With proper care, sweet pepper seedlings at home are practically not affected by diseases. The main reason for their appearance is improper care of plants.
Treatment of pepper disease during the seedling period
At the beginning of the growing season, pepper is mainly threatened by 3 diseases. This is the familiar blackleg, late blight and fusarium.How to prevent diseases and how to treat pepper seedlings if they do get sick will be discussed in this article.
Black leg on pepper
The most common and dangerous disease of sweet pepper seedlings, which is very difficult to treat. It affects seedlings from the moment the cotyledon leaves appear and up to 3-4 true leaves. Blackleg also appears when sowing directly into the ground. Can affect healthy plants after picking. The damage depends on the age of the seedlings: seedlings up to 3-4 true leaves die; at an older age, the plant does not die, but will be severely retarded in growth. It is useless to treat such seedlings; they are rejected.
Pathogen is a pathogenic fungus that lives in the soil. Spores overwinter and remain on plant debris and in the soil. Widely distributed when soil from a greenhouse is used for seedlings. In greenhouses and hotbeds, the pathogen feeds on plant debris, but in a small volume of seedling containers it does not have enough nutrition, and it switches to seedlings.
Conditions for the development of the disease
It always attacks seedlings with high soil moisture. If the humidity is normal, black leg rarely appears.
Other reasons:
- Thickened crops. The soil here is poorly ventilated, and the humidity is always high. Therefore, it is better to sow peppers in separate containers.
- Strong temperature changes contribute to the appearance of disease on pepper seedlings even with normal soil moisture.
- Lack of ventilation. Stagnant air near the ground always contains a lot of moisture, which settles on the surface of the soil.
- Infected seeds. The fungus can survive on seeds and infect seedlings. Therefore, before sowing, all seeds must be treated.
If seeds are infected, they may not sprout.
Signs of defeat
At the very early stage of infection, the plants look absolutely healthy, but they stop growing, and no feeding has the desired effect. After 2-4 days, the stem near the ground becomes thinner and dries out.
After another day, a constriction forms on it, the plant falls and dries out. Often, several hours pass from thinning of the stem to lodging of the plants. The disease can destroy all seedlings within 2-4 days.
When you pull a plant by its stem, it is difficult to remove; the constriction does not break.
Treatment of the disease
Control measures At the same time they are also disease prevention.
When the stem has thinned, it is too late to treat the pepper seedlings; they will die no matter what.
Urgent action must be taken if the pepper has stopped developing and, despite its healthy appearance, does not grow. Spill the soil with a raspberry solution of potassium permanganate. Sometimes this is a salvation.
If small seedlings do not grow despite warmth, fertilizing and lighting, then the parasite has already penetrated inside, but has not yet clogged the vessels. A strong solution of potassium permanganate kills the pathogen. If a week after watering the plants look healthy but are not growing, they are watered with a solution of Trichodermin or Fitosporin and fed.
Fertilizing is done with liquid fertilizers: Malyshok, Ideal, Krepysh for tomatoes and peppers. It is advisable to water the plants again with potassium permanganate a week later.
Even if there are no signs of damage, for preventive purposes, every 15 days the seedlings are shed with a solution of potassium permanganate in combination with fertilizing. When the peppers produce 5-6 true leaves, they will not be afraid of the black leg.
We always remember! Any disease of pepper seedlings is easier to prevent than to treat later.
How to protect pepper seedlings from disease
Before sowing, the land must be disinfected. If it is not possible to freeze or calcinate it, then spill the soil with a dark solution of potassium permanganate and let it sit for 2-4 days.
Before sowing, seeds must be pickled in a pink solution of potassium permanganate or in Trichodermin.
Pepper seedlings should be regularly ventilated. But at temperatures below 18°C, plants are brought indoors, otherwise, having become hypothermic, they will also die.
Watering is carried out only with settled water at room temperature. The soil should neither dry out nor become waterlogged. To determine the humidity, touch it with your finger; if it is dry to the touch and lumps of earth do not stick to your hand, then watering is necessary.
Late blight
Pepper is much more resistant to late blight than tomatoes and potatoes. But when using soil from contaminated crops, it can get sick. It is also affected when pepper seedlings are close to diseased tomato seedlings or diseased potato tubers.
Pathogen - pathogenic fungus. Pepper seedlings are more often affected by southern late blight. As a rule, he does not get sick with ordinary late blight, since the rooms are too hot for this type of pathogen. The fungus persists in the soil, on plant debris, seeds, and fruits.
Terms of distribution
The disease appears on seedlings when there is high humidity in the air and soil and strong fluctuations in air temperature.
