer residents who treat cultivated varieties with copper-containing preparations in the spring. The copper contained in the preparation is enough to fight diseases and nourish the apple tree.
Do not miss:
Conclusion
Apple trees need good nutrition. But when feeding, you don’t need to get carried away. The principle “the more the better” does not apply to this situation. Cultivated varieties need a balance of elements, and their deficiency, as well as their excess, negatively affects the fruiting and longevity of apple trees.












 CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.