The content of the article:
- How to choose and buy fruit tree seedlings.
- How to choose currant and gooseberry seedlings.
- How to choose raspberry seedlings.
The choice of fruit tree seedlings is a responsible matter, since the selected plant is a perennial plant that will begin to bear fruit in 3 - 7 years, and can grow on the site for more than 30 years. Whatever To buy some other planting material instead of the desired variety, or weak, poor quality, infected with pathogens and pests, you need to know a few simple rules.
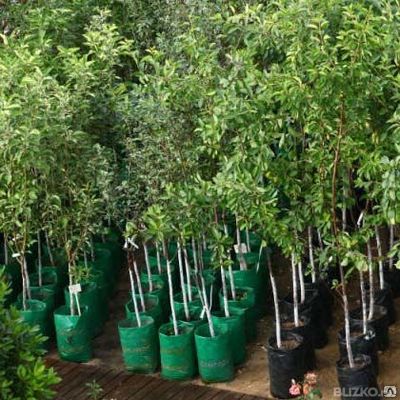
How to choose and buy fruit tree seedlings
When choosing and purchasing seedlings, a very important point is the age, power of the root system, diameter of the trunk, how many side shoots there are on the trunk and their length.
Age. First of all, pay attention to the age of the seedlings. Many novice gardeners choose the tallest trees in the hope that they will grow faster and begin to bear fruit faster. But this is not entirely correct, in this way you can buy plants three or even four years old that were not sold last season.
Such specimens will not only not begin to bear fruit earlier, but will also lag behind younger plants in development. The thing is that adult seedlings have already formed a powerful root system and it is not possible to dig it out of the ground without damaging it.
In three-year-old plants, at least 80% of the roots remain in the ground, on which most of the suction roots - lobes - are located. The remaining part of the root system is not able to fully nourish the young tree.
It is recommended to choose two-year-old apple and pear seedlings for purchase, and it is better to plant cherries, plums, apricots and cherries as one-year-olds.
Thickness of the stem. When choosing a seedling, you need to pay attention to the thickness of the stem. There are even certain standards for trunk thickness of seedlings:
- Pome crops not less than 12 mm.
- Stone fruits no less than 15 mm.
- For low-growing rootstocks, at least 10 mm.
Branching of the trunk. To purchase, it is better to choose seedlings with an even stem, without visible damage and without many side branches.
Annuals can have no branching at all, especially low-growing rootstocks, as well as many varieties of plums and cherries. Two-year-old seedlings should have three lateral branches 30 - 40 cm long.
Root system. The closest attention should be paid to the condition of the root system. You should choose planting material with a well-developed, fibrous root system. The length of the roots should be at least 25 - 30 cm, they should not be dry or have mechanical damage.
Choose and buy only young seedlings that look healthy. No cracks in the bark or fungal infections, with well-developed roots. It is better to buy zoned varieties that are sold in local nurseries. Such plants will quickly take root and bear fruit longer.
Seedlings with a closed root system. In recent years, seedlings with a closed root system - in containers or burlap - have often begun to go on sale. In this case, choosing a plant with good roots is quite difficult.
It is better to buy such seedlings, as well as other planting material, in certified nurseries or specialized stores that sell certified products and to whom you can contact with a complaint.
If you purchase a plant in a container, keep in mind that they are usually grown in a greenhouse and can be planted on the site in the spring, when the threat of frost has passed, or in early autumn.
What are the diseases of seedlings?
Sometimes seedlings of pome and stone fruit trees are affected by root canker, or root goiter, caused by bacteria.Bacteria secrete toxins that cause active cell pressure, as a result of which growths of various sizes and a dense woody consistency are formed on the roots and root collar.
Trees with such growths are less accepted and often die, especially in dry and hot climates. You cannot buy such plants, they will not only die themselves, but will also contaminate the soil.
When choosing planting material, pay attention to the plant bark. Sometimes the bark of shoots, especially pears, cracks and wrinkles due to severe scab damage, which weakens the plants.
