For more than 250 years, Japanese quince was cultivated in Europe only as an ornamental shrub with inedible fruits. The work of breeders was carried out only with the aim of improving the decorative qualities of the plant.
Only at the beginning of the 20th century was Japanese quince recognized as a necessary fruit and berry crop, after which breeders changed the direction of their activities and created a collection of high-yielding varieties distinguished by large fruits.
Description of Japanese quince
Japanese quince is a deciduous shrub 0.5-3 m high. In central Russia its height does not exceed 1 m. Flowering of Japanese quince lasts 20 days, from late May to mid-June. It begins to bear fruit at 4 years of age. Fruit ripening is delayed until the end of October.
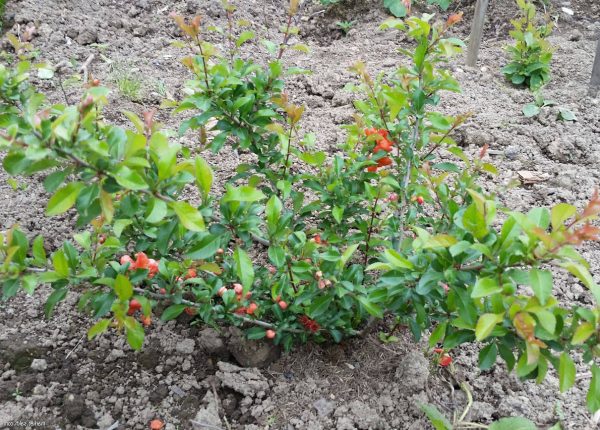
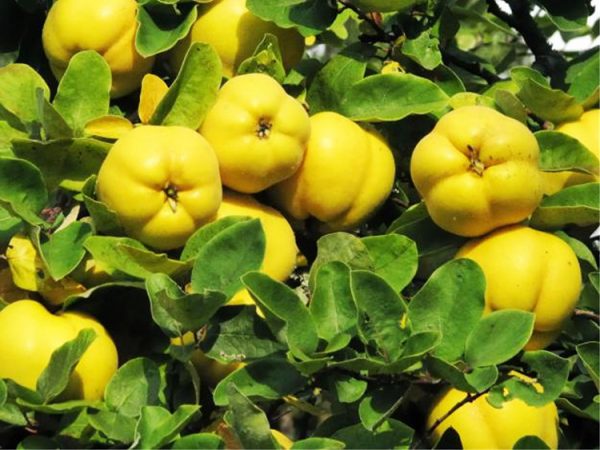
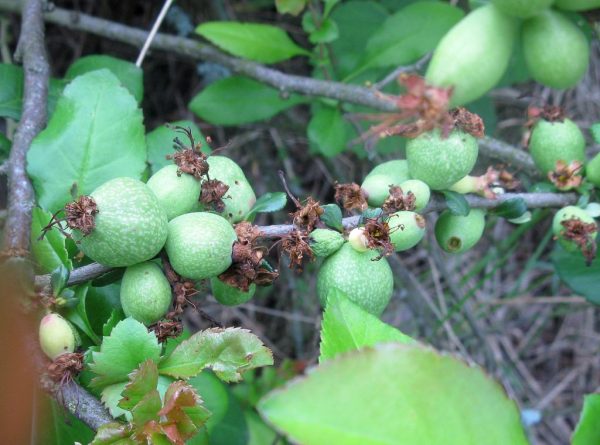
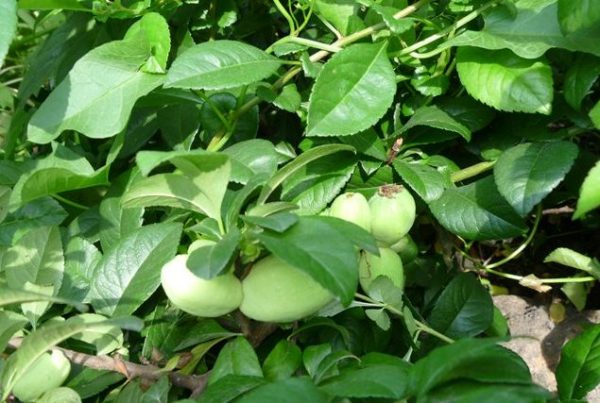
As you can see in the photo, the color of ripe fruits ranges from green to bright orange. If the plants do not have enough sun, the fruits may remain green and ripen after harvesting. A waxy coating on fruits increases their shelf life. To increase the fruiting of Japanese quince, you need to have at least three bushes of the plant on your site.