Maliciousness 100%. If the seedlings become infected with late blight, they are thrown away. Although sweet peppers do not suffer so much from the disease, and during the seedling period of its appearance the crop can even be cured, but in the future, the pepper will become a source of infection for tomatoes and eggplants growing next to it.
You can leave the crop only if it is grown in isolation from other plants (for example, in a separate greenhouse). Peppers during the seedling period are quite resistant to the disease and are affected only when the growing technology is grossly violated.
Signs of the disease
Pepper can get sick at any stage of growth - from germination to the end of fruiting. Seedlings, as a rule, become diseased in the 3-5 leaf phase. At a young age, late blight is not so harmful to peppers.
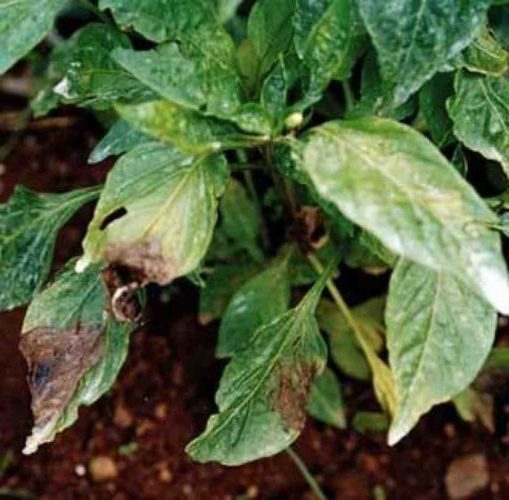
If the disease appears in the germination phase, then a brown-gray spot appears on the stem at a height of 3-5 cm above the ground, which quickly increases in size and rings the entire stem. Unlike blackleg, late blight does not appear on the stem near the ground. At the same time, small brown spots appear on the leaves (even on cotyledons), which gradually merge. The seedlings lie down and dry out.
When the disease appears on large seedlings, brown stripes appear on the stem, which gradually spread along the stem to large areas. Brown spots appear on the leaves with a characteristic pale green border around them. If the humidity in the room is high, then the fabrics begin to rot; if it is low, they dry out.
Phytophthora does not spread as rapidly on seedlings and young plants as on adults.
Treatment of the disease
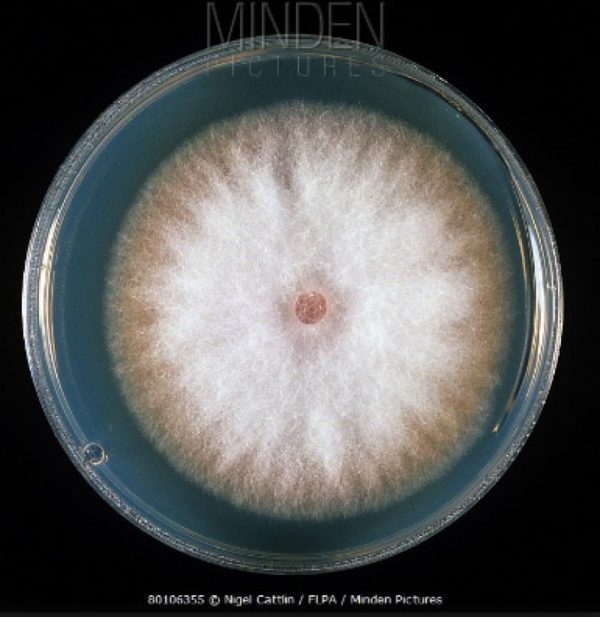
If there is a suspicion of late blight, then the pepper and surrounding seedlings are sprayed with Trichodermin. This is a pathogen antagonist fungus; it completely destroys late blight. They can carry out treatments even indoors.

Trichoderma helps well in the fight against late blight
At home, adhesives are usually not added to the working solution, since the drug will not disappear from the leaves.For better colonization by Trichoderma, you can add starch glue to the solution. A few days after spraying, greenish-white spots will appear on the leaves - a sign that Trichoderma has taken root and started working.
With a small spread of late blight, after treatment with a biological product, pepper seedlings are completely cured of the disease. Its signs disappear. Treatments are carried out once every 10 days until the seedlings are planted in a permanent place. To prevent Trichoderma from dying, pepper is sprayed with water at room temperature every 2-4 days.
During the seedling period, an infusion of onion peels helps a lot at home. 10 g of onion peels are infused in 1.5 liters of water for 10-15 hours, an adhesive (laundry soap) is added and the plants are sprayed.