Typical symptoms of the disease appear on the leaves (rounded black and olive spots), which are usually removed by the time of implementation. When purchasing seedlings, it is important to pay attention to dried annual shoots, which could be caused by monilial burn or severe development of clusterosporiasis on stone fruits.
Young stone fruit seedlings are susceptible to verticillium drying, in which a continuous or intermittent darkening of the pith vessels is clearly visible on a cross section of the affected branch. Treatment of such affected trees is practically impossible; after a few years they die.
Nurseries in the southern zone may receive pear seedlings affected by brownish leaves or entomosporia (small brown necrosis on the leaves, shoots bend like a snake and develop poorly).
How to choose currant and gooseberry seedlings
It is necessary to select planting material for gooseberries and currants as carefully as seedlings of fruit trees. You should buy young plants, as they take root well and grow better.
First of all, inspect the root system; it should be branched, healthy, have many small roots and a length of 20 - 25 cm. The above-ground part should have one or two branches 30 to 40 cm long, with smooth, crack-free bark and live, healthy buds.
Since currants easily take root when watered, they are sold with swollen, blossoming buds. When choosing a seedling, you must make sure that the buds are normally elongated and not spherical (as when infested by the currant bud mite - the carrier of the terry virus), that near the buds and in the cracks of the bark there are no eggs and larvae of shoot gooseberry and redcurrant aphids, as well as scale insects (scutes gray, pear-shaped, 3 - 4 mm, easily removable).
The wood when cut should be light-colored, without signs of damage by glassworm caterpillars (wormholes) or verticillium.
How to choose raspberry seedlings
You should not buy large raspberry bushes with a lot of shoots. Such bushes are expensive and do not take root well. It is better to purchase bushes with two to three mature shoots of medium thickness.
Carefully examine the roots; they should be well developed, without signs of cancer (woody growths on the roots and root collar), without peeling or necrosis of the bark. The roots should not show signs of root rot when cut.
The roots of raspberry seedlings should not be exposed to the sun, especially in hot weather. The raspberry root system dies in such conditions within a few hours!
Raspberry roots must be covered with a wet cloth, and dug in at the first opportunity. However, keeping wet roots in plastic bags for a long time can be just as detrimental to them.
Before planting, raspberry stems are cut leaving 30 - 35 cm. Therefore, there is no point in choosing tall seedlings.
You cannot buy seedlings that have signs of fungal diseases: didimella, or purple spotting, when there are red-purple blurry spots on the shoots. They are located mainly near the place of attachment of leaves, and on the shoots of the second year of life - cracking of the bark and gray spots or damage to septoria (gray, vague, inconspicuous spots, with black dots - pycnidia, peeling of the bark), or signs of anthracnose (grayish with a purple border). ulcers).
If you see a grayish-white coating on the leaves and young shoots of fruit and berry crops (these are signs of powdery mildew), such seedlings should also not be purchased.








 CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE!
CUCUMBERS NEVER GET SICK, I'VE BEEN USING ONLY THIS FOR 40 YEARS! I SHARE A SECRET WITH YOU, CUCUMBERS ARE LIKE THE PICTURE! You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
You can dig a bucket of potatoes from each bush. Do you think these are fairy tales? Watch the video
 How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch.
How our fellow gardeners work in Korea. There is a lot to learn and just fun to watch. Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored.They don't charge money for views.
Eye trainer. The author claims that with daily viewing, vision is restored.They don't charge money for views. A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty.
A 3-ingredient cake recipe in 30 minutes is better than Napoleon. Simple and very tasty. Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises.
Therapeutic exercises for cervical osteochondrosis. A complete set of exercises. Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign?
Which indoor plants match your zodiac sign? What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
What about them? Excursion to German dachas.
Choose and buy any seedlings from local fruit nurseries, then you won’t have any problems.
Oh thank you)) will come in handy))