The crop has a powerful central root, which contributes to drought resistance and low demands on the composition and nutritional value of the soil. The same factor significantly complicates replanting quince, during which the tap root is inevitably damaged. The lifespan of Japanese quince in one place without transplantation is about 60 years.
Photos of Chaenomeles varieties
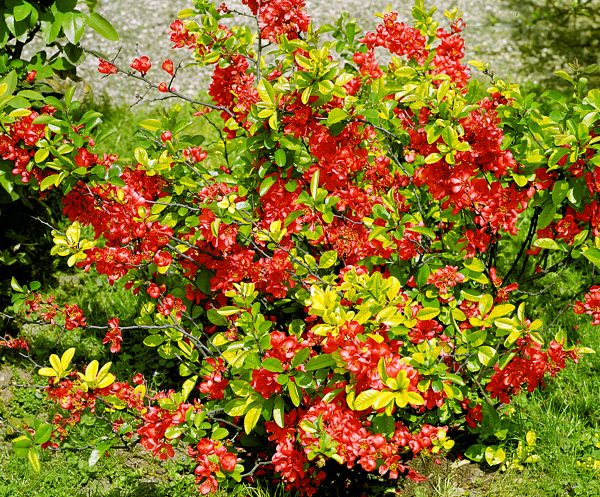
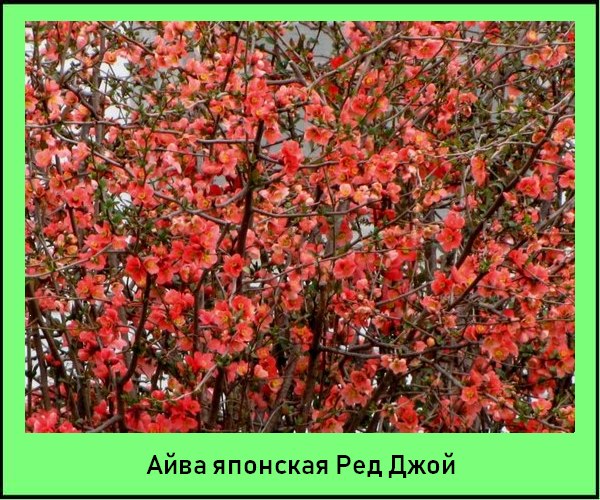
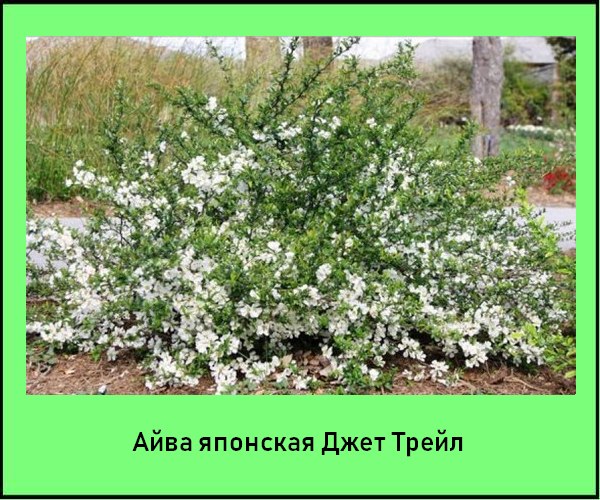
Of the more than 500 varieties of Japanese quince, only a few are grown in Russia, shown in the photo, characterized by frost resistance and original, lush flowering:
Red Joy (Chaenomeles japonica Red Joy) – bush height 1.6 m. Flowers are dark red, semi-double. The leaves are small.
Jet Trail - bush height 1.5 m, with sparse thorns. Blooms abundantly with white flowers.