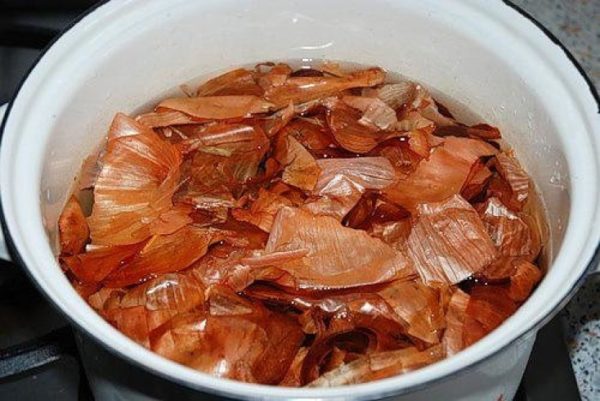

Traditional methods of treating diseases on seedlings.
Trichodermin and onion peel should not be alternated with each other. Having a strong antifungal effect, the infusion kills all microflora, including Trichoderma. These drugs are used independently.
Disease prevention
Prevention consists of eliminating pathogenic factors.
- Sweet pepper seedlings are kept isolated from seedlings of other crops. You cannot store potatoes in the same room with it. Although the pepper itself may not get sick, it becomes a carrier of the pathogen's spores, and subsequently develops early blight.
- Mandatory treatment of seeds before sowing in a strong solution of potassium permanganate. The solution temperature must be at least 50°C.
- After the emergence of seedlings, once every 10 days, water the soil with a burgundy solution of potassium permanganate until 4-6 true leaves appear.
- Regular ventilation reduces the humidity of the surrounding air and reduces the risk of late blight on seedlings.
When a disease appears, it does not affect all plants at once. 1-2 diseased peppers appear, which are thrown away, the rest are treated with Trichodermin or, in extreme cases, potassium permanganate.
Fusarium
This is the common name for root rot. Often found on seedlings of sweet and hot peppers and other crops grown through seedlings.
Pathogen - pathogenic fungi that live in the soil. Under normal conditions they live on plant debris, but in a favorable environment they settle on the roots. In a cramped container they can cause significant damage, including loss of seedlings.
Favorable conditions are high temperature and high soil moisture. In soil with normal moisture, even at high temperatures, pathogens are inactive. The disease begins after a pick. The pathogen penetrates into the roots through damaged root hairs and affects the conducting vessels.
Signs of the disease
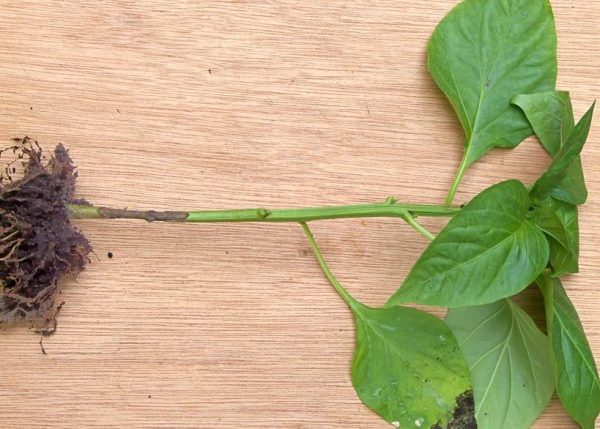
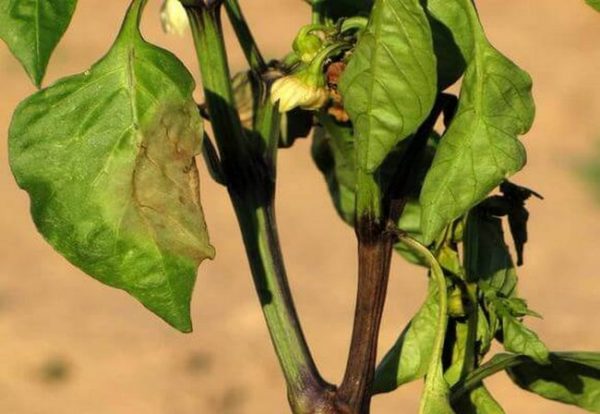
In apparently healthy plants, the lower leaves begin to wither, and the upper leaves lose turgor. Despite normal watering, they become discolored and dry out. A pink coating appears on the root part of the stem, and brown stripes appear on the stem, on which plaque also subsequently appears. The disease develops instantly. Plants fall, often before they even have time to wither. But if the temperature drops sharply, the death of the pepper lasts for 4-7 days.
Control measures
If the disease appears in a common seedling box, the plants cannot be cured. When grown in separate containers, immediately after picking, peppers are watered with Previkur (3 ml per 2 liters of water), Maxim Dachanik.Biological drugs are useless at the onset of the disease, since their effect occurs after 2-3 days, and you need the fastest possible effect on the pathogen.
If a disease appears in a common box, healthy plants are immediately dived into separate containers. Before planting, the roots are dipped in a solution of the preparations Maxim Dachanik, Baktofit or Trichodermin.