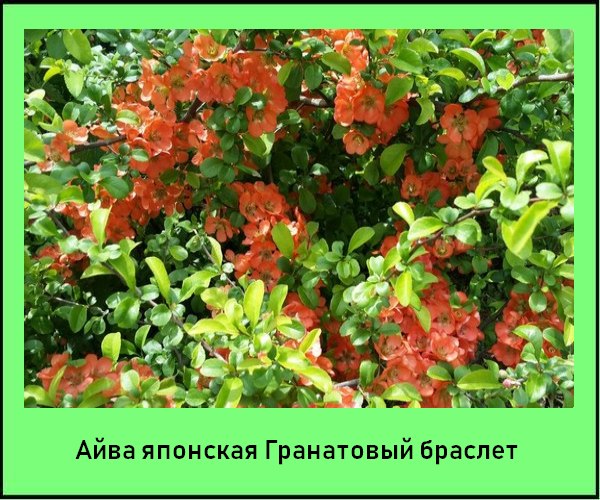
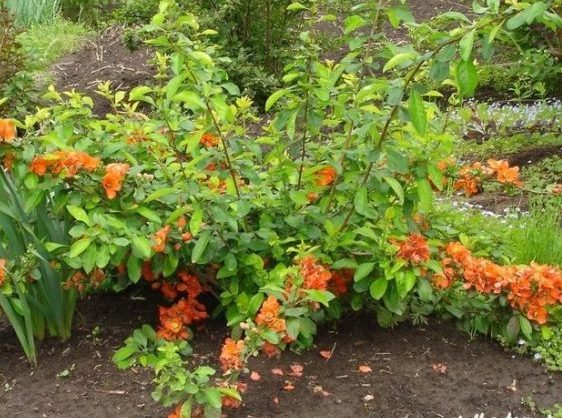
Pomegranate bracelet is a bush with shoots up to 1 m. The flowers are large, up to 5 cm, scarlet-red in color.
Crimson and Gold is a highly branched shrub up to a meter in height. A characteristic feature is yellow stamens combined with dark red petals. Flowers up to 3 cm in diameter.
Nikolin - flowers are deep red, large, with distinct yellow stamens.
Rules for planting Japanese quince
Proper placement of the plant on the site is an important stage in caring for Japanese quince. How and where chaenomeles is planted will largely determine its decorative value and the amount of harvest. Therefore, before planting, you should take into account the crop’s preferences for soil, moisture and light.
Choosing a landing site
When choosing a place to plant Japanese quince, you should take into account the fact that it is a light-loving crop. In the shade, quince develops poorly, which affects flowering and fruiting. Priority should be given to areas on the south side of buildings or a place protected from north winds.
If the garden plot is located on a hilly area, the southern and southwestern slopes of the terrain are used for planting. Light soils rich in humus with a slightly acidic reaction (pH 6.5) are suitable for growing Chaenomeles japonica. Alkaline soils cause leaf chlorosis in Japanese quince.
In the middle zone, the frost-resistant Japanese quince overwinters without shelter. In the northern regions, at temperatures below -30°C, flower buds and annual shoots located above the snow cover freeze. This affects the reduction of spring flowering, while those shoots that are covered with snow in the spring will definitely bloom.
Important! Japanese Chaenomeles bushes do not tolerate transplantation well, so you should decide on the planting site right away.
Soil preparation and planting
For spring planting of Japanese quince, the soil must be prepared in the fall. An area heavily infested with weeds must be weeded. Poor and heavy soil is fed with leaf humus, compost and sand, as well as phosphorus-potassium fertilizers with a depth of 10-15 cm. This promotes water and air permeability of the soil. Planting is done before the buds open.

The photo shows the planting of Chaenomeles
Planting quince in the fall is ineffective, since the heat-loving plant may die before it has time to take root. Japanese quince, which has a closed root system, is more likely to take root in the fall. 2-year-old seedlings are most suitable for this.
Planting Japanese quince seedlings:
- Prepare planting holes with a diameter of 50 cm and a depth of 50-80 cm, fill them with nutritious soil.
- The root collar of Chaenomeles japonica is not buried, but is placed at ground level.
- Plants are watered abundantly and mulched with sawdust and humus.
How to care for Chaenomeles
Japanese quince must be cared for in the same way as any cultivated plant, taking into account some nuances.
Watering
The crop is drought-resistant and requires watering only in drought conditions. Regular, but moderate, moisture is required only for young seedlings and plants immediately after planting.
Loosening and weeding
In order for the Japanese Chaenomeles bushes to bloom more abundantly, in the summer it is necessary to loosen the soil around them. It is advisable to combine loosening with weed removal. You can prevent the growth of weeds by using mulch in a layer of 3-5 cm. For mulch, peat, coconut shavings, sawdust or crushed bark are used. The soil must be moistened before adding mulch.
Top dressing
When caring for Japanese quince, you should remember that in the year of planting the crop does not require fertilizing, since the nutrients added to the planting holes are sufficient for the development of the plant. Then, every 2-3 years, in early spring, a bucket of leaf humus, 300 g of superphosphate and 100 g of potassium fertilizer are added to the tree trunk circle. During the summer season, quince needs fertilizing in the form of ammonium nitrate (20 g/bush) or bird droppings (3 liters of 10% solution).
Quince pruning
For abundant fruiting, it is necessary to leave 12-15 branches on the bush. The largest harvest appears on 3-year-old shoots. All branches older than 5 years are deleted.
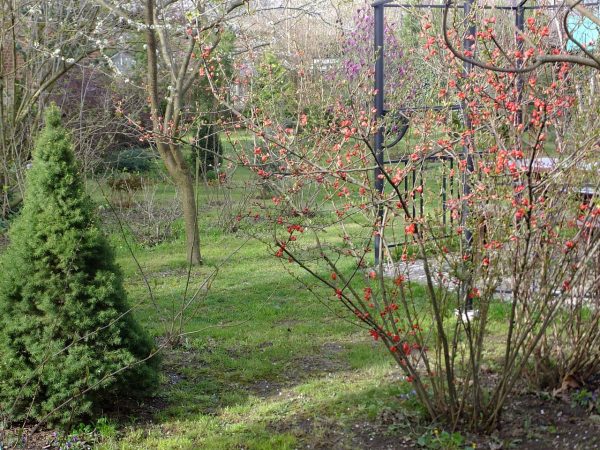

The photo shows chaenomeles after trimming
Preparing the bush for winter
If quince bushes are located in an open place and are regularly damaged by frost, they should be covered with leaf litter or spruce branches for the winter. Young plants are covered with non-woven material for the winter. It is convenient to cover compact bushes with cardboard boxes or wooden boxes.
Quince bushes should be mulched after the onset of persistent cold weather. The area covered with mulch should exceed the perimeter area of the plant crown by 15-20 cm.
Reproduction of Chaenomeles japonica
You can increase the number of Japanese quince bushes on your personal plot in the following ways:
- Rooting cuttings
- Cuttings
- Transplanting root shoots
- Seeds
Important! The advantage of vegetative methods, in addition to simplicity, is the preservation of the varietal qualities of the mother bush.
Reproduction by layering
When propagating by layering in the spring, the side branches are bent to the ground and covered with earth.
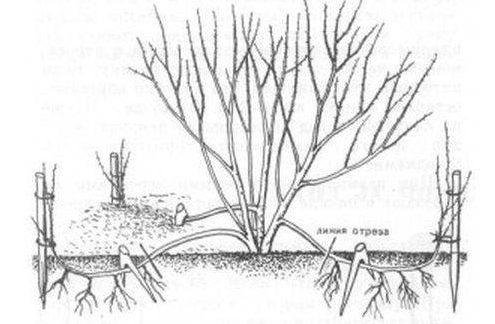
Rooting cuttings
By autumn, the rooted shoots are separated from the mother bush and planted in a permanent place.
Propagation by cuttings
For green cuttings, the material is prepared early in the morning in early June in dry and not hot weather.Each cutting, 15-25 cm long, should contain 1-2 internodes; the sections are treated with biostimulants. The prepared cuttings are placed obliquely in a mixture of sand and peat (in a ratio of 3:1) according to a 7x5 cm pattern, as in the photo.
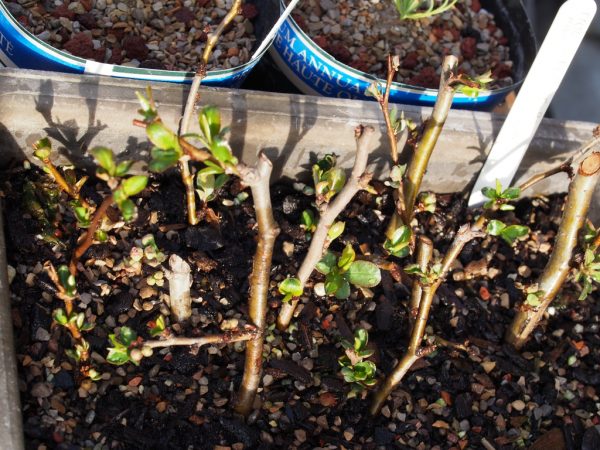

The photo shows cuttings of Chaenomeles
The plantings are covered with film. For reliable rooting at a temperature of +20°...+25°C it will take 35-40 days. The percentage of rooted cuttings is about 40%, biostimulants of growth and root formers increase survival rate by 15%.