How to protect seedlings from disease
- Treating seeds in potassium permanganate. If there is no confidence in the quality of the soil, then they are treated with Vitaros or Vectra.
- After picking, for preventive purposes, while the roots have not yet recovered, the peppers are watered with biological products: Gamair, Trichodermin, Fitosporin, Baktofit, Planriz. Treatment is carried out 2 times with an interval of 5 days.
- Before picking, water the soil in a new container with a strong solution of potassium permanganate or Trichodermin.
- Reduce watering of seedlings, and reduce the temperature in the room. The soil should be moist, not damp. Favorable conditions for the growth of sweet peppers are a temperature of 25-28°C and slightly moist soil.
Fusarium is often found on seedlings when using old soil (from indoor plants or a greenhouse) that has not been properly treated.
Non-infectious pathologies
They are much more common than diseases. Both sweet and hot peppers are very demanding on growing conditions. Improper care is also a kind of disease and if no action is taken, the plants will die.
Pimples have appeared on the leaves, the leaves are curling - waterlogging
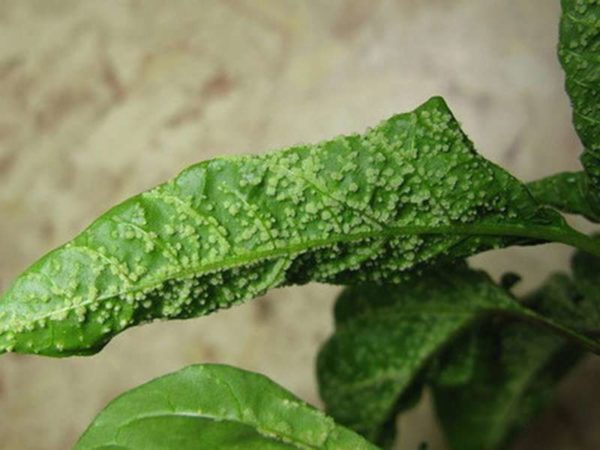
Pepper loves frequent but small watering. If you dry it and then water it abundantly, tissue swelling occurs (edema, oedema).
Signs of defeat. Depending on the degree of waterlogging, watery pimples appear on the petioles and on the underside of the leaves closer to the petiole. With severe waterlogging, they appear all over the leaf. They are hard to the touch, like beads. The affected tissue becomes cork, the diseased leaf does not recover and dies. If the petiole is severely damaged, it bends.
The plant itself continues to grow and develop. Edema can also appear in adult plants, especially in a greenhouse, but the damage there is not so severe.
Troubleshooting. When pimples appear and leaves curl, reduce watering and place plants more freely on the windowsill, since greater crowding slows down the evaporation of excess moisture from the soil surface. No spraying or fertilizing is done.
Video about these scary bumps on pepper leaves
cold soil
If the soil in the container gets very cold, the sweet pepper stops growing and the plants gradually die. The root system of the crop functions normally at a ground temperature of 20-22°C. At lower temperatures, the roots stop functioning, and at 15°C they die.
Signs of defeat. When plants are overcooled, the leaves gradually become light green in color and begin to wither. Many summer residents mistake this for root rot and begin to treat seedlings for it. But root rot destroys pepper instantly (in 2-4 days), while in cold soil the crop gradually withers. Before taking action, you need to touch the container.
Solution. If the soil is cold, then it needs to be warmed up by placing containers with seedlings on or near the radiator. The earth will warm up and the functions of the roots will be restored.
When placing containers on the battery, the above-ground part is sprayed so that it does not die from dry air. When further placed on the windowsill, the seedlings are insulated by placing them on pallets or, if it is very windy from the windows, on blankets, rags, or cotton wool. Do not place containers near the glass, since there is always cold air there, cooling the soil in the containers.
Dry air
In residential areas, the air humidity is low, and besides, the seedlings are placed on the windowsill, where it is even drier. Low air humidity is especially dangerous for seedlings and seedlings with 2-3 true leaves. At a later age, plants adapt to such conditions.
Signs. The seedlings begin to dry out. First leaves wither and dry out at the top, then the lower ones, the stalk dries out last. The color of the plants does not change. The cotyledon leaves dry out at the same time.
When a pepper has 4 or more true leaves, then at low air humidity the lower leaves begin to dry out (cotyledons do not count, they themselves fall off with age). They wither, curl and dry out.
How to save plants. If seedlings are exposed to dry air, they die. If there are real leaves, the plants are sprayed immediately. Subsequently, spraying is carried out every 2-3 days. Since moisture also gets onto the soil, the watering rate is reduced.













 (12 ratings, average: 4,33 out of 5)
(12 ratings, average: 4,33 out of 5) CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.