Reproduction by root shoots
Japanese quince produces a lot of root shoots, which can be used for propagation of the crop. When choosing shoots, you should choose branches 10-15 cm long and 0.5 cm thick. It is necessary to separate shoots from the bush with the largest number of roots. From one adult bush you can get 6-8 root shoots.
Due to the insufficient number of roots in the shoots, seedlings are grown in seedling beds or in containers.
Seed propagation of Japanese quince
When processing quince fruits, the seeds should be saved; they are suitable for growing quince from seeds. When propagated by seeds, the varietal characteristics of the crop are not always preserved. More often this method is used to obtain rootstocks.
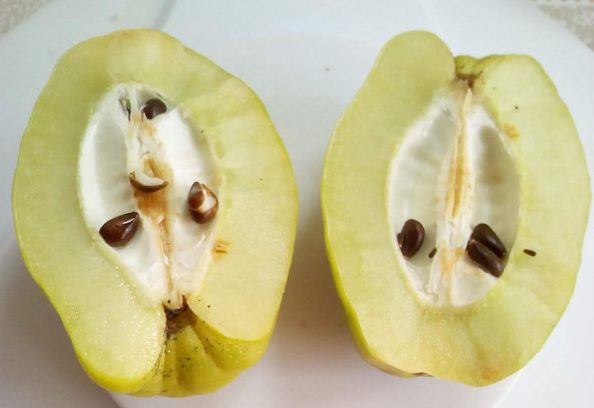

Japanese quince seeds
Also, propagation by seeds allows you to obtain many seedlings for decorative plots. Ripe seeds are sown in the ground in autumn or spring. 80% of seeds germinate smoothly, regardless of soil quality.
If sowing is done in the spring, then cold stratification is necessary, for which the seed is kept for 2-3 months in damp sand in a refrigerator or room with a temperature of +4 ° C. The seedlings that appear in May - June are grown for 2 years, only after that they are planted in a permanent place.
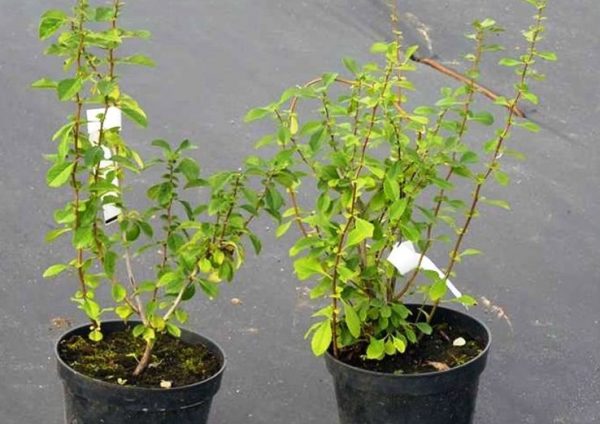

The photo shows seedlings grown from seeds
Since the root system suffers during transplantation, it is recommended to plant the seedlings in individual containers in order to further replant with the least damage to the roots.
Chaenomeles Japanese in landscape design
Japanese quince is used by gardeners not only as a fruit plant, but also in landscape design as an ornamental crop.
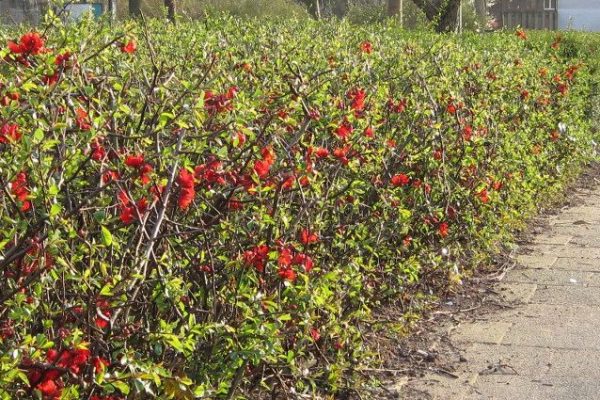

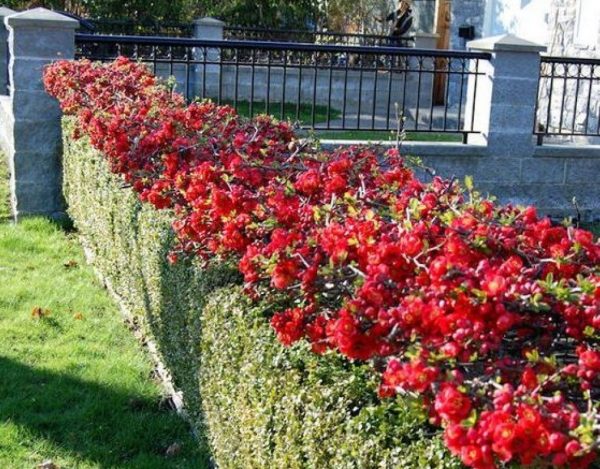
Japanese quince hedge
Chaenomeles bushes tolerate pruning well and are suitable for use as a hedge. In a row, plants are placed at a distance of 50-60 cm from each other. Between single plantings maintain a distance of 70-90 cm.
The photo shows how Japanese quince borders highlight recreation areas and decorate garden paths.
Low-growing creeping forms look impressive in rock gardens and alpine slide compositions. Some hybrids are used for growing bonsai.
In urban environments, Japanese quince is used in the design of recreation areas, flower beds and flower beds in parks.
Due to its powerful root system, quince is used to prevent erosion on loose soils.
Photo of quince in landscape design
Pests and diseases
Japanese quince is rarely attacked by pests and diseases.More often this happens at high humidity and low ambient temperature, which create favorable conditions for the development of diseases and the appearance of pests, with improper care.
An effective method of combating diseases is treatment with Fundazol or copper sulfate solution. Plants are treated with the same agents to prevent diseases.
Important! Treatment should be carried out before the leaves unfold.
An effective insect repellent is an infusion of onion peels, which is used 3 times every 7 days.
To save plants from attack by pests and protect them from diseases, preventive measures should be taken to care for quince:
- at the end of the season, remove any remaining vegetation;
- dig deep around the tree trunk in the fall;
- Fertilize regularly and correctly to increase immunity from diseases and pests;
- trim damaged shoots;
- inspect plants to detect parasites and infections.
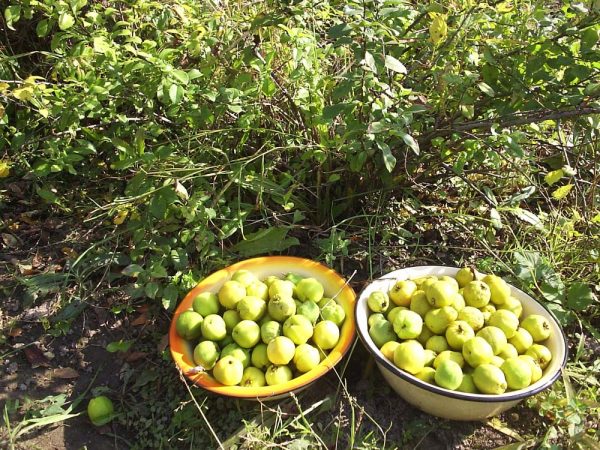
Harvest and storage
Before preparing Japanese quince plantings for winter, all the fruits should be collected before frost. Unripe fruits are also removed from the branches, and they ripen in storage. After 3 months of storage at a temperature of +3°...+5°C, the taste of the fruit improves.
The density and sour taste of the fruit do not allow Japanese quince to be consumed fresh. Thanks to processing, tasty and healthy jams, jellies, preserves, compotes, and wines are obtained from quince.
Continuation of the topic:
- Growing weigela in the garden
- Growing Jasmine
- How to prune ornamental shrubs correctly
- Privet bush: cultivation and care
- Planting and caring for lilacs in the garden


















 CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored. They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.